Compare commits
merge into: 10225501432:main
10225501432:homework1
10225501432:homework2
10225501432:homework3
10225501432:homework4
10225501432:homework5
10225501432:main
pull from: 10225501432:homework4
10225501432:homework1
10225501432:homework2
10225501432:homework3
10225501432:homework4
10225501432:homework5
10225501432:main
79 changed files with 212763 additions and 2374 deletions
Split View
Diff Options
-
+0 -52.gitignore
-
+0 -12LAB1/Driverhdrs.pm
-
+0 -138LAB1/Driverlib.pm
-
+0 -33LAB1/Makefile
-
+0 -140LAB1/README
-
+0 -388LAB1/bits.c
-
+0 -65LAB1/bits.h
-
+0 -583LAB1/btest.c
-
+0 -32LAB1/btest.h
-
+0 -86LAB1/decl.c
-
+0 -0LAB1/dlc
-
+0 -439LAB1/driver.pl
-
+0 -151LAB1/fshow.c
-
+0 -75LAB1/ishow.c
-
+0 -124LAB1/tests.c
-
+0 -21LICENSE
-
+30 -0Makefile
-
+52 -0README
-
+0 -35README.md
-
+279 -0clock.c
-
+22 -0clock.h
-
BINclock.o
-
+72 -0config.h
-
+251 -0fcyc.c
-
+68 -0fcyc.h
-
BINfcyc.o
-
+57 -0fsecs.c
-
+4 -0fsecs.h
-
BINfsecs.o
-
+106 -0ftimer.c
-
+14 -0ftimer.h
-
BINftimer.o
-
BINmdriver
-
+1017 -0mdriver.c
-
BINmdriver.o
-
+101 -0memlib.c
-
+11 -0memlib.h
-
BINmemlib.o
-
+439 -0mm.c
-
+23 -0mm.h
-
BINmm.o
-
+16 -0short1-bal.rep
-
+16 -0short2-bal.rep
-
+42 -0traces/Makefile
-
+116 -0traces/README
-
+5698 -0traces/amptjp-bal.rep
-
+4809 -0traces/amptjp.rep
-
+12004 -0traces/binary-bal.rep
-
+8004 -0traces/binary.rep
-
+24004 -0traces/binary2-bal.rep
-
+16004 -0traces/binary2.rep
-
+5852 -0traces/cccp-bal.rep
-
+5036 -0traces/cccp.rep
-
+155 -0traces/checktrace.pl
-
+14404 -0traces/coalescing-bal.rep
-
+14404 -0traces/coalescing.rep
-
+6652 -0traces/cp-decl-bal.rep
-
+5687 -0traces/cp-decl.rep
-
+5384 -0traces/expr-bal.rep
-
+4541 -0traces/expr.rep
-
+39 -0traces/gen_binary.pl
-
+38 -0traces/gen_binary2.pl
-
+36 -0traces/gen_coalescing.pl
-
+62 -0traces/gen_random.pl
-
+57 -0traces/gen_realloc.pl
-
+46 -0traces/gen_realloc2.pl
-
+4804 -0traces/random-bal.rep
-
+4804 -0traces/random.rep
-
+4804 -0traces/random2-bal.rep
-
+4804 -0traces/random2.rep
-
+14405 -0traces/realloc-bal.rep
-
+14405 -0traces/realloc.rep
-
+14405 -0traces/realloc2-bal.rep
-
+14405 -0traces/realloc2.rep
-
+16 -0traces/short1-bal.rep
-
+16 -0traces/short1.rep
-
+16 -0traces/short2-bal.rep
-
+16 -0traces/short2.rep
-
+211 -0实验报告.md
+ 0
- 52
.gitignore
View File
| @ -1,52 +0,0 @@ | |||
| # Prerequisites | |||
| *.d | |||
| # Object files | |||
| *.o | |||
| *.ko | |||
| *.obj | |||
| *.elf | |||
| # Linker output | |||
| *.ilk | |||
| *.map | |||
| *.exp | |||
| # Precompiled Headers | |||
| *.gch | |||
| *.pch | |||
| # Libraries | |||
| *.lib | |||
| *.a | |||
| *.la | |||
| *.lo | |||
| # Shared objects (inc. Windows DLLs) | |||
| *.dll | |||
| *.so | |||
| *.so.* | |||
| *.dylib | |||
| # Executables | |||
| *.exe | |||
| *.out | |||
| *.app | |||
| *.i*86 | |||
| *.x86_64 | |||
| *.hex | |||
| # Debug files | |||
| *.dSYM/ | |||
| *.su | |||
| *.idb | |||
| *.pdb | |||
| # Kernel Module Compile Results | |||
| *.mod* | |||
| *.cmd | |||
| .tmp_versions/ | |||
| modules.order | |||
| Module.symvers | |||
| Mkfile.old | |||
| dkms.conf | |||
+ 0
- 12
LAB1/Driverhdrs.pm
View File
| @ -1,12 +0,0 @@ | |||
| # | |||
| # This file contains configuration variables for drivers. | |||
| # It was generated by genhdrs.pl. Do not modify it. | |||
| # | |||
| package Driverhdrs; | |||
| $LAB = "datalab"; | |||
| $SERVER_NAME = "changeme.ics.cs.cmu.edu"; | |||
| $SERVER_PORT = 8081; | |||
| $COURSE_NAME = "csapp"; | |||
| $AUTOGRADE_TIMEOUT = 0; | |||
| 1; | |||
+ 0
- 138
LAB1/Driverlib.pm
View File
| @ -1,138 +0,0 @@ | |||
| ############################################################### | |||
| # Driverlib.pm - A package of helper functions for Perl drivers | |||
| # | |||
| # Copyright (c) 2005 David R. O'Hallaron, All rights reserved. | |||
| ############################################################### | |||
| package Driverlib; | |||
| use Socket; | |||
| # Autogenerated header file with lab-specific constants | |||
| use lib "."; | |||
| use Driverhdrs; | |||
| require Exporter; | |||
| @ISA = qw(Exporter); | |||
| @EXPORT = qw( | |||
| driver_post | |||
| ); | |||
| use strict; | |||
| ##### | |||
| # Public functions | |||
| # | |||
| # | |||
| # driver_post - This is the routine that a driver calls when | |||
| # it needs to transmit an autoresult string to the result server. | |||
| # | |||
| sub driver_post ($$) { | |||
| my $userid = shift; # User id for this submission | |||
| my $result = shift; # Autoresult string | |||
| my $autograded = shift; # Set if called by an autograder | |||
| # Echo the autoresult string to stdout if the driver was called | |||
| # by an autograder | |||
| if ($autograded) { | |||
| print "\n"; | |||
| print "AUTORESULT_STRING=$result\n"; | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| # If the driver was called with a specific userid, then submit | |||
| # the autoresult string to the result server over the Internet. | |||
| if ($userid) { | |||
| my $status = submitr($Driverhdrs::SERVER_NAME, | |||
| $Driverhdrs::SERVER_PORT, | |||
| $Driverhdrs::COURSE_NAME, | |||
| $userid, | |||
| $Driverhdrs::LAB, | |||
| $result); | |||
| # Print the status of the transfer | |||
| if (!($status =~ /OK/)) { | |||
| print "$status\n"; | |||
| print "Did not send autoresult string to the result server.\n"; | |||
| exit(1); | |||
| } | |||
| print "Success: Sent autoresult string for $userid to the result server.\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| ##### | |||
| # Private functions | |||
| # | |||
| # | |||
| # submitr - Sends an autoresult string to the result server | |||
| # | |||
| sub submitr ($$$$$$) { | |||
| my $hostname = shift; | |||
| my $port = shift; | |||
| my $course = shift; | |||
| my $userid = shift; | |||
| my $lab = shift; | |||
| my $result = shift; | |||
| my $internet_addr; | |||
| my $enc_result; | |||
| my $paddr; | |||
| my $line; | |||
| my $http_version; | |||
| my $errcode; | |||
| my $errmsg; | |||
| # Establish the connection to the server | |||
| socket(SERVER, PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, getprotobyname('tcp')); | |||
| $internet_addr = inet_aton($hostname) | |||
| or die "Could not convert $hostname to an internet address: $!\n"; | |||
| $paddr = sockaddr_in($port, $internet_addr); | |||
| connect(SERVER, $paddr) | |||
| or die "Could not connect to $hostname:$port:$!\n"; | |||
| select((select(SERVER), $| = 1)[0]); # enable command buffering | |||
| # Send HTTP request to server | |||
| $enc_result = url_encode($result); | |||
| print SERVER "GET /$course/submitr.pl/?userid=$userid&lab=$lab&result=$enc_result&submit=submit HTTP/1.0\r\n\r\n"; | |||
| # Get first HTTP response line | |||
| $line = <SERVER>; | |||
| chomp($line); | |||
| ($http_version, $errcode, $errmsg) = split(/\s+/, $line); | |||
| if ($errcode != 200) { | |||
| return "Error: HTTP request failed with error $errcode: $errmsg"; | |||
| } | |||
| # Read the remaining HTTP response header lines | |||
| while ($line = <SERVER>) { | |||
| if ($line =~ /^\r\n/) { | |||
| last; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| # Read and return the response from the result server | |||
| $line = <SERVER>; | |||
| chomp($line); | |||
| close SERVER; | |||
| return $line; | |||
| } | |||
| # | |||
| # url_encode - Encode text string so it can be included in URI of GET request | |||
| # | |||
| sub url_encode ($) { | |||
| my $value = shift; | |||
| $value =~s/([^a-zA-Z0-9_\-.])/uc sprintf("%%%02x",ord($1))/eg; | |||
| return $value; | |||
| } | |||
| # Always end a module with a 1 so that it returns TRUE | |||
| 1; | |||
+ 0
- 33
LAB1/Makefile
View File
| @ -1,33 +0,0 @@ | |||
| # | |||
| # Makefile that builds btest and other helper programs for the CS:APP data lab | |||
| # | |||
| CC = gcc | |||
| CFLAGS = -O -Wall -m32 | |||
| LIBS = -lm | |||
| all: btest fshow ishow | |||
| btest: btest.c bits.c decl.c tests.c btest.h bits.h | |||
| $(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(LIBS) -o btest bits.c btest.c decl.c tests.c | |||
| fshow: fshow.c | |||
| $(CC) $(CFLAGS) -o fshow fshow.c | |||
| ishow: ishow.c | |||
| $(CC) $(CFLAGS) -o ishow ishow.c | |||
| # Forces a recompile. Used by the driver program. | |||
| btestexplicit: | |||
| $(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(LIBS) -o btest bits.c btest.c decl.c tests.c | |||
| clean: | |||
| rm -f *.o btest fshow ishow *~ | |||
| oneshoot: | |||
| make clean; \ | |||
| ./dlc bits.c; \ | |||
| make btest; \ | |||
| ./btest bits.c; \ | |||
| make clean \ | |||
+ 0
- 140
LAB1/README
View File
| @ -1,140 +0,0 @@ | |||
| *********************** | |||
| The CS:APP Data Lab | |||
| Directions to Students | |||
| *********************** | |||
| Your goal is to modify your copy of bits.c so that it passes all the | |||
| tests in btest without violating any of the coding guidelines. | |||
| ********* | |||
| 0. Files: | |||
| ********* | |||
| Makefile - Makes btest, fshow, and ishow | |||
| README - This file | |||
| bits.c - The file you will be modifying and handing in | |||
| bits.h - Header file | |||
| btest.c - The main btest program | |||
| btest.h - Used to build btest | |||
| decl.c - Used to build btest | |||
| tests.c - Used to build btest | |||
| tests-header.c- Used to build btest | |||
| dlc* - Rule checking compiler binary (data lab compiler) | |||
| driver.pl* - Driver program that uses btest and dlc to autograde bits.c | |||
| Driverhdrs.pm - Header file for optional "Beat the Prof" contest | |||
| fshow.c - Utility for examining floating-point representations | |||
| ishow.c - Utility for examining integer representations | |||
| *********************************************************** | |||
| 1. Modifying bits.c and checking it for compliance with dlc | |||
| *********************************************************** | |||
| IMPORTANT: Carefully read the instructions in the bits.c file before | |||
| you start. These give the coding rules that you will need to follow if | |||
| you want full credit. | |||
| Use the dlc compiler (./dlc) to automatically check your version of | |||
| bits.c for compliance with the coding guidelines: | |||
| unix> ./dlc bits.c | |||
| dlc returns silently if there are no problems with your code. | |||
| Otherwise it prints messages that flag any problems. Running dlc with | |||
| the -e switch: | |||
| unix> ./dlc -e bits.c | |||
| causes dlc to print counts of the number of operators used by each function. | |||
| Once you have a legal solution, you can test it for correctness using | |||
| the ./btest program. | |||
| ********************* | |||
| 2. Testing with btest | |||
| ********************* | |||
| The Makefile in this directory compiles your version of bits.c with | |||
| additional code to create a program (or test harness) named btest. | |||
| To compile and run the btest program, type: | |||
| unix> make btest | |||
| unix> ./btest [optional cmd line args] | |||
| You will need to recompile btest each time you change your bits.c | |||
| program. When moving from one platform to another, you will want to | |||
| get rid of the old version of btest and generate a new one. Use the | |||
| commands: | |||
| unix> make clean | |||
| unix> make btest | |||
| Btest tests your code for correctness by running millions of test | |||
| cases on each function. It tests wide swaths around well known corner | |||
| cases such as Tmin and zero for integer puzzles, and zero, inf, and | |||
| the boundary between denormalized and normalized numbers for floating | |||
| point puzzles. When btest detects an error in one of your functions, | |||
| it prints out the test that failed, the incorrect result, and the | |||
| expected result, and then terminates the testing for that function. | |||
| Here are the command line options for btest: | |||
| unix> ./btest -h | |||
| Usage: ./btest [-hg] [-r <n>] [-f <name> [-1|-2|-3 <val>]*] [-T <time limit>] | |||
| -1 <val> Specify first function argument | |||
| -2 <val> Specify second function argument | |||
| -3 <val> Specify third function argument | |||
| -f <name> Test only the named function | |||
| -g Format output for autograding with no error messages | |||
| -h Print this message | |||
| -r <n> Give uniform weight of n for all problems | |||
| -T <lim> Set timeout limit to lim | |||
| Examples: | |||
| Test all functions for correctness and print out error messages: | |||
| unix> ./btest | |||
| Test all functions in a compact form with no error messages: | |||
| unix> ./btest -g | |||
| Test function foo for correctness: | |||
| unix> ./btest -f foo | |||
| Test function foo for correctness with specific arguments: | |||
| unix> ./btest -f foo -1 27 -2 0xf | |||
| Btest does not check your code for compliance with the coding | |||
| guidelines. Use dlc to do that. | |||
| ******************* | |||
| 3. Helper Programs | |||
| ******************* | |||
| We have included the ishow and fshow programs to help you decipher | |||
| integer and floating point representations respectively. Each takes a | |||
| single decimal or hex number as an argument. To build them type: | |||
| unix> make | |||
| Example usages: | |||
| unix> ./ishow 0x27 | |||
| Hex = 0x00000027, Signed = 39, Unsigned = 39 | |||
| unix> ./ishow 27 | |||
| Hex = 0x0000001b, Signed = 27, Unsigned = 27 | |||
| unix> ./fshow 0x15213243 | |||
| Floating point value 3.255334057e-26 | |||
| Bit Representation 0x15213243, sign = 0, exponent = 0x2a, fraction = 0x213243 | |||
| Normalized. +1.2593463659 X 2^(-85) | |||
| linux> ./fshow 15213243 | |||
| Floating point value 2.131829405e-38 | |||
| Bit Representation 0x00e822bb, sign = 0, exponent = 0x01, fraction = 0x6822bb | |||
| Normalized. +1.8135598898 X 2^(-126) | |||
+ 0
- 388
LAB1/bits.c
View File
| @ -1,388 +0,0 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * CS:APP Data Lab | |||
| * | |||
| * <Please put your name and userid here> | |||
| * | |||
| * bits.c - Source file with your solutions to the Lab. | |||
| * This is the file you will hand in to your instructor. | |||
| * | |||
| * WARNING: Do not include the <stdio.h> header; it confuses the dlc | |||
| * compiler. You can still use printf for debugging without including | |||
| * <stdio.h>, although you might get a compiler warning. In general, | |||
| * it's not good practice to ignore compiler warnings, but in this | |||
| * case it's OK. | |||
| */ | |||
| #if 0 | |||
| /* | |||
| * Instructions to Students: | |||
| * | |||
| * STEP 1: Read the following instructions carefully. | |||
| */ | |||
| You will provide your solution to the Data Lab by | |||
| editing the collection of functions in this source file. | |||
| INTEGER CODING RULES: | |||
| Replace the "return" statement in each function with one | |||
| or more lines of C code that implements the function. Your code | |||
| must conform to the following style: | |||
| int Funct(arg1, arg2, ...) { | |||
| /* brief description of how your implementation works */ | |||
| int var1 = Expr1; | |||
| ... | |||
| int varM = ExprM; | |||
| varJ = ExprJ; | |||
| ... | |||
| varN = ExprN; | |||
| return ExprR; | |||
| } | |||
| Each "Expr" is an expression using ONLY the following: | |||
| 1. Integer constants 0 through 255 (0xFF), inclusive. You are | |||
| not allowed to use big constants such as 0xffffffff. | |||
| 2. Function arguments and local variables (no global variables). | |||
| 3. Unary integer operations ! ~ | |||
| 4. Binary integer operations & ^ | + << >> | |||
| Some of the problems restrict the set of allowed operators even further. | |||
| Each "Expr" may consist of multiple operators. You are not restricted to | |||
| one operator per line. | |||
| You are expressly forbidden to: | |||
| 1. Use any control constructs such as if, do, while, for, switch, etc. | |||
| 2. Define or use any macros. | |||
| 3. Define any additional functions in this file. | |||
| 4. Call any functions. | |||
| 5. Use any other operations, such as &&, ||, -, or ?: | |||
| 6. Use any form of casting. | |||
| 7. Use any data type other than int. This implies that you | |||
| cannot use arrays, structs, or unions. | |||
| You may assume that your machine: | |||
| 1. Uses 2s complement, 32-bit representations of integers. | |||
| 2. Performs right shifts arithmetically. | |||
| 3. Has unpredictable behavior when shifting if the shift amount | |||
| is less than 0 or greater than 31. | |||
| EXAMPLES OF ACCEPTABLE CODING STYLE: | |||
| /* | |||
| * pow2plus1 - returns 2^x + 1, where 0 <= x <= 31 | |||
| */ | |||
| int pow2plus1(int x) { | |||
| /* exploit ability of shifts to compute powers of 2 */ | |||
| return (1 << x) + 1; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * pow2plus4 - returns 2^x + 4, where 0 <= x <= 31 | |||
| */ | |||
| int pow2plus4(int x) { | |||
| /* exploit ability of shifts to compute powers of 2 */ | |||
| int result = (1 << x); | |||
| result += 4; | |||
| return result; | |||
| } | |||
| FLOATING POINT CODING RULES | |||
| For the problems that require you to implement floating-point operations, | |||
| the coding rules are less strict. You are allowed to use looping and | |||
| conditional control. You are allowed to use both ints and unsigneds. | |||
| You can use arbitrary integer and unsigned constants. You can use any arithmetic, | |||
| logical, or comparison operations on int or unsigned data. | |||
| You are expressly forbidden to: | |||
| 1. Define or use any macros. | |||
| 2. Define any additional functions in this file. | |||
| 3. Call any functions. | |||
| 4. Use any form of casting. | |||
| 5. Use any data type other than int or unsigned. This means that you | |||
| cannot use arrays, structs, or unions. | |||
| 6. Use any floating point data types, operations, or constants. | |||
| NOTES: | |||
| 1. Use the dlc (data lab checker) compiler (described in the handout) to | |||
| check the legality of your solutions. | |||
| 2. Each function has a maximum number of operations (integer, logical, | |||
| or comparison) that you are allowed to use for your implementation | |||
| of the function. The max operator count is checked by dlc. | |||
| Note that assignment ('=') is not counted; you may use as many of | |||
| these as you want without penalty. | |||
| 3. Use the btest test harness to check your functions for correctness. | |||
| 4. Use the BDD checker to formally verify your functions | |||
| 5. The maximum number of ops for each function is given in the | |||
| header comment for each function. If there are any inconsistencies | |||
| between the maximum ops in the writeup and in this file, consider | |||
| this file the authoritative source. | |||
| /* | |||
| * STEP 2: Modify the following functions according the coding rules. | |||
| * | |||
| * IMPORTANT. TO AVOID GRADING SURPRISES: | |||
| * 1. Use the dlc compiler to check that your solutions conform | |||
| * to the coding rules. | |||
| * 2. Use the BDD checker to formally verify that your solutions produce | |||
| * the correct answers. | |||
| */ | |||
| #endif | |||
| /* Copyright (C) 1991-2020 Free Software Foundation, Inc. | |||
| This file is part of the GNU C Library. | |||
| The GNU C Library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or | |||
| modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public | |||
| License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either | |||
| version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version. | |||
| The GNU C Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU | |||
| Lesser General Public License for more details. | |||
| You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public | |||
| License along with the GNU C Library; if not, see | |||
| <https://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. */ | |||
| /* This header is separate from features.h so that the compiler can | |||
| include it implicitly at the start of every compilation. It must | |||
| not itself include <features.h> or any other header that includes | |||
| <features.h> because the implicit include comes before any feature | |||
| test macros that may be defined in a source file before it first | |||
| explicitly includes a system header. GCC knows the name of this | |||
| header in order to preinclude it. */ | |||
| /* glibc's intent is to support the IEC 559 math functionality, real | |||
| and complex. If the GCC (4.9 and later) predefined macros | |||
| specifying compiler intent are available, use them to determine | |||
| whether the overall intent is to support these features; otherwise, | |||
| presume an older compiler has intent to support these features and | |||
| define these macros by default. */ | |||
| /* wchar_t uses Unicode 10.0.0. Version 10.0 of the Unicode Standard is | |||
| synchronized with ISO/IEC 10646:2017, fifth edition, plus | |||
| the following additions from Amendment 1 to the fifth edition: | |||
| - 56 emoji characters | |||
| - 285 hentaigana | |||
| - 3 additional Zanabazar Square characters */ | |||
| //1 | |||
| /* | |||
| * bitXor - x^y using only ~ and & | |||
| * Example: bitXor(4, 5) = 1 | |||
| * Legal ops: ~ & | |||
| * Max ops: 14 | |||
| * Rating: 1 | |||
| */ | |||
| int bitXor(int x, int y) { | |||
| return ~(~x&~y)&~(x&y); | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * tmin - return minimum two's complement integer | |||
| * Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >> | |||
| * Max ops: 4 | |||
| * Rating: 1 | |||
| */ | |||
| int tmin(void) { | |||
| return 0x1<<31; | |||
| } | |||
| //2 | |||
| /* | |||
| * isTmax - returns 1 if x is the maximum, two's complement number, | |||
| * and 0 otherwise | |||
| * Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + | |||
| * Max ops: 10 | |||
| * Rating: 1 | |||
| */ | |||
| int isTmax(int x) { | |||
| int i =x+1; | |||
| x = x+i; | |||
| x = ~x; | |||
| i = !i; | |||
| x = x+i; | |||
| return !x; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * allOddBits - return 1 if all odd-numbered bits in word set to 1 | |||
| * where bits are numbered from 0 (least significant) to 31 (most significant) | |||
| * Examples allOddBits(0xFFFFFFFD) = 0, allOddBits(0xAAAAAAAA) = 1 | |||
| * Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >> | |||
| * Max ops: 12 | |||
| * Rating: 2 | |||
| */ | |||
| int allOddBits(int x) { | |||
| int a = 0xaaaaaaaa; | |||
| return !((a&x)^a); | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * negate - return -x | |||
| * Example: negate(1) = -1. | |||
| * Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >> | |||
| * Max ops: 5 | |||
| * Rating: 2 | |||
| */ | |||
| int negate(int x) { | |||
| return ~x+1; | |||
| } | |||
| //3 | |||
| /* | |||
| * isAsciiDigit - return 1 if 0x30 <= x <= 0x39 (ASCII codes for characters '0' to '9') | |||
| * Example: isAsciiDigit(0x35) = 1. | |||
| * isAsciiDigit(0x3a) = 0. | |||
| * isAsciiDigit(0x05) = 0. | |||
| * Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >> | |||
| * Max ops: 15 | |||
| * Rating: 3 | |||
| */ | |||
| int isAsciiDigit(int x) { | |||
| //下边界为加够了就溢出,比这个大 | |||
| //上边界为加不够就不溢出 | |||
| int downstream = ~0x30+1; | |||
| int upstream = ~0x39; | |||
| int leftside = !((downstream+x)>>31); //超过0x30就符号变为0 | |||
| int rightside = !!((upstream+x)>>31); //小于0x39就符号仍然为1 | |||
| return leftside&rightside; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * conditional - same as x ? y : z | |||
| * Example: conditional(2,4,5) = 4 | |||
| * Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >> | |||
| * Max ops: 16 | |||
| * Rating: 3 | |||
| */ | |||
| int conditional(int x, int y, int z) { | |||
| x = !!(x); | |||
| x = ~x+1; | |||
| return (x&y)|(~x&z); | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * isLessOrEqual - if x <= y then return 1, else return 0 | |||
| * Example: isLessOrEqual(4,5) = 1. | |||
| * Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >> | |||
| * Max ops: 24 | |||
| * Rating: 3 | |||
| */ | |||
| int isLessOrEqual(int x, int y) { | |||
| int tmp = ~y+1; | |||
| tmp = tmp+x-1; | |||
| tmp = tmp >> 31;//如果比y大,则为0,比y小等于,为1 | |||
| return !!tmp; | |||
| } | |||
| //4 | |||
| /* | |||
| * logicalNeg - implement the ! operator, using all of | |||
| * the legal operators except ! | |||
| * Examples: logicalNeg(3) = 0, logicalNeg(0) = 1 | |||
| * Legal ops: ~ & ^ | + << >> | |||
| * Max ops: 12 | |||
| * Rating: 4 | |||
| */ | |||
| int logicalNeg(int x) { | |||
| return ((x|(~x+1))>>31)+1; | |||
| } | |||
| /* howManyBits - return the minimum number of bits required to represent x in | |||
| * two's complement | |||
| * Examples: howManyBits(12) = 5 | |||
| * howManyBits(298) = 10 | |||
| * howManyBits(-5) = 4 | |||
| * howManyBits(0) = 1 | |||
| * howManyBits(-1) = 1 | |||
| * howManyBits(0x80000000) = 32 | |||
| * Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >> | |||
| * Max ops: 90 | |||
| * Rating: 4 | |||
| */ | |||
| int howManyBits(int x) { | |||
| x = ((~(x>>31))&x)|(x>>31&~x);//左边为如果为正数,则保留;右边为如果为负数,则取反 | |||
| //先从最大开始查找 | |||
| int tf = !!(x>>16); //如果小于等于16位,则为0,否则为1 | |||
| int b16 = tf << 4; //长度超过16位,记录值b16为16,否则为0,代表至少16位 | |||
| x = x>>b16; //右移动b16位,超过16位则探讨16位以上的,少于16位则探讨16位以下的 | |||
| tf = !!(x>>8); //开始探讨剩余部位是否超过8位,超过看超过多少,没超过看余下多少 | |||
| int b8 = tf << 3;//长度超过8位,记录值b8为8,否则为0,代表再多至少8位 | |||
| x = x>>b8; | |||
| tf = !!(x>>4); | |||
| int b4 = tf << 2 ; //8找4,长度超过4位,记录值b4为4,否则为0,代表再多至少4位 | |||
| x = x>>b4; | |||
| tf = !!(x>>2); | |||
| int b2 = tf << 1; //4找2,长度超过2位,记录值b2为2,否则为0,代表再多至少2位 | |||
| x = x>>b2; | |||
| tf = !!(x>>1); //2找1,长度超过1位,记录值b1为1,否则为0,代表再多至少1位 | |||
| int b1 = tf << 0; | |||
| x = x>>b1; | |||
| int b0 = x;//截断到只剩单个数字,这个数字是1就再多一位,是0就不会增加 | |||
| return b0+b1+b2+b4+b8+b16+1; //正数多一位补码最高位,负数因为取反未+1,理应再加1,故两个输出表达式一致 | |||
| } | |||
| //float | |||
| /* | |||
| * floatScale2 - Return bit-level equivalent of expression 2*f for | |||
| * floating point argument f. | |||
| * Both the argument and result are passed as unsigned int's, but | |||
| * they are to be interpreted as the bit-level representation of | |||
| * single-precision floating point values. | |||
| * When argument is NaN, return argument | |||
| * Legal ops: Any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. also if, while | |||
| * Max ops: 30 | |||
| * Rating: 4 | |||
| */ | |||
| unsigned floatScale2(unsigned uf) { | |||
| unsigned sign = (0x80000000)&uf; | |||
| unsigned exp = (0x7f800000)&uf; | |||
| unsigned frac = (0x007fffff)&uf; | |||
| if(exp == 0x7f800000) | |||
| return uf; //如果是exp全为255,frac全是0就是无穷,不是就是NaN,都直接return | |||
| if(exp == 0x00000000){ | |||
| if(frac == 0x00000000) | |||
| return uf; //exp全为0,frac全为0,则为0,0*2=0,原样不动 | |||
| return (frac<<1)|sign|exp;//exp全为0,frac不全为0,注意到非规格化极小和规格化之间是连续的,即frac第一位为1时,左移会把exp变为非全0,回到规格化 | |||
| } | |||
| return (exp+0x00800000)|sign|frac; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * floatFloat2Int - Return bit-level equivalent of expression (int) f | |||
| * for floating point argument f. | |||
| * Argument is passed as unsigned int, but | |||
| * it is to be interpreted as the bit-level representation of a | |||
| * single-precision floating point value. | |||
| * Anything out of range (including NaN and infinity) should return | |||
| * 0x80000000u. | |||
| * Legal ops: Any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. also if, while | |||
| * Max ops: 30 | |||
| * Rating: 4 | |||
| */ | |||
| int floatFloat2Int(unsigned uf) { | |||
| unsigned sign = ((0x80000000)&uf)>>31; | |||
| unsigned exp = ((0x7f800000)&uf)>>23; | |||
| unsigned frac = (0x007fffff)&uf; | |||
| unsigned base = (frac+0x00800000);//加1后的基底(对于常规数) | |||
| int bias = (exp-127)-23;//真实需要左移的 | |||
| if(sign==0) | |||
| sign = 1; | |||
| else | |||
| sign = -1; | |||
| if(exp == 255) | |||
| return 0x80000000u;//足够大 | |||
| if(exp == 0) | |||
| return 0;//足够小 | |||
| if(bias <=0){ | |||
| if(bias<=-24) | |||
| bias = -24; | |||
| return sign*(base>>(-bias)); | |||
| } | |||
| else{ | |||
| if(bias>=9) | |||
| return 0x80000000u; | |||
| return sign*(base<<bias); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // #include "floatPower2.c" | |||
+ 0
- 65
LAB1/bits.h
View File
| @ -1,65 +0,0 @@ | |||
| /* Copyright (C) 1991-2020 Free Software Foundation, Inc. | |||
| This file is part of the GNU C Library. | |||
| The GNU C Library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or | |||
| modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public | |||
| License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either | |||
| version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version. | |||
| The GNU C Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU | |||
| Lesser General Public License for more details. | |||
| You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public | |||
| License along with the GNU C Library; if not, see | |||
| <https://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. */ | |||
| /* This header is separate from features.h so that the compiler can | |||
| include it implicitly at the start of every compilation. It must | |||
| not itself include <features.h> or any other header that includes | |||
| <features.h> because the implicit include comes before any feature | |||
| test macros that may be defined in a source file before it first | |||
| explicitly includes a system header. GCC knows the name of this | |||
| header in order to preinclude it. */ | |||
| /* glibc's intent is to support the IEC 559 math functionality, real | |||
| and complex. If the GCC (4.9 and later) predefined macros | |||
| specifying compiler intent are available, use them to determine | |||
| whether the overall intent is to support these features; otherwise, | |||
| presume an older compiler has intent to support these features and | |||
| define these macros by default. */ | |||
| /* wchar_t uses Unicode 10.0.0. Version 10.0 of the Unicode Standard is | |||
| synchronized with ISO/IEC 10646:2017, fifth edition, plus | |||
| the following additions from Amendment 1 to the fifth edition: | |||
| - 56 emoji characters | |||
| - 285 hentaigana | |||
| - 3 additional Zanabazar Square characters */ | |||
| //1 | |||
| int bitXor(int, int); | |||
| int test_bitXor(int, int); | |||
| int tmin(); | |||
| int test_tmin(); | |||
| //2 | |||
| int isTmax(int); | |||
| int test_isTmax(int); | |||
| int allOddBits(); | |||
| int test_allOddBits(); | |||
| int negate(int); | |||
| int test_negate(int); | |||
| //3 | |||
| int isAsciiDigit(int); | |||
| int test_isAsciiDigit(int); | |||
| int conditional(int, int, int); | |||
| int test_conditional(int, int, int); | |||
| int isLessOrEqual(int, int); | |||
| int test_isLessOrEqual(int, int); | |||
| //4 | |||
| int logicalNeg(int); | |||
| int test_logicalNeg(int); | |||
| int howManyBits(int); | |||
| int test_howManyBits(int); | |||
| //float | |||
| unsigned floatScale2(unsigned); | |||
| unsigned test_floatScale2(unsigned); | |||
| int floatFloat2Int(unsigned); | |||
| int test_floatFloat2Int(unsigned); | |||
| // #include "floatPower2.c" | |||
+ 0
- 583
LAB1/btest.c
View File
| @ -1,583 +0,0 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * CS:APP Data Lab | |||
| * | |||
| * btest.c - A test harness that checks a student's solution in bits.c | |||
| * for correctness. | |||
| * | |||
| * Copyright (c) 2001-2011, R. Bryant and D. O'Hallaron, All rights | |||
| * reserved. May not be used, modified, or copied without permission. | |||
| * | |||
| * This is an improved version of btest that tests large windows | |||
| * around zero and tmin and tmax for integer puzzles, and zero, norm, | |||
| * and denorm boundaries for floating point puzzles. | |||
| * | |||
| * Note: not 64-bit safe. Always compile with gcc -m32 option. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <stdio.h> | |||
| #include <unistd.h> | |||
| #include <stdlib.h> | |||
| #include <string.h> | |||
| #include <limits.h> | |||
| #include <signal.h> | |||
| #include <setjmp.h> | |||
| #include <math.h> | |||
| #include "btest.h" | |||
| /* Not declared in some stdlib.h files, so define here */ | |||
| float strtof(const char *nptr, char **endptr); | |||
| /************************* | |||
| * Configuration Constants | |||
| *************************/ | |||
| /* Handle infinite loops by setting upper limit on execution time, in | |||
| seconds */ | |||
| #define TIMEOUT_LIMIT 10 | |||
| /* For functions with a single argument, generate TEST_RANGE values | |||
| above and below the min and max test values, and above and below | |||
| zero. Functions with two or three args will use square and cube | |||
| roots of this value, respectively, to avoid combinatorial | |||
| explosion */ | |||
| #define TEST_RANGE 500000 | |||
| /* This defines the maximum size of any test value array. The | |||
| gen_vals() routine creates k test values for each value of | |||
| TEST_RANGE, thus MAX_TEST_VALS must be at least k*TEST_RANGE */ | |||
| #define MAX_TEST_VALS 13*TEST_RANGE | |||
| /********************************** | |||
| * Globals defined in other modules | |||
| **********************************/ | |||
| /* This characterizes the set of puzzles to test. | |||
| Defined in decl.c and generated from templates in ./puzzles dir */ | |||
| extern test_rec test_set[]; | |||
| /************************************************ | |||
| * Write-once globals defined by command line args | |||
| ************************************************/ | |||
| /* Emit results in a format for autograding, without showing | |||
| and counter-examples */ | |||
| static int grade = 0; | |||
| /* Time out after this number of seconds */ | |||
| static int timeout_limit = TIMEOUT_LIMIT; /* -T */ | |||
| /* If non-NULL, test only one function (-f) */ | |||
| static char* test_fname = NULL; | |||
| /* Special case when only use fixed argument(s) (-1, -2, or -3) */ | |||
| static int has_arg[3] = {0,0,0}; | |||
| static unsigned argval[3] = {0,0,0}; | |||
| /* Use fixed weight for rating, and if so, what should it be? (-r) */ | |||
| static int global_rating = 0; | |||
| /****************** | |||
| * Helper functions | |||
| ******************/ | |||
| /* | |||
| * Signal - installs a signal handler | |||
| */ | |||
| typedef void handler_t(int); | |||
| handler_t *Signal(int signum, handler_t *handler) | |||
| { | |||
| struct sigaction action, old_action; | |||
| action.sa_handler = handler; | |||
| sigemptyset(&action.sa_mask); /* block sigs of type being handled */ | |||
| action.sa_flags = SA_RESTART; /* restart syscalls if possible */ | |||
| if (sigaction(signum, &action, &old_action) < 0) | |||
| perror("Signal error"); | |||
| return (old_action.sa_handler); | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * timeout_handler - SIGALARM hander | |||
| */ | |||
| sigjmp_buf envbuf; | |||
| void timeout_handler(int sig) { | |||
| siglongjmp(envbuf, 1); | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * random_val - Return random integer value between min and max | |||
| */ | |||
| static int random_val(int min, int max) | |||
| { | |||
| double weight = rand()/(double) RAND_MAX; | |||
| int result = min * (1-weight) + max * weight; | |||
| return result; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * gen_vals - Generate the integer values we'll use to test a function | |||
| */ | |||
| static int gen_vals(int test_vals[], int min, int max, int test_range, int arg) | |||
| { | |||
| int i; | |||
| int test_count = 0; | |||
| /* Special case: If the user has specified a specific function | |||
| argument using the -1, -2, or -3 flags, then simply use this | |||
| argument and return */ | |||
| if (has_arg[arg]) { | |||
| test_vals[0] = argval[arg]; | |||
| return 1; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * Special case: Generate test vals for floating point functions | |||
| * where the input argument is an unsigned bit-level | |||
| * representation of a float. For this case we want to test the | |||
| * regions around zero, the smallest normalized and largest | |||
| * denormalized numbers, one, and the largest normalized number, | |||
| * as well as inf and nan. | |||
| */ | |||
| if ((min == 1 && max == 1)) { | |||
| unsigned smallest_norm = 0x00800000; | |||
| unsigned one = 0x3f800000; | |||
| unsigned largest_norm = 0x7f000000; | |||
| unsigned inf = 0x7f800000; | |||
| unsigned nan = 0x7fc00000; | |||
| unsigned sign = 0x80000000; | |||
| /* Test range should be at most 1/2 the range of one exponent | |||
| value */ | |||
| if (test_range > (1 << 23)) { | |||
| test_range = 1 << 23; | |||
| } | |||
| /* Functions where the input argument is an unsigned bit-level | |||
| representation of a float. The number of tests generated | |||
| inside this loop body is the value k referenced in the | |||
| comment for the global variable MAX_TEST_VALS. */ | |||
| for (i = 0; i < test_range; i++) { | |||
| /* Denorms around zero */ | |||
| test_vals[test_count++] = i; | |||
| test_vals[test_count++] = sign | i; | |||
| /* Region around norm to denorm transition */ | |||
| test_vals[test_count++] = smallest_norm + i; | |||
| test_vals[test_count++] = smallest_norm - i; | |||
| test_vals[test_count++] = sign | (smallest_norm + i); | |||
| test_vals[test_count++] = sign | (smallest_norm - i); | |||
| /* Region around one */ | |||
| test_vals[test_count++] = one + i; | |||
| test_vals[test_count++] = one - i; | |||
| test_vals[test_count++] = sign | (one + i); | |||
| test_vals[test_count++] = sign | (one - i); | |||
| /* Region below largest norm */ | |||
| test_vals[test_count++] = largest_norm - i; | |||
| test_vals[test_count++] = sign | (largest_norm - i); | |||
| } | |||
| /* special vals */ | |||
| test_vals[test_count++] = inf; /* inf */ | |||
| test_vals[test_count++] = sign | inf; /* -inf */ | |||
| test_vals[test_count++] = nan; /* nan */ | |||
| test_vals[test_count++] = sign | nan; /* -nan */ | |||
| return test_count; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * Normal case: Generate test vals for integer functions | |||
| */ | |||
| /* If the range is small enough, then do exhaustively */ | |||
| if (max - MAX_TEST_VALS <= min) { | |||
| for (i = min; i <= max; i++) | |||
| test_vals[test_count++] = i; | |||
| return test_count; | |||
| } | |||
| /* Otherwise, need to sample. Do so near the boundaries, around | |||
| zero, and for some random cases. */ | |||
| for (i = 0; i < test_range; i++) { | |||
| /* Test around the boundaries */ | |||
| test_vals[test_count++] = min + i; | |||
| test_vals[test_count++] = max - i; | |||
| /* If zero falls between min and max, then also test around zero */ | |||
| if (i >= min && i <= max) | |||
| test_vals[test_count++] = i; | |||
| if (-i >= min && -i <= max) | |||
| test_vals[test_count++] = -i; | |||
| /* Random case between min and max */ | |||
| test_vals[test_count++] = random_val(min, max); | |||
| } | |||
| return test_count; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * test_0_arg - Test a function with zero arguments | |||
| */ | |||
| static int test_0_arg(funct_t f, funct_t ft, char *name) | |||
| { | |||
| int r = f(); | |||
| int rt = ft(); | |||
| int error = (r != rt); | |||
| if (error && !grade) | |||
| printf("ERROR: Test %s() failed...\n...Gives %d[0x%x]. Should be %d[0x%x]\n", name, r, r, rt, rt); | |||
| return error; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * test_1_arg - Test a function with one argument | |||
| */ | |||
| static int test_1_arg(funct_t f, funct_t ft, int arg1, char *name) | |||
| { | |||
| funct1_t f1 = (funct1_t) f; | |||
| funct1_t f1t = (funct1_t) ft; | |||
| int r, rt, error; | |||
| r = f1(arg1); | |||
| rt = f1t(arg1); | |||
| error = (r != rt); | |||
| if (error && !grade) | |||
| printf("ERROR: Test %s(%d[0x%x]) failed...\n...Gives %d[0x%x]. Should be %d[0x%x]\n", name, arg1, arg1, r, r, rt, rt); | |||
| return error; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * test_2_arg - Test a function with two arguments | |||
| */ | |||
| static int test_2_arg(funct_t f, funct_t ft, int arg1, int arg2, char *name) | |||
| { | |||
| funct2_t f2 = (funct2_t) f; | |||
| funct2_t f2t = (funct2_t) ft; | |||
| int r = f2(arg1, arg2); | |||
| int rt = f2t(arg1, arg2); | |||
| int error = (r != rt); | |||
| if (error && !grade) | |||
| printf("ERROR: Test %s(%d[0x%x],%d[0x%x]) failed...\n...Gives %d[0x%x]. Should be %d[0x%x]\n", name, arg1, arg1, arg2, arg2, r, r, rt, rt); | |||
| return error; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * test_3_arg - Test a function with three arguments | |||
| */ | |||
| static int test_3_arg(funct_t f, funct_t ft, | |||
| int arg1, int arg2, int arg3, char *name) | |||
| { | |||
| funct3_t f3 = (funct3_t) f; | |||
| funct3_t f3t = (funct3_t) ft; | |||
| int r = f3(arg1, arg2, arg3); | |||
| int rt = f3t(arg1, arg2, arg3); | |||
| int error = (r != rt); | |||
| if (error && !grade) | |||
| printf("ERROR: Test %s(%d[0x%x],%d[0x%x],%d[0x%x]) failed...\n...Gives %d[0x%x]. Should be %d[0x%x]\n", name, arg1, arg1, arg2, arg2, arg3, arg3, r, r, rt, rt); | |||
| return error; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * test_function - Test a function. Return number of errors | |||
| */ | |||
| static int test_function(test_ptr t) { | |||
| int test_counts[3]; /* number of test values for each arg */ | |||
| int args = t->args; /* number of function arguments */ | |||
| int arg_test_range[3]; /* test range for each argument */ | |||
| int i, a1, a2, a3; | |||
| int errors = 0; | |||
| /* These are the test values for each arg. Declared with the | |||
| static attribute so that the array will be allocated in bss | |||
| rather than the stack */ | |||
| static int arg_test_vals[3][MAX_TEST_VALS]; | |||
| /* Sanity check on the number of args */ | |||
| if (args < 0 || args > 3) { | |||
| printf("Configuration error: invalid number of args (%d) for function %s\n", args, t->name); | |||
| exit(1); | |||
| } | |||
| /* Assign range of argument test vals so as to conserve the total | |||
| number of tests, independent of the number of arguments */ | |||
| if (args == 1) { | |||
| arg_test_range[0] = TEST_RANGE; | |||
| } | |||
| else if (args == 2) { | |||
| arg_test_range[0] = pow((double)TEST_RANGE, 0.5); /* sqrt */ | |||
| arg_test_range[1] = arg_test_range[0]; | |||
| } | |||
| else { | |||
| arg_test_range[0] = pow((double)TEST_RANGE, 0.333); /* cbrt */ | |||
| arg_test_range[1] = arg_test_range[0]; | |||
| arg_test_range[2] = arg_test_range[0]; | |||
| } | |||
| /* Sanity check on the ranges */ | |||
| if (arg_test_range[0] < 1) | |||
| arg_test_range[0] = 1; | |||
| if (arg_test_range[1] < 1) | |||
| arg_test_range[1] = 1; | |||
| if (arg_test_range[2] < 1) | |||
| arg_test_range[2] = 1; | |||
| /* Create a test set for each argument */ | |||
| for (i = 0; i < args; i++) { | |||
| test_counts[i] = gen_vals(arg_test_vals[i], | |||
| t->arg_ranges[i][0], /* min */ | |||
| t->arg_ranges[i][1], /* max */ | |||
| arg_test_range[i], | |||
| i); | |||
| } | |||
| /* Handle timeouts in the test code */ | |||
| if (timeout_limit > 0) { | |||
| int rc; | |||
| rc = sigsetjmp(envbuf, 1); | |||
| if (rc) { | |||
| /* control will reach here if there is a timeout */ | |||
| errors = 1; | |||
| printf("ERROR: Test %s failed.\n Timed out after %d secs (probably infinite loop)\n", t->name, timeout_limit); | |||
| return errors; | |||
| } | |||
| alarm(timeout_limit); | |||
| } | |||
| /* Test function has no arguments */ | |||
| if (args == 0) { | |||
| errors += test_0_arg(t->solution_funct, t->test_funct, t->name); | |||
| return errors; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * Test function has at least one argument | |||
| */ | |||
| /* Iterate over the values for first argument */ | |||
| for (a1 = 0; a1 < test_counts[0]; a1++) { | |||
| if (args == 1) { | |||
| errors += test_1_arg(t->solution_funct, | |||
| t->test_funct, | |||
| arg_test_vals[0][a1], | |||
| t->name); | |||
| /* Stop testing if there is an error */ | |||
| if (errors) | |||
| return errors; | |||
| } | |||
| else { | |||
| /* if necessary, iterate over values for second argument */ | |||
| for (a2 = 0; a2 < test_counts[1]; a2++) { | |||
| if (args == 2) { | |||
| errors += test_2_arg(t->solution_funct, | |||
| t->test_funct, | |||
| arg_test_vals[0][a1], | |||
| arg_test_vals[1][a2], | |||
| t->name); | |||
| /* Stop testing if there is an error */ | |||
| if (errors) | |||
| return errors; | |||
| } | |||
| else { | |||
| /* if necessary, iterate over vals for third arg */ | |||
| for (a3 = 0; a3 < test_counts[2]; a3++) { | |||
| errors += test_3_arg(t->solution_funct, | |||
| t->test_funct, | |||
| arg_test_vals[0][a1], | |||
| arg_test_vals[1][a2], | |||
| arg_test_vals[2][a3], | |||
| t->name); | |||
| /* Stop testing if there is an error */ | |||
| if (errors) | |||
| return errors; | |||
| } /* a3 */ | |||
| } | |||
| } /* a2 */ | |||
| } | |||
| } /* a1 */ | |||
| return errors; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * run_tests - Run series of tests. Return number of errors | |||
| */ | |||
| static int run_tests() | |||
| { | |||
| int i; | |||
| int errors = 0; | |||
| double points = 0.0; | |||
| double max_points = 0.0; | |||
| printf("Score\tRating\tErrors\tFunction\n"); | |||
| for (i = 0; test_set[i].solution_funct; i++) { | |||
| int terrors; | |||
| double tscore; | |||
| double tpoints; | |||
| if (!test_fname || strcmp(test_set[i].name,test_fname) == 0) { | |||
| int rating = global_rating ? global_rating : test_set[i].rating; | |||
| terrors = test_function(&test_set[i]); | |||
| errors += terrors; | |||
| tscore = terrors == 0 ? 1.0 : 0.0; | |||
| tpoints = rating * tscore; | |||
| points += tpoints; | |||
| max_points += rating; | |||
| if (grade || terrors < 1) | |||
| printf(" %.0f\t%d\t%d\t%s\n", | |||
| tpoints, rating, terrors, test_set[i].name); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| printf("Total points: %.0f/%.0f\n", points, max_points); | |||
| return errors; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * get_num_val - Extract hex/decimal/or float value from string | |||
| */ | |||
| static int get_num_val(char *sval, unsigned *valp) { | |||
| char *endp; | |||
| /* See if it's an integer or floating point */ | |||
| int ishex = 0; | |||
| int isfloat = 0; | |||
| int i; | |||
| for (i = 0; sval[i]; i++) { | |||
| switch (sval[i]) { | |||
| case 'x': | |||
| case 'X': | |||
| ishex = 1; | |||
| break; | |||
| case 'e': | |||
| case 'E': | |||
| if (!ishex) | |||
| isfloat = 1; | |||
| break; | |||
| case '.': | |||
| isfloat = 1; | |||
| break; | |||
| default: | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| if (isfloat) { | |||
| float fval = strtof(sval, &endp); | |||
| if (!*endp) { | |||
| *valp = *(unsigned *) &fval; | |||
| return 1; | |||
| } | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } else { | |||
| long long int llval = strtoll(sval, &endp, 0); | |||
| long long int upperbits = llval >> 31; | |||
| /* will give -1 for negative, 0 or 1 for positive */ | |||
| if (!*valp && (upperbits == 0 || upperbits == -1 || upperbits == 1)) { | |||
| *valp = (unsigned) llval; | |||
| return 1; | |||
| } | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * usage - Display usage info | |||
| */ | |||
| static void usage(char *cmd) { | |||
| printf("Usage: %s [-hg] [-r <n>] [-f <name> [-1|-2|-3 <val>]*] [-T <time limit>]\n", cmd); | |||
| printf(" -1 <val> Specify first function argument\n"); | |||
| printf(" -2 <val> Specify second function argument\n"); | |||
| printf(" -3 <val> Specify third function argument\n"); | |||
| printf(" -f <name> Test only the named function\n"); | |||
| printf(" -g Compact output for grading (with no error msgs)\n"); | |||
| printf(" -h Print this message\n"); | |||
| printf(" -r <n> Give uniform weight of n for all problems\n"); | |||
| printf(" -T <lim> Set timeout limit to lim\n"); | |||
| exit(1); | |||
| } | |||
| /************** | |||
| * Main routine | |||
| **************/ | |||
| int main(int argc, char *argv[]) | |||
| { | |||
| char c; | |||
| /* parse command line args */ | |||
| while ((c = getopt(argc, argv, "hgf:r:T:1:2:3:")) != -1) | |||
| switch (c) { | |||
| case 'h': /* help */ | |||
| usage(argv[0]); | |||
| break; | |||
| case 'g': /* grading option for autograder */ | |||
| grade = 1; | |||
| break; | |||
| case 'f': /* test only one function */ | |||
| test_fname = strdup(optarg); | |||
| break; | |||
| case 'r': /* set global rating for each problem */ | |||
| global_rating = atoi(optarg); | |||
| if (global_rating < 0) | |||
| usage(argv[0]); | |||
| break; | |||
| case '1': /* Get first argument */ | |||
| has_arg[0] = get_num_val(optarg, &argval[0]); | |||
| if (!has_arg[0]) { | |||
| printf("Bad argument '%s'\n", optarg); | |||
| exit(0); | |||
| } | |||
| break; | |||
| case '2': /* Get first argument */ | |||
| has_arg[1] = get_num_val(optarg, &argval[1]); | |||
| if (!has_arg[1]) { | |||
| printf("Bad argument '%s'\n", optarg); | |||
| exit(0); | |||
| } | |||
| break; | |||
| case '3': /* Get first argument */ | |||
| has_arg[2] = get_num_val(optarg, &argval[2]); | |||
| if (!has_arg[2]) { | |||
| printf("Bad argument '%s'\n", optarg); | |||
| exit(0); | |||
| } | |||
| break; | |||
| case 'T': /* Set timeout limit */ | |||
| timeout_limit = atoi(optarg); | |||
| break; | |||
| default: | |||
| usage(argv[0]); | |||
| } | |||
| if (timeout_limit > 0) { | |||
| Signal(SIGALRM, timeout_handler); | |||
| } | |||
| /* test each function */ | |||
| run_tests(); | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
+ 0
- 32
LAB1/btest.h
View File
| @ -1,32 +0,0 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * CS:APP Data Lab | |||
| */ | |||
| /* Declare different function types */ | |||
| typedef int (*funct_t) (void); | |||
| typedef int (*funct1_t)(int); | |||
| typedef int (*funct2_t)(int, int); | |||
| typedef int (*funct3_t)(int, int, int); | |||
| /* Combine all the information about a function and its tests as structure */ | |||
| typedef struct { | |||
| char *name; /* String name */ | |||
| funct_t solution_funct; /* Function */ | |||
| funct_t test_funct; /* Test function */ | |||
| int args; /* Number of function arguments */ | |||
| char *ops; /* List of legal operators. Special case: "$" for floating point */ | |||
| int op_limit; /* Max number of ops allowed in solution */ | |||
| int rating; /* Problem rating (1 -- 4) */ | |||
| int arg_ranges[3][2]; /* Argument ranges. Always defined for 3 args, even if */ | |||
| /* the function takes fewer. Special case: First arg */ | |||
| /* must be set to {1,1} for f.p. puzzles */ | |||
| } test_rec, *test_ptr; | |||
| extern test_rec test_set[]; | |||
+ 0
- 86
LAB1/decl.c
View File
| @ -1,86 +0,0 @@ | |||
| #include <stdio.h> | |||
| #include <stdlib.h> | |||
| #include <limits.h> | |||
| #define TMin INT_MIN | |||
| #define TMax INT_MAX | |||
| #include "btest.h" | |||
| #include "bits.h" | |||
| test_rec test_set[] = { | |||
| /* Copyright (C) 1991-2020 Free Software Foundation, Inc. | |||
| This file is part of the GNU C Library. | |||
| The GNU C Library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or | |||
| modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public | |||
| License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either | |||
| version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version. | |||
| The GNU C Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU | |||
| Lesser General Public License for more details. | |||
| You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public | |||
| License along with the GNU C Library; if not, see | |||
| <https://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. */ | |||
| /* This header is separate from features.h so that the compiler can | |||
| include it implicitly at the start of every compilation. It must | |||
| not itself include <features.h> or any other header that includes | |||
| <features.h> because the implicit include comes before any feature | |||
| test macros that may be defined in a source file before it first | |||
| explicitly includes a system header. GCC knows the name of this | |||
| header in order to preinclude it. */ | |||
| /* glibc's intent is to support the IEC 559 math functionality, real | |||
| and complex. If the GCC (4.9 and later) predefined macros | |||
| specifying compiler intent are available, use them to determine | |||
| whether the overall intent is to support these features; otherwise, | |||
| presume an older compiler has intent to support these features and | |||
| define these macros by default. */ | |||
| /* wchar_t uses Unicode 10.0.0. Version 10.0 of the Unicode Standard is | |||
| synchronized with ISO/IEC 10646:2017, fifth edition, plus | |||
| the following additions from Amendment 1 to the fifth edition: | |||
| - 56 emoji characters | |||
| - 285 hentaigana | |||
| - 3 additional Zanabazar Square characters */ | |||
| //1 | |||
| {"bitXor", (funct_t) bitXor, (funct_t) test_bitXor, 2, "& ~", 14, 1, | |||
| {{TMin, TMax},{TMin,TMax},{TMin,TMax}}}, | |||
| {"tmin", (funct_t) tmin, (funct_t) test_tmin, 0, "! ~ & ^ | + << >>", 4, 1, | |||
| {{TMin, TMax},{TMin,TMax},{TMin,TMax}}}, | |||
| //2 | |||
| {"isTmax", (funct_t) isTmax, (funct_t) test_isTmax, 1, "! ~ & ^ | +", 10, 1, | |||
| {{TMin, TMax},{TMin,TMax},{TMin,TMax}}}, | |||
| {"allOddBits", (funct_t) allOddBits, (funct_t) test_allOddBits, 1, | |||
| "! ~ & ^ | + << >>", 12, 2, | |||
| {{TMin, TMax},{TMin,TMax},{TMin,TMax}}}, | |||
| {"negate", (funct_t) negate, (funct_t) test_negate, 1, | |||
| "! ~ & ^ | + << >>", 5, 2, | |||
| {{TMin, TMax},{TMin,TMax},{TMin,TMax}}}, | |||
| //3 | |||
| {"isAsciiDigit", (funct_t) isAsciiDigit, (funct_t) test_isAsciiDigit, 1, | |||
| "! ~ & ^ | + << >>", 15, 3, | |||
| {{TMin, TMax},{TMin,TMax},{TMin,TMax}}}, | |||
| {"conditional", (funct_t) conditional, (funct_t) test_conditional, 3, "! ~ & ^ | << >>", 16, 3, | |||
| {{TMin, TMax},{TMin,TMax},{TMin,TMax}}}, | |||
| {"isLessOrEqual", (funct_t) isLessOrEqual, (funct_t) test_isLessOrEqual, 2, | |||
| "! ~ & ^ | + << >>", 24, 3, | |||
| {{TMin, TMax},{TMin,TMax},{TMin,TMax}}}, | |||
| //4 | |||
| {"logicalNeg", (funct_t) logicalNeg, (funct_t) test_logicalNeg, 1, | |||
| "~ & ^ | + << >>", 12, 4, | |||
| {{TMin, TMax},{TMin,TMax},{TMin,TMax}}}, | |||
| {"howManyBits", (funct_t) howManyBits, (funct_t) test_howManyBits, 1, "! ~ & ^ | + << >>", 90, 4, | |||
| {{TMin, TMax},{TMin,TMax},{TMin,TMax}}}, | |||
| //float | |||
| {"floatScale2", (funct_t) floatScale2, (funct_t) test_floatScale2, 1, | |||
| "$", 30, 4, | |||
| {{1, 1},{1,1},{1,1}}}, | |||
| {"floatFloat2Int", (funct_t) floatFloat2Int, (funct_t) test_floatFloat2Int, 1, | |||
| "$", 30, 4, | |||
| {{1, 1},{1,1},{1,1}}}, | |||
| // #include "floatPower2.c" | |||
| {"", NULL, NULL, 0, "", 0, 0, | |||
| {{0, 0},{0,0},{0,0}}} | |||
| }; | |||
+ 0
- 0
LAB1/dlc
View File
+ 0
- 439
LAB1/driver.pl
View File
| @ -1,439 +0,0 @@ | |||
| #!/usr/bin/perl | |||
| ####################################################################### | |||
| # driver.pl - CS:APP Data Lab driver | |||
| # | |||
| # Copyright (c) 2004-2011, R. Bryant and D. O'Hallaron, All rights | |||
| # reserved. May not be used, modified, or copied without permission. | |||
| # | |||
| # Note: The driver can use either btest or the BDD checker to check | |||
| # puzzles for correctness. This version of the lab uses btest, which | |||
| # has been extended to do better testing of both integer and | |||
| # floating-point puzzles. | |||
| # | |||
| ####################################################################### | |||
| use strict 'vars'; | |||
| use Getopt::Std; | |||
| use lib "."; | |||
| use Driverlib; | |||
| # Set to 1 to use btest, 0 to use the BDD checker. | |||
| my $USE_BTEST = 1; | |||
| # Generic settings | |||
| $| = 1; # Flush stdout each time | |||
| umask(0077); # Files created by the user in tmp readable only by that user | |||
| $ENV{PATH} = "/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin"; | |||
| # | |||
| # usage - print help message and terminate | |||
| # | |||
| sub usage { | |||
| printf STDERR "$_[0]\n"; | |||
| printf STDERR "Usage: $0 [-h] [-u \"nickname\"]\n"; | |||
| printf STDERR "Options:\n"; | |||
| printf STDERR " -h Print this message.\n"; | |||
| printf STDERR " -u \"nickname\" Send autoresult to server, using nickname on scoreboard)\n"; | |||
| die "\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| ############## | |||
| # Main routine | |||
| ############## | |||
| my $login = getlogin() || (getpwuid($<))[0] || "unknown"; | |||
| my $tmpdir = "/var/tmp/datalab.$login.$$"; | |||
| my $diemsg = "The files are in $tmpdir."; | |||
| my $driverfiles; | |||
| my $infile; | |||
| my $autograded; | |||
| my $status; | |||
| my $inpuzzles; | |||
| my $puzzlecnt; | |||
| my $line; | |||
| my $blank; | |||
| my $name; | |||
| my $c_points; | |||
| my $c_rating; | |||
| my $c_errors; | |||
| my $p_points; | |||
| my $p_rating; | |||
| my $p_errors; | |||
| my $total_c_points; | |||
| my $total_c_rating; | |||
| my $total_p_points; | |||
| my $total_p_rating; | |||
| my $tops; | |||
| my $tpoints; | |||
| my $trating; | |||
| my $foo; | |||
| my $name; | |||
| my $msg; | |||
| my $nickname; | |||
| my $autoresult; | |||
| my %puzzle_c_points; | |||
| my %puzzle_c_rating; | |||
| my %puzzle_c_errors; | |||
| my %puzzle_p_points; | |||
| my %puzzle_p_ops; | |||
| my %puzzle_p_maxops; | |||
| my %puzzle_number; | |||
| # Parse the command line arguments | |||
| no strict; | |||
| getopts('hu:f:A'); | |||
| if ($opt_h) { | |||
| usage(); | |||
| } | |||
| # The default input file is bits.c (change with -f) | |||
| $infile = "bits.c"; | |||
| $nickname = ""; | |||
| ##### | |||
| # These are command line args that every driver must support | |||
| # | |||
| # Causes the driver to send an autoresult to the server on behalf of user | |||
| if ($opt_u) { | |||
| $nickname = $opt_u; | |||
| check_nickname($nickname); | |||
| } | |||
| # Hidden flag that indicates that the driver was invoked by an autograder | |||
| if ($opt_A) { | |||
| $autograded = $opt_A; | |||
| } | |||
| ##### | |||
| # Drivers can also define an arbitary number of other command line args | |||
| # | |||
| # Optional hidden flag used by the autograder | |||
| if ($opt_f) { | |||
| $infile = $opt_f; | |||
| } | |||
| use strict 'vars'; | |||
| ################################################ | |||
| # Compute the correctness and performance scores | |||
| ################################################ | |||
| # Make sure that an executable dlc (data lab compiler) exists | |||
| (-e "./dlc" and -x "./dlc") | |||
| or die "$0: ERROR: No executable dlc binary.\n"; | |||
| # If using the bdd checker, then make sure it exists | |||
| if (!$USE_BTEST) { | |||
| (-e "./bddcheck/cbit/cbit" and -x "./bddcheck/cbit/cbit") | |||
| or die "$0: ERROR: No executable cbit binary.\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| # | |||
| # Set up the contents of the scratch directory | |||
| # | |||
| system("mkdir $tmpdir") == 0 | |||
| or die "$0: Could not make scratch directory $tmpdir.\n"; | |||
| # Copy the student's work to the scratch directory | |||
| unless (system("cp $infile $tmpdir/bits.c") == 0) { | |||
| clean($tmpdir); | |||
| die "$0: Could not copy file $infile to scratch directory $tmpdir.\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| # Copy the various autograding files to the scratch directory | |||
| if ($USE_BTEST) { | |||
| $driverfiles = "Makefile dlc btest.c decl.c tests.c btest.h bits.h"; | |||
| unless (system("cp -r $driverfiles $tmpdir") == 0) { | |||
| clean($tmpdir); | |||
| die "$0: Could not copy autogradingfiles to $tmpdir.\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| else { | |||
| $driverfiles = "dlc tests.c bddcheck"; | |||
| unless (system("cp -r $driverfiles $tmpdir") == 0) { | |||
| clean($tmpdir); | |||
| die "$0: Could not copy support files to $tmpdir.\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| # Change the current working directory to the scratch directory | |||
| unless (chdir($tmpdir)) { | |||
| clean($tmpdir); | |||
| die "$0: Could not change directory to $tmpdir.\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| # | |||
| # Generate a zapped (for coding rules) version of bits.c. In this | |||
| # zapped version of bits.c, any functions with illegal operators are | |||
| # transformed to have empty function bodies. | |||
| # | |||
| print "1. Running './dlc -z' to identify coding rules violations.\n"; | |||
| system("cp bits.c save-bits.c") == 0 | |||
| or die "$0: ERROR: Could not create backup copy of bits.c. $diemsg\n"; | |||
| system("./dlc -z -o zap-bits.c bits.c") == 0 | |||
| or die "$0: ERROR: zapped bits.c did not compile. $diemsg\n"; | |||
| # | |||
| # Run btest or BDD checker to determine correctness score | |||
| # | |||
| if ($USE_BTEST) { | |||
| print "\n2. Compiling and running './btest -g' to determine correctness score.\n"; | |||
| system("cp zap-bits.c bits.c"); | |||
| # Compile btest | |||
| system("make btestexplicit") == 0 | |||
| or die "$0: Could not make btest in $tmpdir. $diemsg\n"; | |||
| # Run btest | |||
| $status = system("./btest -g > btest-zapped.out 2>&1"); | |||
| if ($status != 0) { | |||
| die "$0: ERROR: btest check failed. $diemsg\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| else { | |||
| print "\n2. Running './bddcheck/check.pl -g' to determine correctness score.\n"; | |||
| system("cp zap-bits.c bits.c"); | |||
| $status = system("./bddcheck/check.pl -g > btest-zapped.out 2>&1"); | |||
| if ($status != 0) { | |||
| die "$0: ERROR: BDD check failed. $diemsg\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| # | |||
| # Run dlc to identify operator count violations. | |||
| # | |||
| print "\n3. Running './dlc -Z' to identify operator count violations.\n"; | |||
| system("./dlc -Z -o Zap-bits.c save-bits.c") == 0 | |||
| or die "$0: ERROR: dlc unable to generated Zapped bits.c file.\n"; | |||
| # | |||
| # Run btest or the bdd checker to compute performance score | |||
| # | |||
| if ($USE_BTEST) { | |||
| print "\n4. Compiling and running './btest -g -r 2' to determine performance score.\n"; | |||
| system("cp Zap-bits.c bits.c"); | |||
| # Compile btest | |||
| system("make btestexplicit") == 0 | |||
| or die "$0: Could not make btest in $tmpdir. $diemsg\n"; | |||
| print "\n"; | |||
| # Run btest | |||
| $status = system("./btest -g -r 2 > btest-Zapped.out 2>&1"); | |||
| if ($status != 0) { | |||
| die "$0: ERROR: Zapped btest failed. $diemsg\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| else { | |||
| print "\n4. Running './bddcheck/check.pl -g -r 2' to determine performance score.\n"; | |||
| system("cp Zap-bits.c bits.c"); | |||
| $status = system("./bddcheck/check.pl -g -r 2 > btest-Zapped.out 2>&1"); | |||
| if ($status != 0) { | |||
| die "$0: ERROR: Zapped bdd checker failed. $diemsg\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| # | |||
| # Run dlc to get the operator counts on the zapped input file | |||
| # | |||
| print "\n5. Running './dlc -e' to get operator count of each function.\n"; | |||
| $status = system("./dlc -W1 -e zap-bits.c > dlc-opcount.out 2>&1"); | |||
| if ($status != 0) { | |||
| die "$0: ERROR: bits.c did not compile. $diemsg\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| ################################################################# | |||
| # Collect the correctness and performance results for each puzzle | |||
| ################################################################# | |||
| # | |||
| # Collect the correctness results | |||
| # | |||
| %puzzle_c_points = (); # Correctness score computed by btest | |||
| %puzzle_c_errors = (); # Correctness error discovered by btest | |||
| %puzzle_c_rating = (); # Correctness puzzle rating (max points) | |||
| $inpuzzles = 0; # Becomes true when we start reading puzzle results | |||
| $puzzlecnt = 0; # Each puzzle gets a unique number | |||
| $total_c_points = 0; | |||
| $total_c_rating = 0; | |||
| open(INFILE, "$tmpdir/btest-zapped.out") | |||
| or die "$0: ERROR: could not open input file $tmpdir/btest-zapped.out\n"; | |||
| while ($line = <INFILE>) { | |||
| chomp($line); | |||
| # Notice that we're ready to read the puzzle scores | |||
| if ($line =~ /^Score/) { | |||
| $inpuzzles = 1; | |||
| next; | |||
| } | |||
| # Notice that we're through reading the puzzle scores | |||
| if ($line =~ /^Total/) { | |||
| $inpuzzles = 0; | |||
| next; | |||
| } | |||
| # Read and record a puzzle's name and score | |||
| if ($inpuzzles) { | |||
| ($blank, $c_points, $c_rating, $c_errors, $name) = split(/\s+/, $line); | |||
| $puzzle_c_points{$name} = $c_points; | |||
| $puzzle_c_errors{$name} = $c_errors; | |||
| $puzzle_c_rating{$name} = $c_rating; | |||
| $puzzle_number{$name} = $puzzlecnt++; | |||
| $total_c_points += $c_points; | |||
| $total_c_rating += $c_rating; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| close(INFILE); | |||
| # | |||
| # Collect the performance results | |||
| # | |||
| %puzzle_p_points = (); # Performance points | |||
| $inpuzzles = 0; # Becomes true when we start reading puzzle results | |||
| $total_p_points = 0; | |||
| $total_p_rating = 0; | |||
| open(INFILE, "$tmpdir/btest-Zapped.out") | |||
| or die "$0: ERROR: could not open input file $tmpdir/btest-Zapped.out\n"; | |||
| while ($line = <INFILE>) { | |||
| chomp($line); | |||
| # Notice that we're ready to read the puzzle scores | |||
| if ($line =~ /^Score/) { | |||
| $inpuzzles = 1; | |||
| next; | |||
| } | |||
| # Notice that we're through reading the puzzle scores | |||
| if ($line =~ /^Total/) { | |||
| $inpuzzles = 0; | |||
| next; | |||
| } | |||
| # Read and record a puzzle's name and score | |||
| if ($inpuzzles) { | |||
| ($blank, $p_points, $p_rating, $p_errors, $name) = split(/\s+/, $line); | |||
| $puzzle_p_points{$name} = $p_points; | |||
| $total_p_points += $p_points; | |||
| $total_p_rating += $p_rating; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| close(INFILE); | |||
| # | |||
| # Collect the operator counts generated by dlc | |||
| # | |||
| open(INFILE, "$tmpdir/dlc-opcount.out") | |||
| or die "$0: ERROR: could not open input file $tmpdir/dlc-opcount.out\n"; | |||
| $tops = 0; | |||
| while ($line = <INFILE>) { | |||
| chomp($line); | |||
| if ($line =~ /(\d+) operators/) { | |||
| ($foo, $foo, $foo, $name, $msg) = split(/:/, $line); | |||
| $puzzle_p_ops{$name} = $1; | |||
| $tops += $1; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| close(INFILE); | |||
| # | |||
| # Print a table of results sorted by puzzle number | |||
| # | |||
| print "\n"; | |||
| printf("%s\t%s\n", "Correctness Results", "Perf Results"); | |||
| printf("%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\n", "Points", "Rating", "Errors", | |||
| "Points", "Ops", "Puzzle"); | |||
| foreach $name (sort {$puzzle_number{$a} <=> $puzzle_number{$b}} | |||
| keys %puzzle_number) { | |||
| printf("%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\t\%s\n", | |||
| $puzzle_c_points{$name}, | |||
| $puzzle_c_rating{$name}, | |||
| $puzzle_c_errors{$name}, | |||
| $puzzle_p_points{$name}, | |||
| $puzzle_p_ops{$name}, | |||
| $name); | |||
| } | |||
| $tpoints = $total_c_points + $total_p_points; | |||
| $trating = $total_c_rating + $total_p_rating; | |||
| print "\nScore = $tpoints/$trating [$total_c_points/$total_c_rating Corr + $total_p_points/$total_p_rating Perf] ($tops total operators)\n"; | |||
| # | |||
| # Optionally send the autoresult to the contest server if the driver | |||
| # was called with the -u command line flag. | |||
| # | |||
| if ($nickname) { | |||
| # Generate the autoresult | |||
| $autoresult = "$tpoints|$total_c_points|$total_p_points|$tops"; | |||
| foreach $name (sort {$puzzle_number{$a} <=> $puzzle_number{$b}} | |||
| keys %puzzle_number) { | |||
| $autoresult .= " |$name:$puzzle_c_points{$name}:$puzzle_c_rating{$name}:$puzzle_p_points{$name}:$puzzle_p_ops{$name}"; | |||
| } | |||
| # Post the autoresult to the server. The Linux login id is | |||
| # concatenated with the user-supplied nickname for some (very) loose | |||
| # authentication of submissions. | |||
| &Driverlib::driver_post("$login:$nickname", $autoresult, $autograded); | |||
| } | |||
| # Clean up and exit | |||
| clean ($tmpdir); | |||
| exit; | |||
| ################## | |||
| # Helper functions | |||
| # | |||
| # | |||
| # check_nickname - Check a nickname for legality | |||
| # | |||
| sub check_nickname { | |||
| my $nickname = shift; | |||
| # Nicknames can't be empty | |||
| if (length($nickname) < 1) { | |||
| die "$0: Error: Empty nickname.\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| # Nicknames can't be too long | |||
| if (length($nickname) > 35) { | |||
| die "$0: Error: Nickname exceeds 35 characters.\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| # Nicknames can have restricted set of metacharacters (e.g., no # | |||
| # HTML tags) | |||
| if (!($nickname =~ /^[_-\w.,'@ ]+$/)) { | |||
| die "$0: Error: Illegal character in nickname. Only alphanumerics, apostrophes, commas, periods, dashes, underscores, and ampersands are allowed.\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| # Nicknames can't be all whitespace | |||
| if ($nickname =~ /^\s*$/) { | |||
| die "$0: Error: Nickname is all whitespace.\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| # | |||
| # clean - remove the scratch directory | |||
| # | |||
| sub clean { | |||
| my $tmpdir = shift; | |||
| system("rm -rf $tmpdir"); | |||
| } | |||
+ 0
- 151
LAB1/fshow.c
View File
| @ -1,151 +0,0 @@ | |||
| /* Display structure of floating-point numbers */ | |||
| #include <stdio.h> | |||
| #include <stdlib.h> | |||
| float strtof(const char *nptr, char **endptr); | |||
| #define FLOAT_SIZE 32 | |||
| #define FRAC_SIZE 23 | |||
| #define EXP_SIZE 8 | |||
| #define BIAS ((1<<(EXP_SIZE-1))-1) | |||
| #define FRAC_MASK ((1<<FRAC_SIZE)-1) | |||
| #define EXP_MASK ((1<<EXP_SIZE)-1) | |||
| /* Floating point helpers */ | |||
| unsigned f2u(float f) | |||
| { | |||
| union { | |||
| unsigned u; | |||
| float f; | |||
| } v; | |||
| v.u = 0; | |||
| v.f = f; | |||
| return v.u; | |||
| } | |||
| static float u2f(unsigned u) | |||
| { | |||
| union { | |||
| unsigned u; | |||
| float f; | |||
| } v; | |||
| v.u = u; | |||
| return v.f; | |||
| } | |||
| /* Get exponent */ | |||
| unsigned get_exp(unsigned uf) | |||
| { | |||
| return (uf>>FRAC_SIZE) & EXP_MASK; | |||
| } | |||
| /* Get fraction */ | |||
| unsigned get_frac(unsigned uf) | |||
| { | |||
| return uf & FRAC_MASK; | |||
| } | |||
| /* Get sign */ | |||
| unsigned get_sign(unsigned uf) | |||
| { | |||
| return (uf>>(FLOAT_SIZE-1)) & 0x1; | |||
| } | |||
| void show_float(unsigned uf) | |||
| { | |||
| float f = u2f(uf); | |||
| unsigned exp = get_exp(uf); | |||
| unsigned frac = get_frac(uf); | |||
| unsigned sign = get_sign(uf); | |||
| printf("\nFloating point value %.10g\n", f); | |||
| printf("Bit Representation 0x%.8x, sign = %x, exponent = 0x%.2x, fraction = 0x%.6x\n", | |||
| uf, sign, exp, frac); | |||
| if (exp == EXP_MASK) { | |||
| if (frac == 0) { | |||
| printf("%cInfinity\n", sign ? '-' : '+'); | |||
| } else | |||
| printf("Not-A-Number\n"); | |||
| } else { | |||
| int denorm = (exp == 0); | |||
| int uexp = denorm ? 1-BIAS : exp - BIAS; | |||
| int mantissa = denorm ? frac : frac + (1<<FRAC_SIZE); | |||
| float fman = (float) mantissa / (float) (1<<FRAC_SIZE); | |||
| printf("%s. %c%.10f X 2^(%d)\n", | |||
| denorm ? "Denormalized" : "Normalized", | |||
| sign ? '-' : '+', | |||
| fman, uexp); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| /* Extract hex/decimal/or float value from string */ | |||
| static int get_num_val(char *sval, unsigned *valp) { | |||
| char *endp; | |||
| /* See if it's an integer or floating point */ | |||
| int ishex = 0; | |||
| int isfloat = 0; | |||
| int i; | |||
| for (i = 0; sval[i]; i++) { | |||
| switch (sval[i]) { | |||
| case 'x': | |||
| case 'X': | |||
| ishex = 1; | |||
| break; | |||
| case 'e': | |||
| case 'E': | |||
| if (!ishex) | |||
| isfloat = 1; | |||
| break; | |||
| case '.': | |||
| isfloat = 1; | |||
| break; | |||
| default: | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| if (isfloat) { | |||
| float fval = strtof(sval, &endp); | |||
| if (!*endp) { | |||
| *valp = *(unsigned *) &fval; | |||
| return 1; | |||
| } | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } else { | |||
| long long int llval = strtoll(sval, &endp, 0); | |||
| long long int upperbits = llval >> 31; | |||
| /* will give -1 for negative, 0 or 1 for positive */ | |||
| if (valp && (upperbits == 0 || upperbits == -1 || upperbits == 1)) { | |||
| *valp = (unsigned) llval; | |||
| return 1; | |||
| } | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| void usage(char *fname) { | |||
| printf("Usage: %s val1 val2 ...\n", fname); | |||
| printf("Values may be given as hex patterns or as floating point numbers\n"); | |||
| exit(0); | |||
| } | |||
| int main(int argc, char *argv[]) | |||
| { | |||
| int i; | |||
| unsigned uf; | |||
| if (argc < 2) | |||
| usage(argv[0]); | |||
| for (i = 1; i < argc; i++) { | |||
| char *sval = argv[i]; | |||
| if (get_num_val(sval, &uf)) { | |||
| show_float(uf); | |||
| } else { | |||
| printf("Invalid 32-bit number: '%s'\n", sval); | |||
| usage(argv[0]); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
+ 0
- 75
LAB1/ishow.c
View File
| @ -1,75 +0,0 @@ | |||
| /* Display value of fixed point numbers */ | |||
| #include <stdlib.h> | |||
| #include <stdio.h> | |||
| /* Extract hex/decimal/or float value from string */ | |||
| static int get_num_val(char *sval, unsigned *valp) { | |||
| char *endp; | |||
| /* See if it's an integer or floating point */ | |||
| int ishex = 0; | |||
| int isfloat = 0; | |||
| int i; | |||
| for (i = 0; sval[i]; i++) { | |||
| switch (sval[i]) { | |||
| case 'x': | |||
| case 'X': | |||
| ishex = 1; | |||
| break; | |||
| case 'e': | |||
| case 'E': | |||
| if (!ishex) | |||
| isfloat = 1; | |||
| break; | |||
| case '.': | |||
| isfloat = 1; | |||
| break; | |||
| default: | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| if (isfloat) { | |||
| return 0; /* Not supposed to have a float here */ | |||
| } else { | |||
| long long int llval = strtoll(sval, &endp, 0); | |||
| long long int upperbits = llval >> 31; | |||
| /* will give -1 for negative, 0 or 1 for positive */ | |||
| if (valp && (upperbits == 0 || upperbits == -1 || upperbits == 1)) { | |||
| *valp = (unsigned) llval; | |||
| return 1; | |||
| } | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| void show_int(unsigned uf) | |||
| { | |||
| printf("Hex = 0x%.8x,\tSigned = %d,\tUnsigned = %u\n", | |||
| uf, (int) uf, uf); | |||
| } | |||
| void usage(char *fname) { | |||
| printf("Usage: %s val1 val2 ...\n", fname); | |||
| printf("Values may be given in hex or decimal\n"); | |||
| exit(0); | |||
| } | |||
| int main(int argc, char *argv[]) | |||
| { | |||
| int i; | |||
| unsigned uf; | |||
| if (argc < 2) | |||
| usage(argv[0]); | |||
| for (i = 1; i < argc; i++) { | |||
| char *sval = argv[i]; | |||
| if (get_num_val(sval, &uf)) { | |||
| show_int(uf); | |||
| } else { | |||
| printf("Cannot convert '%s' to 32-bit number\n", sval); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
+ 0
- 124
LAB1/tests.c
View File
| @ -1,124 +0,0 @@ | |||
| /* Testing Code */ | |||
| #include <limits.h> | |||
| #include <math.h> | |||
| /* Routines used by floation point test code */ | |||
| /* Convert from bit level representation to floating point number */ | |||
| float u2f(unsigned u) { | |||
| union { | |||
| unsigned u; | |||
| float f; | |||
| } a; | |||
| a.u = u; | |||
| return a.f; | |||
| } | |||
| /* Convert from floating point number to bit-level representation */ | |||
| unsigned f2u(float f) { | |||
| union { | |||
| unsigned u; | |||
| float f; | |||
| } a; | |||
| a.f = f; | |||
| return a.u; | |||
| } | |||
| /* Copyright (C) 1991-2020 Free Software Foundation, Inc. | |||
| This file is part of the GNU C Library. | |||
| The GNU C Library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or | |||
| modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public | |||
| License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either | |||
| version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version. | |||
| The GNU C Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU | |||
| Lesser General Public License for more details. | |||
| You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public | |||
| License along with the GNU C Library; if not, see | |||
| <https://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. */ | |||
| /* This header is separate from features.h so that the compiler can | |||
| include it implicitly at the start of every compilation. It must | |||
| not itself include <features.h> or any other header that includes | |||
| <features.h> because the implicit include comes before any feature | |||
| test macros that may be defined in a source file before it first | |||
| explicitly includes a system header. GCC knows the name of this | |||
| header in order to preinclude it. */ | |||
| /* glibc's intent is to support the IEC 559 math functionality, real | |||
| and complex. If the GCC (4.9 and later) predefined macros | |||
| specifying compiler intent are available, use them to determine | |||
| whether the overall intent is to support these features; otherwise, | |||
| presume an older compiler has intent to support these features and | |||
| define these macros by default. */ | |||
| /* wchar_t uses Unicode 10.0.0. Version 10.0 of the Unicode Standard is | |||
| synchronized with ISO/IEC 10646:2017, fifth edition, plus | |||
| the following additions from Amendment 1 to the fifth edition: | |||
| - 56 emoji characters | |||
| - 285 hentaigana | |||
| - 3 additional Zanabazar Square characters */ | |||
| //1 | |||
| int test_bitXor(int x, int y) | |||
| { | |||
| return x^y; | |||
| } | |||
| int test_tmin(void) { | |||
| return 0x80000000; | |||
| } | |||
| //2 | |||
| int test_isTmax(int x) { | |||
| return x == 0x7FFFFFFF; | |||
| } | |||
| int test_allOddBits(int x) { | |||
| int i; | |||
| for (i = 1; i < 32; i+=2) | |||
| if ((x & (1<<i)) == 0) | |||
| return 0; | |||
| return 1; | |||
| } | |||
| int test_negate(int x) { | |||
| return -x; | |||
| } | |||
| //3 | |||
| int test_isAsciiDigit(int x) { | |||
| return (0x30 <= x) && (x <= 0x39); | |||
| } | |||
| int test_conditional(int x, int y, int z) | |||
| { | |||
| return x?y:z; | |||
| } | |||
| int test_isLessOrEqual(int x, int y) | |||
| { | |||
| return x <= y; | |||
| } | |||
| //4 | |||
| int test_logicalNeg(int x) | |||
| { | |||
| return !x; | |||
| } | |||
| int test_howManyBits(int x) { | |||
| unsigned int a, cnt; | |||
| x = x<0 ? -x-1 : x; | |||
| a = (unsigned int)x; | |||
| for (cnt=0; a; a>>=1, cnt++) | |||
| ; | |||
| return (int)(cnt + 1); | |||
| } | |||
| //float | |||
| unsigned test_floatScale2(unsigned uf) { | |||
| float f = u2f(uf); | |||
| float tf = 2*f; | |||
| if (isnan(f)) | |||
| return uf; | |||
| else | |||
| return f2u(tf); | |||
| } | |||
| int test_floatFloat2Int(unsigned uf) { | |||
| float f = u2f(uf); | |||
| int x = (int) f; | |||
| return x; | |||
| } | |||
| // #include "floatPower2.c" | |||
+ 0
- 21
LICENSE
View File
| @ -1,21 +0,0 @@ | |||
| MIT License | |||
| Copyright (c) 2023 AquaOH | |||
| Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy | |||
| of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal | |||
| in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights | |||
| to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell | |||
| copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is | |||
| furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions: | |||
| The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all | |||
| copies or substantial portions of the Software. | |||
| THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR | |||
| IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, | |||
| FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE | |||
| AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER | |||
| LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, | |||
| OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE | |||
| SOFTWARE. | |||
+ 30
- 0
Makefile
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,30 @@ | |||
| # | |||
| # Students' Makefile for the Malloc Lab | |||
| # | |||
| TEAM = bovik | |||
| VERSION = 1 | |||
| HANDINDIR = /afs/cs.cmu.edu/academic/class/15213-f01/malloclab/handin | |||
| CC = gcc | |||
| CFLAGS = -Wall -O2 -m32 -ggdb | |||
| OBJS = mdriver.o mm.o memlib.o fsecs.o fcyc.o clock.o ftimer.o | |||
| mdriver: $(OBJS) | |||
| $(CC) $(CFLAGS) -o mdriver $(OBJS) | |||
| mdriver.o: mdriver.c fsecs.h fcyc.h clock.h memlib.h config.h mm.h | |||
| memlib.o: memlib.c memlib.h | |||
| mm.o: mm.c mm.h memlib.h | |||
| fsecs.o: fsecs.c fsecs.h config.h | |||
| fcyc.o: fcyc.c fcyc.h | |||
| ftimer.o: ftimer.c ftimer.h config.h | |||
| clock.o: clock.c clock.h | |||
| handin: | |||
| cp mm.c $(HANDINDIR)/$(TEAM)-$(VERSION)-mm.c | |||
| clean: | |||
| rm -f *~ *.o mdriver | |||
+ 52
- 0
README
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,52 @@ | |||
| ##################################################################### | |||
| # CS:APP Malloc Lab | |||
| # Handout files for students | |||
| # | |||
| # Copyright (c) 2002, R. Bryant and D. O'Hallaron, All rights reserved. | |||
| # May not be used, modified, or copied without permission. | |||
| # | |||
| ###################################################################### | |||
| *********** | |||
| Main Files: | |||
| *********** | |||
| mm.{c,h} | |||
| Your solution malloc package. mm.c is the file that you | |||
| will be handing in, and is the only file you should modify. | |||
| mdriver.c | |||
| The malloc driver that tests your mm.c file | |||
| short{1,2}-bal.rep | |||
| Two tiny tracefiles to help you get started. | |||
| Makefile | |||
| Builds the driver | |||
| ********************************** | |||
| Other support files for the driver | |||
| ********************************** | |||
| config.h Configures the malloc lab driver | |||
| fsecs.{c,h} Wrapper function for the different timer packages | |||
| clock.{c,h} Routines for accessing the Pentium and Alpha cycle counters | |||
| fcyc.{c,h} Timer functions based on cycle counters | |||
| ftimer.{c,h} Timer functions based on interval timers and gettimeofday() | |||
| memlib.{c,h} Models the heap and sbrk function | |||
| ******************************* | |||
| Building and running the driver | |||
| ******************************* | |||
| To build the driver, type "make" to the shell. | |||
| To run the driver on a tiny test trace: | |||
| unix> mdriver -V -f short1-bal.rep | |||
| The -V option prints out helpful tracing and summary information. | |||
| To get a list of the driver flags: | |||
| unix> mdriver -h | |||
+ 0
- 35
README.md
View File
| @ -1,35 +0,0 @@ | |||
| ### All | |||
| A CSAPP LAB | |||
| ### 2023/10/7 Update: | |||
| 1. Create A Repo | |||
| 2. Finish bitXor | |||
| 3. Finish tmin | |||
| ### 2023/10/8 Update: | |||
| 1. Finish isTmax | |||
| 2. Finish allOddBits | |||
| 3. Finish negate | |||
| 4. Finish isAsciiDigit | |||
| 5. Finish isLessOrEqual | |||
| 6. Finish logicalNeg | |||
| 7. Update Makefile | |||
| ### 2023/10/9 Update: | |||
| 1. Finish howManyBits | |||
| ### 2023/10/9 Update: | |||
| 1. Finish floatScale2 | |||
| 2. Finish floatFloat2Int | |||
| 3. Congratulations!Finish datalab! | |||
+ 279
- 0
clock.c
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,279 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * clock.c - Routines for using the cycle counters on x86, | |||
| * Alpha, and Sparc boxes. | |||
| * | |||
| * Copyright (c) 2002, R. Bryant and D. O'Hallaron, All rights reserved. | |||
| * May not be used, modified, or copied without permission. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <stdio.h> | |||
| #include <stdlib.h> | |||
| #include <unistd.h> | |||
| #include <sys/times.h> | |||
| #include "clock.h" | |||
| /******************************************************* | |||
| * Machine dependent functions | |||
| * | |||
| * Note: the constants __i386__ and __alpha | |||
| * are set by GCC when it calls the C preprocessor | |||
| * You can verify this for yourself using gcc -v. | |||
| *******************************************************/ | |||
| #if defined(__i386__) | |||
| /******************************************************* | |||
| * Pentium versions of start_counter() and get_counter() | |||
| *******************************************************/ | |||
| /* $begin x86cyclecounter */ | |||
| /* Initialize the cycle counter */ | |||
| static unsigned cyc_hi = 0; | |||
| static unsigned cyc_lo = 0; | |||
| /* Set *hi and *lo to the high and low order bits of the cycle counter. | |||
| Implementation requires assembly code to use the rdtsc instruction. */ | |||
| void access_counter(unsigned *hi, unsigned *lo) | |||
| { | |||
| asm("rdtsc; movl %%edx,%0; movl %%eax,%1" /* Read cycle counter */ | |||
| : "=r" (*hi), "=r" (*lo) /* and move results to */ | |||
| : /* No input */ /* the two outputs */ | |||
| : "%edx", "%eax"); | |||
| } | |||
| /* Record the current value of the cycle counter. */ | |||
| void start_counter() | |||
| { | |||
| access_counter(&cyc_hi, &cyc_lo); | |||
| } | |||
| /* Return the number of cycles since the last call to start_counter. */ | |||
| double get_counter() | |||
| { | |||
| unsigned ncyc_hi, ncyc_lo; | |||
| unsigned hi, lo, borrow; | |||
| double result; | |||
| /* Get cycle counter */ | |||
| access_counter(&ncyc_hi, &ncyc_lo); | |||
| /* Do double precision subtraction */ | |||
| lo = ncyc_lo - cyc_lo; | |||
| borrow = lo > ncyc_lo; | |||
| hi = ncyc_hi - cyc_hi - borrow; | |||
| result = (double) hi * (1 << 30) * 4 + lo; | |||
| if (result < 0) { | |||
| fprintf(stderr, "Error: counter returns neg value: %.0f\n", result); | |||
| } | |||
| return result; | |||
| } | |||
| /* $end x86cyclecounter */ | |||
| #elif defined(__alpha) | |||
| /**************************************************** | |||
| * Alpha versions of start_counter() and get_counter() | |||
| ***************************************************/ | |||
| /* Initialize the cycle counter */ | |||
| static unsigned cyc_hi = 0; | |||
| static unsigned cyc_lo = 0; | |||
| /* Use Alpha cycle timer to compute cycles. Then use | |||
| measured clock speed to compute seconds | |||
| */ | |||
| /* | |||
| * counterRoutine is an array of Alpha instructions to access | |||
| * the Alpha's processor cycle counter. It uses the rpcc | |||
| * instruction to access the counter. This 64 bit register is | |||
| * divided into two parts. The lower 32 bits are the cycles | |||
| * used by the current process. The upper 32 bits are wall | |||
| * clock cycles. These instructions read the counter, and | |||
| * convert the lower 32 bits into an unsigned int - this is the | |||
| * user space counter value. | |||
| * NOTE: The counter has a very limited time span. With a | |||
| * 450MhZ clock the counter can time things for about 9 | |||
| * seconds. */ | |||
| static unsigned int counterRoutine[] = | |||
| { | |||
| 0x601fc000u, | |||
| 0x401f0000u, | |||
| 0x6bfa8001u | |||
| }; | |||
| /* Cast the above instructions into a function. */ | |||
| static unsigned int (*counter)(void)= (void *)counterRoutine; | |||
| void start_counter() | |||
| { | |||
| /* Get cycle counter */ | |||
| cyc_hi = 0; | |||
| cyc_lo = counter(); | |||
| } | |||
| double get_counter() | |||
| { | |||
| unsigned ncyc_hi, ncyc_lo; | |||
| unsigned hi, lo, borrow; | |||
| double result; | |||
| ncyc_lo = counter(); | |||
| ncyc_hi = 0; | |||
| lo = ncyc_lo - cyc_lo; | |||
| borrow = lo > ncyc_lo; | |||
| hi = ncyc_hi - cyc_hi - borrow; | |||
| result = (double) hi * (1 << 30) * 4 + lo; | |||
| if (result < 0) { | |||
| fprintf(stderr, "Error: Cycle counter returning negative value: %.0f\n", result); | |||
| } | |||
| return result; | |||
| } | |||
| #else | |||
| /**************************************************************** | |||
| * All the other platforms for which we haven't implemented cycle | |||
| * counter routines. Newer models of sparcs (v8plus) have cycle | |||
| * counters that can be accessed from user programs, but since there | |||
| * are still many sparc boxes out there that don't support this, we | |||
| * haven't provided a Sparc version here. | |||
| ***************************************************************/ | |||
| void start_counter() | |||
| { | |||
| printf("ERROR: You are trying to use a start_counter routine in clock.c\n"); | |||
| printf("that has not been implemented yet on this platform.\n"); | |||
| printf("Please choose another timing package in config.h.\n"); | |||
| exit(1); | |||
| } | |||
| double get_counter() | |||
| { | |||
| printf("ERROR: You are trying to use a get_counter routine in clock.c\n"); | |||
| printf("that has not been implemented yet on this platform.\n"); | |||
| printf("Please choose another timing package in config.h.\n"); | |||
| exit(1); | |||
| } | |||
| #endif | |||
| /******************************* | |||
| * Machine-independent functions | |||
| ******************************/ | |||
| double ovhd() | |||
| { | |||
| /* Do it twice to eliminate cache effects */ | |||
| int i; | |||
| double result; | |||
| for (i = 0; i < 2; i++) { | |||
| start_counter(); | |||
| result = get_counter(); | |||
| } | |||
| return result; | |||
| } | |||
| /* $begin mhz */ | |||
| /* Estimate the clock rate by measuring the cycles that elapse */ | |||
| /* while sleeping for sleeptime seconds */ | |||
| double mhz_full(int verbose, int sleeptime) | |||
| { | |||
| double rate; | |||
| start_counter(); | |||
| sleep(sleeptime); | |||
| rate = get_counter() / (1e6*sleeptime); | |||
| if (verbose) | |||
| printf("Processor clock rate ~= %.1f MHz\n", rate); | |||
| return rate; | |||
| } | |||
| /* $end mhz */ | |||
| /* Version using a default sleeptime */ | |||
| double mhz(int verbose) | |||
| { | |||
| return mhz_full(verbose, 2); | |||
| } | |||
| /** Special counters that compensate for timer interrupt overhead */ | |||
| static double cyc_per_tick = 0.0; | |||
| #define NEVENT 100 | |||
| #define THRESHOLD 1000 | |||
| #define RECORDTHRESH 3000 | |||
| /* Attempt to see how much time is used by timer interrupt */ | |||
| static void callibrate(int verbose) | |||
| { | |||
| double oldt; | |||
| struct tms t; | |||
| clock_t oldc; | |||
| int e = 0; | |||
| times(&t); | |||
| oldc = t.tms_utime; | |||
| start_counter(); | |||
| oldt = get_counter(); | |||
| while (e <NEVENT) { | |||
| double newt = get_counter(); | |||
| if (newt-oldt >= THRESHOLD) { | |||
| clock_t newc; | |||
| times(&t); | |||
| newc = t.tms_utime; | |||
| if (newc > oldc) { | |||
| double cpt = (newt-oldt)/(newc-oldc); | |||
| if ((cyc_per_tick == 0.0 || cyc_per_tick > cpt) && cpt > RECORDTHRESH) | |||
| cyc_per_tick = cpt; | |||
| /* | |||
| if (verbose) | |||
| printf("Saw event lasting %.0f cycles and %d ticks. Ratio = %f\n", | |||
| newt-oldt, (int) (newc-oldc), cpt); | |||
| */ | |||
| e++; | |||
| oldc = newc; | |||
| } | |||
| oldt = newt; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| if (verbose) | |||
| printf("Setting cyc_per_tick to %f\n", cyc_per_tick); | |||
| } | |||
| static clock_t start_tick = 0; | |||
| void start_comp_counter() | |||
| { | |||
| struct tms t; | |||
| if (cyc_per_tick == 0.0) | |||
| callibrate(0); | |||
| times(&t); | |||
| start_tick = t.tms_utime; | |||
| start_counter(); | |||
| } | |||
| double get_comp_counter() | |||
| { | |||
| double time = get_counter(); | |||
| double ctime; | |||
| struct tms t; | |||
| clock_t ticks; | |||
| times(&t); | |||
| ticks = t.tms_utime - start_tick; | |||
| ctime = time - ticks*cyc_per_tick; | |||
| /* | |||
| printf("Measured %.0f cycles. Ticks = %d. Corrected %.0f cycles\n", | |||
| time, (int) ticks, ctime); | |||
| */ | |||
| return ctime; | |||
| } | |||
+ 22
- 0
clock.h
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,22 @@ | |||
| /* Routines for using cycle counter */ | |||
| /* Start the counter */ | |||
| void start_counter(); | |||
| /* Get # cycles since counter started */ | |||
| double get_counter(); | |||
| /* Measure overhead for counter */ | |||
| double ovhd(); | |||
| /* Determine clock rate of processor (using a default sleeptime) */ | |||
| double mhz(int verbose); | |||
| /* Determine clock rate of processor, having more control over accuracy */ | |||
| double mhz_full(int verbose, int sleeptime); | |||
| /** Special counters that compensate for timer interrupt overhead */ | |||
| void start_comp_counter(); | |||
| double get_comp_counter(); | |||
BIN
clock.o
View File
+ 72
- 0
config.h
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,72 @@ | |||
| #ifndef __CONFIG_H_ | |||
| #define __CONFIG_H_ | |||
| /* | |||
| * config.h - malloc lab configuration file | |||
| * | |||
| * Copyright (c) 2002, R. Bryant and D. O'Hallaron, All rights reserved. | |||
| * May not be used, modified, or copied without permission. | |||
| */ | |||
| /* | |||
| * This is the default path where the driver will look for the | |||
| * default tracefiles. You can override it at runtime with the -t flag. | |||
| */ | |||
| #define TRACEDIR "/home/aqua/malloclab/traces/" | |||
| /* | |||
| * This is the list of default tracefiles in TRACEDIR that the driver | |||
| * will use for testing. Modify this if you want to add or delete | |||
| * traces from the driver's test suite. For example, if you don't want | |||
| * your students to implement realloc, you can delete the last two | |||
| * traces. | |||
| */ | |||
| #define DEFAULT_TRACEFILES \ | |||
| "amptjp-bal.rep",\ | |||
| "cccp-bal.rep",\ | |||
| "cp-decl-bal.rep",\ | |||
| "expr-bal.rep",\ | |||
| "coalescing-bal.rep",\ | |||
| "random-bal.rep",\ | |||
| "random2-bal.rep",\ | |||
| "binary-bal.rep",\ | |||
| "binary2-bal.rep",\ | |||
| "realloc-bal.rep",\ | |||
| "realloc2-bal.rep" | |||
| /* | |||
| * This constant gives the estimated performance of the libc malloc | |||
| * package using our traces on some reference system, typically the | |||
| * same kind of system the students use. Its purpose is to cap the | |||
| * contribution of throughput to the performance index. Once the | |||
| * students surpass the AVG_LIBC_THRUPUT, they get no further benefit | |||
| * to their score. This deters students from building extremely fast, | |||
| * but extremely stupid malloc packages. | |||
| */ | |||
| #define AVG_LIBC_THRUPUT 600E3 /* 600 Kops/sec */ | |||
| /* | |||
| * This constant determines the contributions of space utilization | |||
| * (UTIL_WEIGHT) and throughput (1 - UTIL_WEIGHT) to the performance | |||
| * index. | |||
| */ | |||
| #define UTIL_WEIGHT .60 | |||
| /* | |||
| * Alignment requirement in bytes (either 4 or 8) | |||
| */ | |||
| #define ALIGNMENT 8 | |||
| /* | |||
| * Maximum heap size in bytes | |||
| */ | |||
| #define MAX_HEAP (20*(1<<20)) /* 20 MB */ | |||
| /***************************************************************************** | |||
| * Set exactly one of these USE_xxx constants to "1" to select a timing method | |||
| *****************************************************************************/ | |||
| #define USE_FCYC 0 /* cycle counter w/K-best scheme (x86 & Alpha only) */ | |||
| #define USE_ITIMER 0 /* interval timer (any Unix box) */ | |||
| #define USE_GETTOD 1 /* gettimeofday (any Unix box) */ | |||
| #endif /* __CONFIG_H */ | |||
+ 251
- 0
fcyc.c
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,251 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * fcyc.c - Estimate the time (in CPU cycles) used by a function f | |||
| * | |||
| * Copyright (c) 2002, R. Bryant and D. O'Hallaron, All rights reserved. | |||
| * May not be used, modified, or copied without permission. | |||
| * | |||
| * Uses the cycle timer routines in clock.c to estimate the | |||
| * the time in CPU cycles for a function f. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <stdlib.h> | |||
| #include <sys/times.h> | |||
| #include <stdio.h> | |||
| #include "fcyc.h" | |||
| #include "clock.h" | |||
| /* Default values */ | |||
| #define K 3 /* Value of K in K-best scheme */ | |||
| #define MAXSAMPLES 20 /* Give up after MAXSAMPLES */ | |||
| #define EPSILON 0.01 /* K samples should be EPSILON of each other*/ | |||
| #define COMPENSATE 0 /* 1-> try to compensate for clock ticks */ | |||
| #define CLEAR_CACHE 0 /* Clear cache before running test function */ | |||
| #define CACHE_BYTES (1<<19) /* Max cache size in bytes */ | |||
| #define CACHE_BLOCK 32 /* Cache block size in bytes */ | |||
| static int kbest = K; | |||
| static int maxsamples = MAXSAMPLES; | |||
| static double epsilon = EPSILON; | |||
| static int compensate = COMPENSATE; | |||
| static int clear_cache = CLEAR_CACHE; | |||
| static int cache_bytes = CACHE_BYTES; | |||
| static int cache_block = CACHE_BLOCK; | |||
| static int *cache_buf = NULL; | |||
| static double *values = NULL; | |||
| static int samplecount = 0; | |||
| /* for debugging only */ | |||
| #define KEEP_VALS 0 | |||
| #define KEEP_SAMPLES 0 | |||
| #if KEEP_SAMPLES | |||
| static double *samples = NULL; | |||
| #endif | |||
| /* | |||
| * init_sampler - Start new sampling process | |||
| */ | |||
| static void init_sampler() | |||
| { | |||
| if (values) | |||
| free(values); | |||
| values = calloc(kbest, sizeof(double)); | |||
| #if KEEP_SAMPLES | |||
| if (samples) | |||
| free(samples); | |||
| /* Allocate extra for wraparound analysis */ | |||
| samples = calloc(maxsamples+kbest, sizeof(double)); | |||
| #endif | |||
| samplecount = 0; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * add_sample - Add new sample | |||
| */ | |||
| static void add_sample(double val) | |||
| { | |||
| int pos = 0; | |||
| if (samplecount < kbest) { | |||
| pos = samplecount; | |||
| values[pos] = val; | |||
| } else if (val < values[kbest-1]) { | |||
| pos = kbest-1; | |||
| values[pos] = val; | |||
| } | |||
| #if KEEP_SAMPLES | |||
| samples[samplecount] = val; | |||
| #endif | |||
| samplecount++; | |||
| /* Insertion sort */ | |||
| while (pos > 0 && values[pos-1] > values[pos]) { | |||
| double temp = values[pos-1]; | |||
| values[pos-1] = values[pos]; | |||
| values[pos] = temp; | |||
| pos--; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * has_converged- Have kbest minimum measurements converged within epsilon? | |||
| */ | |||
| static int has_converged() | |||
| { | |||
| return | |||
| (samplecount >= kbest) && | |||
| ((1 + epsilon)*values[0] >= values[kbest-1]); | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * clear - Code to clear cache | |||
| */ | |||
| static volatile int sink = 0; | |||
| static void clear() | |||
| { | |||
| int x = sink; | |||
| int *cptr, *cend; | |||
| int incr = cache_block/sizeof(int); | |||
| if (!cache_buf) { | |||
| cache_buf = malloc(cache_bytes); | |||
| if (!cache_buf) { | |||
| fprintf(stderr, "Fatal error. Malloc returned null when trying to clear cache\n"); | |||
| exit(1); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| cptr = (int *) cache_buf; | |||
| cend = cptr + cache_bytes/sizeof(int); | |||
| while (cptr < cend) { | |||
| x += *cptr; | |||
| cptr += incr; | |||
| } | |||
| sink = x; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * fcyc - Use K-best scheme to estimate the running time of function f | |||
| */ | |||
| double fcyc(test_funct f, void *argp) | |||
| { | |||
| double result; | |||
| init_sampler(); | |||
| if (compensate) { | |||
| do { | |||
| double cyc; | |||
| if (clear_cache) | |||
| clear(); | |||
| start_comp_counter(); | |||
| f(argp); | |||
| cyc = get_comp_counter(); | |||
| add_sample(cyc); | |||
| } while (!has_converged() && samplecount < maxsamples); | |||
| } else { | |||
| do { | |||
| double cyc; | |||
| if (clear_cache) | |||
| clear(); | |||
| start_counter(); | |||
| f(argp); | |||
| cyc = get_counter(); | |||
| add_sample(cyc); | |||
| } while (!has_converged() && samplecount < maxsamples); | |||
| } | |||
| #ifdef DEBUG | |||
| { | |||
| int i; | |||
| printf(" %d smallest values: [", kbest); | |||
| for (i = 0; i < kbest; i++) | |||
| printf("%.0f%s", values[i], i==kbest-1 ? "]\n" : ", "); | |||
| } | |||
| #endif | |||
| result = values[0]; | |||
| #if !KEEP_VALS | |||
| free(values); | |||
| values = NULL; | |||
| #endif | |||
| return result; | |||
| } | |||
| /************************************************************* | |||
| * Set the various parameters used by the measurement routines | |||
| ************************************************************/ | |||
| /* | |||
| * set_fcyc_clear_cache - When set, will run code to clear cache | |||
| * before each measurement. | |||
| * Default = 0 | |||
| */ | |||
| void set_fcyc_clear_cache(int clear) | |||
| { | |||
| clear_cache = clear; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * set_fcyc_cache_size - Set size of cache to use when clearing cache | |||
| * Default = 1<<19 (512KB) | |||
| */ | |||
| void set_fcyc_cache_size(int bytes) | |||
| { | |||
| if (bytes != cache_bytes) { | |||
| cache_bytes = bytes; | |||
| if (cache_buf) { | |||
| free(cache_buf); | |||
| cache_buf = NULL; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * set_fcyc_cache_block - Set size of cache block | |||
| * Default = 32 | |||
| */ | |||
| void set_fcyc_cache_block(int bytes) { | |||
| cache_block = bytes; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * set_fcyc_compensate- When set, will attempt to compensate for | |||
| * timer interrupt overhead | |||
| * Default = 0 | |||
| */ | |||
| void set_fcyc_compensate(int compensate_arg) | |||
| { | |||
| compensate = compensate_arg; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * set_fcyc_k - Value of K in K-best measurement scheme | |||
| * Default = 3 | |||
| */ | |||
| void set_fcyc_k(int k) | |||
| { | |||
| kbest = k; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * set_fcyc_maxsamples - Maximum number of samples attempting to find | |||
| * K-best within some tolerance. | |||
| * When exceeded, just return best sample found. | |||
| * Default = 20 | |||
| */ | |||
| void set_fcyc_maxsamples(int maxsamples_arg) | |||
| { | |||
| maxsamples = maxsamples_arg; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * set_fcyc_epsilon - Tolerance required for K-best | |||
| * Default = 0.01 | |||
| */ | |||
| void set_fcyc_epsilon(double epsilon_arg) | |||
| { | |||
| epsilon = epsilon_arg; | |||
| } | |||
+ 68
- 0
fcyc.h
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,68 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * fcyc.h - prototypes for the routines in fcyc.c that estimate the | |||
| * time in CPU cycles used by a test function f | |||
| * | |||
| * Copyright (c) 2002, R. Bryant and D. O'Hallaron, All rights reserved. | |||
| * May not be used, modified, or copied without permission. | |||
| * | |||
| */ | |||
| /* The test function takes a generic pointer as input */ | |||
| typedef void (*test_funct)(void *); | |||
| /* Compute number of cycles used by test function f */ | |||
| double fcyc(test_funct f, void* argp); | |||
| /********************************************************* | |||
| * Set the various parameters used by measurement routines | |||
| *********************************************************/ | |||
| /* | |||
| * set_fcyc_clear_cache - When set, will run code to clear cache | |||
| * before each measurement. | |||
| * Default = 0 | |||
| */ | |||
| void set_fcyc_clear_cache(int clear); | |||
| /* | |||
| * set_fcyc_cache_size - Set size of cache to use when clearing cache | |||
| * Default = 1<<19 (512KB) | |||
| */ | |||
| void set_fcyc_cache_size(int bytes); | |||
| /* | |||
| * set_fcyc_cache_block - Set size of cache block | |||
| * Default = 32 | |||
| */ | |||
| void set_fcyc_cache_block(int bytes); | |||
| /* | |||
| * set_fcyc_compensate- When set, will attempt to compensate for | |||
| * timer interrupt overhead | |||
| * Default = 0 | |||
| */ | |||
| void set_fcyc_compensate(int compensate_arg); | |||
| /* | |||
| * set_fcyc_k - Value of K in K-best measurement scheme | |||
| * Default = 3 | |||
| */ | |||
| void set_fcyc_k(int k); | |||
| /* | |||
| * set_fcyc_maxsamples - Maximum number of samples attempting to find | |||
| * K-best within some tolerance. | |||
| * When exceeded, just return best sample found. | |||
| * Default = 20 | |||
| */ | |||
| void set_fcyc_maxsamples(int maxsamples_arg); | |||
| /* | |||
| * set_fcyc_epsilon - Tolerance required for K-best | |||
| * Default = 0.01 | |||
| */ | |||
| void set_fcyc_epsilon(double epsilon_arg); | |||
BIN
fcyc.o
View File
+ 57
- 0
fsecs.c
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,57 @@ | |||
| /**************************** | |||
| * High-level timing wrappers | |||
| ****************************/ | |||
| #include <stdio.h> | |||
| #include "fsecs.h" | |||
| #include "fcyc.h" | |||
| #include "clock.h" | |||
| #include "ftimer.h" | |||
| #include "config.h" | |||
| static double Mhz; /* estimated CPU clock frequency */ | |||
| extern int verbose; /* -v option in mdriver.c */ | |||
| /* | |||
| * init_fsecs - initialize the timing package | |||
| */ | |||
| void init_fsecs(void) | |||
| { | |||
| Mhz = 0; /* keep gcc -Wall happy */ | |||
| #if USE_FCYC | |||
| if (verbose) | |||
| printf("Measuring performance with a cycle counter.\n"); | |||
| /* set key parameters for the fcyc package */ | |||
| set_fcyc_maxsamples(20); | |||
| set_fcyc_clear_cache(1); | |||
| set_fcyc_compensate(1); | |||
| set_fcyc_epsilon(0.01); | |||
| set_fcyc_k(3); | |||
| Mhz = mhz(verbose > 0); | |||
| #elif USE_ITIMER | |||
| if (verbose) | |||
| printf("Measuring performance with the interval timer.\n"); | |||
| #elif USE_GETTOD | |||
| if (verbose) | |||
| printf("Measuring performance with gettimeofday().\n"); | |||
| #endif | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * fsecs - Return the running time of a function f (in seconds) | |||
| */ | |||
| double fsecs(fsecs_test_funct f, void *argp) | |||
| { | |||
| #if USE_FCYC | |||
| double cycles = fcyc(f, argp); | |||
| return cycles/(Mhz*1e6); | |||
| #elif USE_ITIMER | |||
| return ftimer_itimer(f, argp, 10); | |||
| #elif USE_GETTOD | |||
| return ftimer_gettod(f, argp, 10); | |||
| #endif | |||
| } | |||
+ 4
- 0
fsecs.h
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,4 @@ | |||
| typedef void (*fsecs_test_funct)(void *); | |||
| void init_fsecs(void); | |||
| double fsecs(fsecs_test_funct f, void *argp); | |||
BIN
fsecs.o
View File
+ 106
- 0
ftimer.c
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,106 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * ftimer.c - Estimate the time (in seconds) used by a function f | |||
| * | |||
| * Copyright (c) 2002, R. Bryant and D. O'Hallaron, All rights reserved. | |||
| * May not be used, modified, or copied without permission. | |||
| * | |||
| * Function timers that estimate the running time (in seconds) of a function f. | |||
| * ftimer_itimer: version that uses the interval timer | |||
| * ftimer_gettod: version that uses gettimeofday | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <stdio.h> | |||
| #include <sys/time.h> | |||
| #include "ftimer.h" | |||
| /* function prototypes */ | |||
| static void init_etime(void); | |||
| static double get_etime(void); | |||
| /* | |||
| * ftimer_itimer - Use the interval timer to estimate the running time | |||
| * of f(argp). Return the average of n runs. | |||
| */ | |||
| double ftimer_itimer(ftimer_test_funct f, void *argp, int n) | |||
| { | |||
| double start, tmeas; | |||
| int i; | |||
| init_etime(); | |||
| start = get_etime(); | |||
| for (i = 0; i < n; i++) | |||
| f(argp); | |||
| tmeas = get_etime() - start; | |||
| return tmeas / n; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * ftimer_gettod - Use gettimeofday to estimate the running time of | |||
| * f(argp). Return the average of n runs. | |||
| */ | |||
| double ftimer_gettod(ftimer_test_funct f, void *argp, int n) | |||
| { | |||
| int i; | |||
| struct timeval stv, etv; | |||
| double diff; | |||
| gettimeofday(&stv, NULL); | |||
| for (i = 0; i < n; i++) | |||
| f(argp); | |||
| gettimeofday(&etv,NULL); | |||
| diff = 1E3*(etv.tv_sec - stv.tv_sec) + 1E-3*(etv.tv_usec-stv.tv_usec); | |||
| diff /= n; | |||
| return (1E-3*diff); | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * Routines for manipulating the Unix interval timer | |||
| */ | |||
| /* The initial value of the interval timer */ | |||
| #define MAX_ETIME 86400 | |||
| /* static variables that hold the initial value of the interval timer */ | |||
| static struct itimerval first_u; /* user time */ | |||
| static struct itimerval first_r; /* real time */ | |||
| static struct itimerval first_p; /* prof time*/ | |||
| /* init the timer */ | |||
| static void init_etime(void) | |||
| { | |||
| first_u.it_interval.tv_sec = 0; | |||
| first_u.it_interval.tv_usec = 0; | |||
| first_u.it_value.tv_sec = MAX_ETIME; | |||
| first_u.it_value.tv_usec = 0; | |||
| setitimer(ITIMER_VIRTUAL, &first_u, NULL); | |||
| first_r.it_interval.tv_sec = 0; | |||
| first_r.it_interval.tv_usec = 0; | |||
| first_r.it_value.tv_sec = MAX_ETIME; | |||
| first_r.it_value.tv_usec = 0; | |||
| setitimer(ITIMER_REAL, &first_r, NULL); | |||
| first_p.it_interval.tv_sec = 0; | |||
| first_p.it_interval.tv_usec = 0; | |||
| first_p.it_value.tv_sec = MAX_ETIME; | |||
| first_p.it_value.tv_usec = 0; | |||
| setitimer(ITIMER_PROF, &first_p, NULL); | |||
| } | |||
| /* return elapsed real seconds since call to init_etime */ | |||
| static double get_etime(void) { | |||
| struct itimerval v_curr; | |||
| struct itimerval r_curr; | |||
| struct itimerval p_curr; | |||
| getitimer(ITIMER_VIRTUAL, &v_curr); | |||
| getitimer(ITIMER_REAL,&r_curr); | |||
| getitimer(ITIMER_PROF,&p_curr); | |||
| return (double) ((first_p.it_value.tv_sec - r_curr.it_value.tv_sec) + | |||
| (first_p.it_value.tv_usec - r_curr.it_value.tv_usec)*1e-6); | |||
| } | |||
+ 14
- 0
ftimer.h
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,14 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * Function timers | |||
| */ | |||
| typedef void (*ftimer_test_funct)(void *); | |||
| /* Estimate the running time of f(argp) using the Unix interval timer. | |||
| Return the average of n runs */ | |||
| double ftimer_itimer(ftimer_test_funct f, void *argp, int n); | |||
| /* Estimate the running time of f(argp) using gettimeofday | |||
| Return the average of n runs */ | |||
| double ftimer_gettod(ftimer_test_funct f, void *argp, int n); | |||
BIN
ftimer.o
View File
BIN
mdriver
View File
+ 1017
- 0
mdriver.c
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
BIN
mdriver.o
View File
+ 101
- 0
memlib.c
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,101 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * memlib.c - a module that simulates the memory system. Needed because it | |||
| * allows us to interleave calls from the student's malloc package | |||
| * with the system's malloc package in libc. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <stdio.h> | |||
| #include <stdlib.h> | |||
| #include <assert.h> | |||
| #include <unistd.h> | |||
| #include <sys/mman.h> | |||
| #include <string.h> | |||
| #include <errno.h> | |||
| #include "memlib.h" | |||
| #include "config.h" | |||
| /* private variables */ | |||
| static char *mem_start_brk; /* points to first byte of heap */ | |||
| static char *mem_brk; /* points to last byte of heap */ | |||
| static char *mem_max_addr; /* largest legal heap address */ | |||
| /* | |||
| * mem_init - initialize the memory system model | |||
| */ | |||
| void mem_init(void) | |||
| { | |||
| /* allocate the storage we will use to model the available VM */ | |||
| if ((mem_start_brk = (char *)malloc(MAX_HEAP)) == NULL) { | |||
| fprintf(stderr, "mem_init_vm: malloc error\n"); | |||
| exit(1); | |||
| } | |||
| mem_max_addr = mem_start_brk + MAX_HEAP; /* max legal heap address */ | |||
| mem_brk = mem_start_brk; /* heap is empty initially */ | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * mem_deinit - free the storage used by the memory system model | |||
| */ | |||
| void mem_deinit(void) | |||
| { | |||
| free(mem_start_brk); | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * mem_reset_brk - reset the simulated brk pointer to make an empty heap | |||
| */ | |||
| void mem_reset_brk() | |||
| { | |||
| mem_brk = mem_start_brk; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * mem_sbrk - simple model of the sbrk function. Extends the heap | |||
| * by incr bytes and returns the start address of the new area. In | |||
| * this model, the heap cannot be shrunk. | |||
| */ | |||
| void *mem_sbrk(int incr) | |||
| { | |||
| char *old_brk = mem_brk; | |||
| if ( (incr < 0) || ((mem_brk + incr) > mem_max_addr)) { | |||
| errno = ENOMEM; | |||
| fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: mem_sbrk failed. Ran out of memory...\n"); | |||
| return (void *)-1; | |||
| } | |||
| mem_brk += incr; | |||
| return (void *)old_brk; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * mem_heap_lo - return address of the first heap byte | |||
| */ | |||
| void *mem_heap_lo() | |||
| { | |||
| return (void *)mem_start_brk; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * mem_heap_hi - return address of last heap byte | |||
| */ | |||
| void *mem_heap_hi() | |||
| { | |||
| return (void *)(mem_brk - 1); | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * mem_heapsize() - returns the heap size in bytes | |||
| */ | |||
| size_t mem_heapsize() | |||
| { | |||
| return (size_t)(mem_brk - mem_start_brk); | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * mem_pagesize() - returns the page size of the system | |||
| */ | |||
| size_t mem_pagesize() | |||
| { | |||
| return (size_t)getpagesize(); | |||
| } | |||
+ 11
- 0
memlib.h
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,11 @@ | |||
| #include <unistd.h> | |||
| void mem_init(void); | |||
| void mem_deinit(void); | |||
| void *mem_sbrk(int incr); | |||
| void mem_reset_brk(void); | |||
| void *mem_heap_lo(void); | |||
| void *mem_heap_hi(void); | |||
| size_t mem_heapsize(void); | |||
| size_t mem_pagesize(void); | |||
BIN
memlib.o
View File
+ 439
- 0
mm.c
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,439 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * mm-naive.c - The fastest, least memory-efficient malloc package. | |||
| * | |||
| * In this naive approach, a block is allocated by simply incrementing | |||
| * the brk pointer. A block is pure payload. There are no headers or | |||
| * footers. Blocks are never coalesced or reused. Realloc is | |||
| * implemented directly using mm_malloc and mm_free. | |||
| * | |||
| * NOTE TO STUDENTS: Replace this header comment with your own header | |||
| * comment that gives a high level description of your solution. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <stdio.h> | |||
| #include <stdlib.h> | |||
| #include <assert.h> | |||
| #include <unistd.h> | |||
| #include <string.h> | |||
| #include "mm.h" | |||
| #include "memlib.h" | |||
| /********************************************************* | |||
| * NOTE TO STUDENTS: Before you do anything else, please | |||
| * provide your team information in the following struct. | |||
| ********************************************************/ | |||
| team_t team = { | |||
| /* Team name */ | |||
| "ateam", | |||
| /* First member's full name */ | |||
| "Deng Bohao", | |||
| /* First member's email address */ | |||
| "10225501432@stu.ecnu.edu.cn", | |||
| /* Second member's full name (leave blank if none) */ | |||
| "Deng Bohao", | |||
| /* Second member's email address (leave blank if none) */ | |||
| "10225501432@stu.ecnu.edu.cn" | |||
| }; | |||
| /* single word (4) or double word (8) alignment */ | |||
| #define ALIGNMENT 8 | |||
| /* rounds up to the nearest multiple of ALIGNMENT */ | |||
| #define ALIGN(size) (((size) + (ALIGNMENT-1)) & ~0x7) | |||
| #define SIZE_T_SIZE (ALIGN(sizeof(size_t))) | |||
| /* Basic constants and macros */ | |||
| #define WSIZE 4 /* Word and header/footer size (bytes) */ | |||
| #define DSIZE 8 /* Double word size (bytes) */ | |||
| #define CHUNKSIZE (1<<12) /* Extend heap by this amount (bytes) */ | |||
| #define MAX(x, y) ((x) > (y) ? (x) : (y)) | |||
| /* Pack a size and allocated bit into word */ | |||
| #define PACK(size, alloc) ((size) | (alloc)) | |||
| /* Read and write a word at address p */ | |||
| #define GET(p) (*(unsigned int *)(p)) | |||
| #define PUT(p, val) (*(unsigned int *)(p) = (val)) | |||
| /* Read and write a pointer at address p */ | |||
| #define GET_PTR(p) ((unsigned int *)(long)(GET(p))) | |||
| #define PUT_PTR(p, ptr) (*(unsigned int *)(p) = ((long)ptr)) | |||
| /* Read the size and allocated fields from address p */ | |||
| #define GET_SIZE(p) (GET(p) & ~0x7) | |||
| #define GET_ALLOC(p) (GET(p) & 0x1) | |||
| /* Given block ptr bp, compute address of its header and footer */ | |||
| #define HDRP(bp) ((char *)(bp) - WSIZE) | |||
| #define FTRP(bp) ((char *)(bp) + GET_SIZE(HDRP(bp)) - DSIZE) | |||
| /* Given block ptr bp, compute address of next and previous blocks */ | |||
| #define NEXT_BLKP(bp) ((char *)(bp) + GET_SIZE(((char *)(bp) - WSIZE))) | |||
| #define PREV_BLKP(bp) ((char *)(bp) - GET_SIZE(((char *)(bp) - DSIZE))) | |||
| /* 每个free list中块的大小范围 */ | |||
| #define SIZE1 (1<<4) | |||
| #define SIZE2 (1<<5) | |||
| #define SIZE3 (1<<6) | |||
| #define SIZE4 (1<<7) | |||
| #define SIZE5 (1<<8) | |||
| #define SIZE6 (1<<9) | |||
| #define SIZE7 (1<<10) /* 1 KB */ | |||
| #define SIZE8 (1<<11) | |||
| #define SIZE9 (1<<12) | |||
| #define SIZE10 (1<<13) | |||
| #define SIZE11 (1<<14) | |||
| #define SIZE12 (1<<15) | |||
| #define SIZE13 (1<<16) | |||
| #define SIZE14 (1<<17) | |||
| #define SIZE15 (1<<18) | |||
| #define SIZE16 (1<<19) | |||
| #define SIZE17 (1<<20) /* 1 MB */ | |||
| #define LISTS_NUM 18 /* free list 的数量 */ | |||
| /* Globe var */ | |||
| static char *heap_listp; | |||
| /* 函数声明 */ | |||
| static void *extend_heap(size_t words); | |||
| static void *coalesce(void *bp); | |||
| static void *find_fit(size_t asize); | |||
| static void place(void *bp, size_t asize); | |||
| static void insert_list(void *bp); | |||
| int getListOffset(size_t size); | |||
| void delete_list(void *bp); | |||
| /* | |||
| * mm_init - initialize the malloc package. | |||
| */ | |||
| int mm_init(void) | |||
| { | |||
| char *bp; | |||
| int i; | |||
| if ((heap_listp = mem_sbrk((LISTS_NUM + 4) * WSIZE)) == (void *)-1) { | |||
| return -1; | |||
| } | |||
| PUT(heap_listp + LISTS_NUM * WSIZE, 0); | |||
| PUT(heap_listp + (1 + LISTS_NUM) * WSIZE, PACK(DSIZE, 1)); | |||
| PUT(heap_listp + (2 + LISTS_NUM) * WSIZE, PACK(DSIZE, 1)); | |||
| PUT(heap_listp + (3 + LISTS_NUM) * WSIZE, PACK(0, 1)); | |||
| for (i = 0; i < LISTS_NUM; i++) { | |||
| PUT_PTR(heap_listp + WSIZE * i, NULL); | |||
| } | |||
| /* Extend the empty heap with a free block of CHUNKSIZE bytes */ | |||
| if ((bp = extend_heap(CHUNKSIZE / WSIZE)) == NULL) { | |||
| return -1; | |||
| } | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * 扩展heap的大小 | |||
| */ | |||
| void *extend_heap(size_t words) | |||
| { | |||
| char *bp; | |||
| size_t size; | |||
| /* Allocate an even number of words to maintain alignment */ | |||
| size = (words % 2) ? ((words + 1) * WSIZE) : (words * WSIZE); | |||
| if ((long)(bp = mem_sbrk(size)) == -1) { | |||
| return NULL; | |||
| } | |||
| /* Initialize free block header/footer and the epilogue header */ | |||
| PUT(HDRP(bp), PACK(size, 0)); /* Free block header */ | |||
| PUT(FTRP(bp), PACK(size, 0)); /* Free block footer */ | |||
| PUT(HDRP(NEXT_BLKP(bp)), PACK(0, 1)); /* New epilogue header */ | |||
| /* Coalesce if the previous block was free */ | |||
| return coalesce(bp); | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * 合并free block | |||
| */ | |||
| void *coalesce(void *bp) | |||
| { | |||
| size_t prev_alloc = GET_ALLOC(FTRP(PREV_BLKP(bp))); | |||
| size_t next_alloc = GET_ALLOC(HDRP(NEXT_BLKP(bp))); | |||
| size_t size = GET_SIZE(HDRP(bp)); | |||
| if (prev_alloc && next_alloc) { /* 前后都分配了 */ | |||
| bp = bp; | |||
| } else if (prev_alloc && !next_alloc) { /* 前分配, 后未分配 */ | |||
| delete_list(NEXT_BLKP(bp)); | |||
| size += GET_SIZE(HDRP(NEXT_BLKP(bp))); | |||
| PUT(HDRP(bp), PACK(size, 0)); | |||
| PUT(FTRP(bp), PACK(size, 0)); | |||
| } else if (!prev_alloc && next_alloc) { /* 前未分配, 后分配 */ | |||
| delete_list(PREV_BLKP(bp)); | |||
| size += GET_SIZE(HDRP(PREV_BLKP(bp))); | |||
| PUT(FTRP(bp), PACK(size, 0)); | |||
| PUT(HDRP(PREV_BLKP(bp)), PACK(size, 0)); | |||
| bp = PREV_BLKP(bp); | |||
| } else { /* 前后都未分配 */ | |||
| delete_list(NEXT_BLKP(bp)); | |||
| delete_list(PREV_BLKP(bp)); | |||
| size = size + GET_SIZE(HDRP(PREV_BLKP(bp))) + | |||
| GET_SIZE(HDRP(NEXT_BLKP(bp))); | |||
| PUT(HDRP(PREV_BLKP(bp)), PACK(size, 0)); | |||
| PUT(FTRP(NEXT_BLKP(bp)), PACK(size, 0)); | |||
| bp = PREV_BLKP(bp); | |||
| } | |||
| insert_list(bp); | |||
| return bp; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * mm_malloc - Allocate a block by searching the free list. | |||
| * Always allocate a block whose size is a multiple of the alignment. | |||
| */ | |||
| void *mm_malloc(size_t size) | |||
| { | |||
| size_t asize; /* Adjusted block size */ | |||
| size_t extendsize; /* Amount to extend heap if no fit */ | |||
| char *bp; | |||
| /* Igore spurious requests */ | |||
| if (0 == size) { | |||
| return NULL; | |||
| } | |||
| /* Adjusted block size to include overhead and alignment reqs */ | |||
| if (size <= DSIZE) { | |||
| asize = 2 * DSIZE; | |||
| } else { | |||
| asize = DSIZE * ((size + (DSIZE) + (DSIZE - 1)) / DSIZE); | |||
| } | |||
| /* Search the free list for a fit */ | |||
| if ((bp = find_fit(asize)) != NULL) { | |||
| place(bp, asize); | |||
| return bp; | |||
| } | |||
| /* No fit found. Get more memory and place the block */ | |||
| extendsize = MAX(asize, CHUNKSIZE); | |||
| if ((bp = extend_heap(extendsize / WSIZE)) == NULL) { | |||
| return NULL; | |||
| } | |||
| place(bp, asize); | |||
| return bp; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * getListOffset - 得到大小为size的块应该在哪个list中 | |||
| */ | |||
| int getListOffset(size_t size) | |||
| { | |||
| if (size <= SIZE1) { | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } else if (size <= SIZE2) { | |||
| return 1; | |||
| } else if (size <= SIZE3) { | |||
| return 2; | |||
| } else if (size <= SIZE4) { | |||
| return 3; | |||
| } else if (size <= SIZE5) { | |||
| return 4; | |||
| } else if (size <= SIZE6) { | |||
| return 5; | |||
| } else if (size <= SIZE7) { | |||
| return 6; | |||
| } else if (size <= SIZE8) { | |||
| return 7; | |||
| } else if (size <= SIZE9) { | |||
| return 8; | |||
| } else if (size <= SIZE10) { | |||
| return 9; | |||
| } else if (size <= SIZE11) { | |||
| return 10; | |||
| } else if (size <= SIZE12) { | |||
| return 11; | |||
| } else if (size <= SIZE13) { | |||
| return 12; | |||
| } else if (size <= SIZE14) { | |||
| return 13; | |||
| } else if (size <= SIZE15) { | |||
| return 14; | |||
| } else if (size <= SIZE16) { | |||
| return 15; | |||
| } else if (size <= SIZE17) { | |||
| return 16; | |||
| } else { | |||
| return 17; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * insert_list - 将free block插入到相应大小的free list中, 插入位置为表头 | |||
| */ | |||
| void insert_list(void *bp) | |||
| { | |||
| int index; | |||
| size_t size; | |||
| size = GET_SIZE(HDRP(bp)); | |||
| index = getListOffset(size); | |||
| if (GET_PTR(heap_listp + WSIZE * index) == NULL) { | |||
| PUT_PTR(heap_listp + WSIZE * index, bp); | |||
| PUT_PTR(bp, NULL); | |||
| PUT_PTR((unsigned int *)bp + 1, NULL); | |||
| } else { | |||
| PUT_PTR(bp, GET_PTR(heap_listp + WSIZE * index)); | |||
| PUT_PTR(GET_PTR(heap_listp + WSIZE * index) + 1, bp); /* 修改前一个位置 */ | |||
| PUT_PTR((unsigned int *)bp + 1, NULL); | |||
| PUT_PTR(heap_listp + WSIZE * index, bp); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * delete_list - 删除链表结点 | |||
| */ | |||
| void delete_list(void *bp) | |||
| { | |||
| int index; | |||
| size_t size; | |||
| size = GET_SIZE(HDRP(bp)); | |||
| index = getListOffset(size); | |||
| if (GET_PTR(bp) == NULL && GET_PTR((unsigned int *)bp + 1) == NULL) { | |||
| /* 链表中唯一结点 */ | |||
| PUT_PTR(heap_listp + WSIZE * index, NULL); | |||
| } else if (GET_PTR(bp) == NULL && GET_PTR((unsigned int *)bp + 1) != NULL) { | |||
| /* 链表中最后一个结点, 不是唯一一个 */ | |||
| PUT_PTR(GET_PTR((unsigned int *)bp + 1), NULL); | |||
| } else if (GET_PTR(bp) != NULL && GET_PTR((unsigned int *)bp + 1) == NULL){ | |||
| /* 链表中第一个结点, 不是唯一一个 */ | |||
| PUT_PTR(heap_listp + WSIZE * index, GET_PTR(bp)); | |||
| PUT_PTR(GET_PTR(bp) + 1, NULL); | |||
| } else if (GET_PTR(bp) != NULL && GET_PTR((unsigned int *)bp + 1) != NULL) { | |||
| /* 链表中的中间结点 */ | |||
| PUT_PTR(GET_PTR((unsigned int *)bp + 1), GET_PTR(bp)); | |||
| PUT_PTR(GET_PTR(bp) + 1, GET_PTR((unsigned int*)bp + 1)); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * find_fit - Search the free list for a fit | |||
| */ | |||
| void *find_fit(size_t asize) | |||
| { | |||
| int index; | |||
| index = getListOffset(asize); | |||
| unsigned int *ptr; | |||
| /* 小的class内找不到就到大的class内找 */ | |||
| while (index < 18) { | |||
| ptr = GET_PTR(heap_listp + 4 * index); | |||
| while (ptr != NULL) { | |||
| if (GET_SIZE(HDRP(ptr)) >= asize) { | |||
| return (void *)ptr; | |||
| } | |||
| ptr = GET_PTR(ptr); | |||
| } | |||
| index++; | |||
| } | |||
| return NULL; | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * place - place the requested block at the beginning of the free block | |||
| */ | |||
| void place(void *bp, size_t asize) | |||
| { | |||
| size_t csize = GET_SIZE(HDRP(bp)); | |||
| delete_list(bp); | |||
| if ((csize - asize) >= (2 * DSIZE)) { | |||
| PUT(HDRP(bp), PACK(asize, 1)); | |||
| PUT(FTRP(bp), PACK(asize, 1)); | |||
| bp = NEXT_BLKP(bp); | |||
| PUT(HDRP(bp), PACK(csize - asize, 0)); | |||
| PUT(FTRP(bp), PACK(csize - asize, 0)); | |||
| insert_list(bp); | |||
| } else { | |||
| PUT(HDRP(bp), PACK(csize, 1)); | |||
| PUT(FTRP(bp), PACK(csize, 1)); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * mm_free - Freeing a block. | |||
| */ | |||
| void mm_free(void *ptr) | |||
| { | |||
| size_t size = GET_SIZE(HDRP(ptr)); | |||
| PUT(HDRP(ptr), PACK(size, 0)); | |||
| PUT(FTRP(ptr), PACK(size, 0)); | |||
| coalesce(ptr); | |||
| } | |||
| /* | |||
| * mm_realloc - 直接用malloc和free组合实现 | |||
| */ | |||
| void *mm_realloc(void *ptr, size_t size) | |||
| { | |||
| size_t asize; | |||
| void *oldptr = ptr; | |||
| void *newptr; | |||
| /* free */ | |||
| if (0 == size) { | |||
| free(oldptr); | |||
| return NULL; | |||
| } | |||
| if (size <= DSIZE) { | |||
| asize = 2 * DSIZE; | |||
| } else { | |||
| asize = DSIZE * ((size + (DSIZE) + (DSIZE - 1)) / DSIZE); | |||
| } | |||
| if (asize == GET_SIZE(HDRP(oldptr))) { | |||
| return oldptr; | |||
| } | |||
| /* 缩小空间 */ | |||
| if (asize < GET_SIZE(HDRP(oldptr))) { | |||
| newptr = mm_malloc(size); | |||
| memmove(newptr, oldptr, size); | |||
| mm_free(oldptr); | |||
| return newptr; | |||
| } | |||
| newptr = mm_malloc(size); | |||
| if (NULL == newptr) | |||
| return NULL; | |||
| memmove(newptr, oldptr, size); | |||
| mm_free(oldptr); | |||
| return newptr; | |||
| } | |||
+ 23
- 0
mm.h
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,23 @@ | |||
| #include <stdio.h> | |||
| extern int mm_init (void); | |||
| extern void *mm_malloc (size_t size); | |||
| extern void mm_free (void *ptr); | |||
| extern void *mm_realloc(void *ptr, size_t size); | |||
| /* | |||
| * Students work in teams of one or two. Teams enter their team name, | |||
| * personal names and login IDs in a struct of this | |||
| * type in their bits.c file. | |||
| */ | |||
| typedef struct { | |||
| char *teamname; /* ID1+ID2 or ID1 */ | |||
| char *name1; /* full name of first member */ | |||
| char *id1; /* login ID of first member */ | |||
| char *name2; /* full name of second member (if any) */ | |||
| char *id2; /* login ID of second member */ | |||
| } team_t; | |||
| extern team_t team; | |||
BIN
mm.o
View File
+ 16
- 0
short1-bal.rep
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,16 @@ | |||
| 20000 | |||
| 6 | |||
| 12 | |||
| 1 | |||
| a 0 2040 | |||
| a 1 2040 | |||
| f 1 | |||
| a 2 48 | |||
| a 3 4072 | |||
| f 3 | |||
| a 4 4072 | |||
| f 0 | |||
| f 2 | |||
| a 5 4072 | |||
| f 4 | |||
| f 5 | |||
+ 16
- 0
short2-bal.rep
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,16 @@ | |||
| 20000 | |||
| 6 | |||
| 12 | |||
| 1 | |||
| a 0 2040 | |||
| a 1 4010 | |||
| a 2 48 | |||
| a 3 4072 | |||
| a 4 4072 | |||
| a 5 4072 | |||
| f 0 | |||
| f 1 | |||
| f 2 | |||
| f 3 | |||
| f 4 | |||
| f 5 | |||
+ 42
- 0
traces/Makefile
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,42 @@ | |||
| all: synthetic-traces balanced-traces check-balance | |||
| synthetic-traces: | |||
| ./gen_binary.pl | |||
| ./gen_binary2.pl | |||
| ./gen_coalescing.pl | |||
| ./gen_random.pl | |||
| ./gen_realloc.pl | |||
| ./gen_realloc2.pl | |||
| balanced-traces: | |||
| ./checktrace.pl < amptjp.rep > amptjp-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl < binary.rep > binary-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl < binary2.rep > binary2-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl < cccp.rep > cccp-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl < coalescing.rep > coalescing-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl < cp-decl.rep > cp-decl-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl < expr.rep > expr-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl < realloc.rep > realloc-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl < realloc2.rep > realloc2-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl < random.rep > random-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl < random2.rep > random2-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl < short1.rep > short1-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl < short2.rep > short2-bal.rep | |||
| check-balance: | |||
| ./checktrace.pl -s < amptjp-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl -s < binary-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl -s < binary2-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl -s < cccp-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl -s < coalescing-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl -s < cp-decl-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl -s < expr-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl -s < realloc-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl -s < realloc2-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl -s < random-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl -s < random2-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl -s < short1-bal.rep | |||
| ./checktrace.pl -s < short2-bal.rep | |||
| clean: | |||
| rm -f *~ | |||
+ 116
- 0
traces/README
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,116 @@ | |||
| ##################################################################### | |||
| # CS:APP Malloc Lab | |||
| # Traces | |||
| # | |||
| # Copyright (c) 2002, R. Bryant and D. O'Hallaron, All rights reserved. | |||
| # May not be used, modified, or copied without permission. | |||
| # | |||
| ###################################################################### | |||
| This directory contains traces of allocate and free requests that are | |||
| used by the test harness to evaluate the student malloc packages. | |||
| ********* | |||
| 1. Files | |||
| ********* | |||
| *.rep Original traces | |||
| *-bal.rep Balanced versions of the original traces | |||
| gen_XXX.pl Perl script that generates *.rep | |||
| checktrace.pl Checks trace for consistency and outputs a balanced version | |||
| Makefile Generates traces | |||
| Note: A "balanced" trace has a matching free request for each allocate | |||
| request. | |||
| ********************** | |||
| 2. Building the traces | |||
| ********************** | |||
| To rebuild the traces from scratch, type | |||
| unix> make | |||
| ******************** | |||
| 3. Trace file format | |||
| ******************** | |||
| A trace file is an ASCII file. It begins with a 4-line header: | |||
| <sugg_heapsize> /* suggested heap size (unused) */ | |||
| <num_ids> /* number of request id's */ | |||
| <num_ops> /* number of requests (operations) */ | |||
| <weight> /* weight for this trace (unused) */ | |||
| The header is followed by num_ops text lines. Each line denotes either | |||
| an allocate [a], reallocate [r], or free [f] request. The <alloc_id> | |||
| is an integer that uniquely identifies an allocate or reallocate | |||
| request. | |||
| a <id> <bytes> /* ptr_<id> = malloc(<bytes>) */ | |||
| r <id> <bytes> /* realloc(ptr_<id>, <bytes>) */ | |||
| f <id> /* free(ptr_<id>) */ | |||
| For example, the following trace file: | |||
| <beginning of file> | |||
| 20000 | |||
| 3 | |||
| 8 | |||
| 1 | |||
| a 0 512 | |||
| a 1 128 | |||
| r 0 640 | |||
| a 2 128 | |||
| f 1 | |||
| r 0 768 | |||
| f 0 | |||
| f 2 | |||
| <end of file> | |||
| is balanced. It has a recommended heap size of 20000 bytes (ignored), | |||
| three distinct request ids (0, 1, and 2), eight different requests | |||
| (one per line), and a weight of 1 (ignored). | |||
| ************************ | |||
| 4. Description of traces | |||
| ************************ | |||
| * short{1,2}-bal.rep | |||
| Tiny synthetic tracefiles for debugging | |||
| * {amptjp,cccp,cp-decl,expr}-bal.rep | |||
| Traces generated from real programs. | |||
| * {binary,binary2}-bal.rep | |||
| The allocation pattern is to alternatively allocate a small-sized | |||
| chunk of memory and a large-sized chunk. The small-sized chunks | |||
| (either 16 or 64 ) are deliberately set to be power of 2 while the | |||
| large-size chunks (either 112 or 448) are not a power of 2. Defeats | |||
| buddy algorithms. However, a simple-minded algorithm might prevail in | |||
| this scenario because a first-fit scheme will be good enough. | |||
| * coalescing-bal.rep | |||
| Repeatedly allocate two equal-sized chunks (4095 in size) and release | |||
| them, and then immediately allocate and free a chunk twice as big | |||
| (8190). This tests if the students' algorithm ever really releases | |||
| memory and does coalescing. The size is chosen to give advantage to | |||
| tree-based or segrated fits algorithms where there is no header or | |||
| footer overhead. | |||
| * {random,random2}-bal.rep | |||
| Random allocate and free requesets that simply test the correctness | |||
| and robustness of the algorithm. | |||
| * {realloc,realloc2}-bal.rep | |||
| Reallocate previously allocated blocks interleaved by other allocation | |||
| request. The purpose is to test whether a certain amount of internal | |||
| fragments are allocated or not. Naive realloc implementations that | |||
| always realloc a brand new block will suffer. | |||
+ 5698
- 0
traces/amptjp-bal.rep
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
+ 4809
- 0
traces/amptjp.rep
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
+ 12004
- 0
traces/binary-bal.rep
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
+ 8004
- 0
traces/binary.rep
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
+ 24004
- 0
traces/binary2-bal.rep
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
+ 16004
- 0
traces/binary2.rep
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
+ 5852
- 0
traces/cccp-bal.rep
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
+ 5036
- 0
traces/cccp.rep
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
+ 155
- 0
traces/checktrace.pl
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,155 @@ | |||
| #!/usr/bin/perl | |||
| #!/usr/local/bin/perl | |||
| use Getopt::Std; | |||
| ####################################################################### | |||
| # checktrace - trace file consistency checker and balancer. | |||
| # | |||
| # Copyright (c) 2002, R. Bryant and D. O'Hallaron, All rights reserved. | |||
| # May not be used, modified, or copied without permission. | |||
| # | |||
| # This script reads a Malloc Lab trace file, checks it for consistency, | |||
| # and outputs a balanced version by appending any necessary free requests. | |||
| # | |||
| ####################################################################### | |||
| $| = 1; # autoflush output on every print statement | |||
| # | |||
| # void usage(void) - print help message and terminate | |||
| # | |||
| sub usage | |||
| { | |||
| printf STDERR "$_[0]\n"; | |||
| printf STDERR "Usage: $0 [-hs]\n"; | |||
| printf STDERR "Options:\n"; | |||
| printf STDERR " -h Print this message\n"; | |||
| printf STDERR " -s Emit only a brief summary\n"; | |||
| die "\n" ; | |||
| } | |||
| ############## | |||
| # Main routine | |||
| ############## | |||
| # | |||
| # Parse and check the command line arguments | |||
| # | |||
| getopts('hs'); | |||
| if ($opt_h) { | |||
| usage(""); | |||
| } | |||
| $summary = $opt_s; | |||
| # | |||
| # HASH keeps a running tally of outstanding alloc/realloc | |||
| # requests. When a free request is encountered, the corresponding | |||
| # hash entry is deleted. When we are finished reading the trace, | |||
| # what is left are the unmatched alloc/realloc requests. | |||
| # | |||
| %HASH = (); | |||
| # Read the trace header values | |||
| $heap_size = <STDIN>; | |||
| chomp($heap_size); | |||
| $num_blocks = <STDIN>; | |||
| chomp($num_blocks); | |||
| $old_num_ops = <STDIN>; | |||
| chomp($old_num_ops); | |||
| $weight = <STDIN>; | |||
| chomp($weight); | |||
| # | |||
| # Find any allocate requests that don't have a matching free requests | |||
| # | |||
| $linenum = 4; | |||
| $requestnum = 0; | |||
| while ($line = <STDIN>) { | |||
| chomp($line); | |||
| $linenum++; | |||
| ($cmd, $id, $size) = split(" ", $line); | |||
| # ignore blank lines | |||
| if (!$cmd) { | |||
| next; | |||
| } | |||
| # save the line for output later | |||
| $lines[$requestnum++] = $line; | |||
| #ignore realloc requests, as long as they are preceeded by an alloc request | |||
| if ($cmd eq "r") { | |||
| if (!$HASH{$id}) { | |||
| die "$0: ERROR[$linenum]: realloc without previous alloc\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| next; | |||
| } | |||
| if ($cmd eq "a" and $HASH{$id} eq "a") { | |||
| die "$0: ERROR[$linenum]: allocate with no intervening free.\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| if ($cmd eq "a" and $HASH{$id} eq "f") { | |||
| die "$0: ERROR[$linenum]: reused ID $id.\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| if ($cmd eq "f" and !exists($HASH{$id})) { | |||
| die "$0: ERROR[$linenum]: freeing unallocated block.\n"; | |||
| next; | |||
| } | |||
| if ($cmd eq "f" and !$HASH{$id} eq "f") { | |||
| die "$0: ERROR[$linenum]: freeing already freed block.\n"; | |||
| next; | |||
| } | |||
| if ($cmd eq "f") { | |||
| delete $HASH{$id}; | |||
| } | |||
| else { | |||
| $HASH{$id} = $cmd; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| # | |||
| # If called with -s argument , print a brief balance summary and exit | |||
| # | |||
| if ($summary) { | |||
| if (!%HASH) { | |||
| print "Balanced trace.\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| else { | |||
| print "Unbalanced tree.\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| exit; | |||
| } | |||
| # | |||
| # Output a balanced version of the trace | |||
| # | |||
| $new_ops = keys %HASH; | |||
| $new_num_ops = $old_num_ops + $new_ops; | |||
| print "$heap_size\n"; | |||
| print "$num_blocks\n"; | |||
| print "$new_num_ops\n"; | |||
| print "$weight\n"; | |||
| # print the old requests | |||
| foreach $item (@lines) { | |||
| print "$item\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| # print a set of free requests that will balance the trace | |||
| foreach $key (sort keys %HASH) { | |||
| if ($HASH{$key} ne "a" and $HASH{$key} ne "r") { | |||
| die "$0: ERROR: Invalid free request in residue.\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| print "f $key\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| exit; | |||
+ 14404
- 0
traces/coalescing-bal.rep
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
+ 14404
- 0
traces/coalescing.rep
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
+ 6652
- 0
traces/cp-decl-bal.rep
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
+ 5687
- 0
traces/cp-decl.rep
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
+ 5384
- 0
traces/expr-bal.rep
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
+ 4541
- 0
traces/expr.rep
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
+ 39
- 0
traces/gen_binary.pl
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,39 @@ | |||
| #!/usr/bin/perl | |||
| #!/usr/local/bin/perl | |||
| $out_filename = "binary.rep"; | |||
| $blk_size1 = 64; | |||
| $blk_size2 = 512 - $blk_size1; | |||
| $num_iters = 2000; | |||
| # Open output file | |||
| open OUTFILE, ">$out_filename" or die "Cannot create $out_filename\n"; | |||
| # Calculate misc parameters | |||
| $blk_size12 = $blk_size1 + $blk_size2; | |||
| $suggested_heap_size = ($blk_size1 + $blk_size2 + $blk_size12)*$num_iters + 100; | |||
| $num_blocks = 3*$num_iters; | |||
| $num_ops = 4*$num_iters; | |||
| print OUTFILE "$suggested_heap_size\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "$num_blocks\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "$num_ops\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "1\n"; | |||
| for ($i = 0; $i < $num_iters; $i += 1) { | |||
| $seq1 = 2*$i; | |||
| $seq2 = 2*$i + 1; | |||
| print OUTFILE "a $seq1 $blk_size1\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "a $seq2 $blk_size2\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| for ($i = 0; $i < $num_iters; $i += 1) { | |||
| $fseq = 2*$i + 1; | |||
| print OUTFILE "f $fseq\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| for ($i = 0; $i < $num_iters; $i += 1) { | |||
| $aseq = 2*$num_iters + $i; | |||
| print OUTFILE "a $aseq $blk_size12\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| close OUTFILE; | |||
+ 38
- 0
traces/gen_binary2.pl
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,38 @@ | |||
| #!/usr/bin/perl | |||
| $out_filename = "binary2.rep"; | |||
| $blk_size1 = 16; | |||
| $blk_size2 = 128 - $blk_size1; | |||
| $num_iters = 4000; | |||
| # Open output file | |||
| open OUTFILE, ">$out_filename" or die "Cannot create $out_filename\n"; | |||
| # Calculate misc parameters | |||
| $blk_size12 = $blk_size1 + $blk_size2; | |||
| $suggested_heap_size = ($blk_size1 + $blk_size2 + $blk_size12)*$num_iters + 100; | |||
| $num_blocks = 3*$num_iters; | |||
| $num_ops = 4*$num_iters; | |||
| print OUTFILE "$suggested_heap_size\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "$num_blocks\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "$num_ops\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "1\n"; | |||
| for ($i = 0; $i < $num_iters; $i += 1) { | |||
| $seq1 = 2*$i; | |||
| $seq2 = 2*$i + 1; | |||
| print OUTFILE "a $seq1 $blk_size1\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "a $seq2 $blk_size2\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| for ($i = 0; $i < $num_iters; $i += 1) { | |||
| $fseq = 2*$i + 1; | |||
| print OUTFILE "f $fseq\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| for ($i = 0; $i < $num_iters; $i += 1) { | |||
| $aseq = 2*$num_iters + $i; | |||
| print OUTFILE "a $aseq $blk_size12\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| close OUTFILE; | |||
+ 36
- 0
traces/gen_coalescing.pl
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,36 @@ | |||
| #!/usr/bin/perl | |||
| #!/usr/local/bin/perl | |||
| $out_filename = "coalescing.rep"; | |||
| $blk_size = 4095; | |||
| $num_iters = 2400; | |||
| # Open output file | |||
| open OUTFILE, ">$out_filename" or die "Cannot create $out_filename\n"; | |||
| # Calculate misc parameters | |||
| $blk_size2 = 2*$blk_size; | |||
| $suggested_heap_size = 2*$blk_size*$num_iters + 100; | |||
| $num_blocks = 3*$num_iters; | |||
| $num_ops = 6*$num_iters; | |||
| print OUTFILE "$suggested_heap_size\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "$num_blocks\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "$num_ops\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "1\n"; | |||
| for ($i = 0; $i < $num_iters; $i += 1) { | |||
| $blk1 = 3*$i; | |||
| $blk2 = $blk1 + 1; | |||
| $blk3 = $blk1 + 2; | |||
| print OUTFILE "a $blk1 $blk_size\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "a $blk2 $blk_size\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "f $blk1\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "f $blk2\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "a $blk3 $blk_size2\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "f $blk3\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| close OUTFILE; | |||
+ 62
- 0
traces/gen_random.pl
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,62 @@ | |||
| #!/usr/bin/perl | |||
| #!/usr/local/bin/perl | |||
| $out_filename = $argv[0]; | |||
| $out_filename = "random.rep" unless $out_filename; | |||
| $num_blocks = $argv[1]; | |||
| # $num_blocks = 1200 unless $num_blocks; | |||
| $num_blocks = 2400 unless $num_blocks; | |||
| $max_blk_size = $argv[2]; | |||
| $max_blk_size = 32768 unless $max_blk_size; | |||
| #print "Output file: $out_filename\n"; | |||
| #print "Number of blocks: $num_blocks\n"; | |||
| #print "Max block size: $max_blk_size\n"; | |||
| # Create trace | |||
| # Make a series of malloc()s | |||
| for ($i = 0; $i < $num_blocks; $i += 1) { | |||
| $size = int(rand $max_blk_size); | |||
| $op = {}; | |||
| $op->{type} = "a"; | |||
| $op->{seq} = $i; | |||
| $op->{size} = $size; | |||
| $total_block_size += $size; | |||
| push @trace, $op; | |||
| } | |||
| # Insert free()s in proper places | |||
| for ($i = 0; $i < $num_blocks; $i += 1) { | |||
| for ($minval = $i; $minval < $num_blocks + $i; $minval += 1) { | |||
| if (($trace[$minval]->{type} eq "a") && ($trace[$minval]->{seq} == $i)) { | |||
| last; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| $pos = int(rand($num_blocks + $i - $minval - 1) + $minval + 1); | |||
| $op = {}; | |||
| $op->{type} = "f"; | |||
| $op->{seq} = $i; | |||
| splice @trace, $pos, 0, $op; | |||
| } | |||
| # Open output file | |||
| open OUTFILE, ">$out_filename" or die "Cannot create $out_filename\n"; | |||
| # Calculate misc parameters | |||
| $suggested_heap_size = $total_block_size + 100; | |||
| $num_ops = 2*$num_blocks; | |||
| print OUTFILE "$suggested_heap_size\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "$num_blocks\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "$num_ops\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "1\n"; | |||
| for ($i = 0; $i < 2*$num_blocks; $i += 1) { | |||
| if ($trace[$i]->{type} eq "a") { | |||
| print OUTFILE "$trace[$i]->{type} $trace[$i]->{seq} $trace[$i]->{size}\n"; | |||
| } else { | |||
| print OUTFILE "$trace[$i]->{type} $trace[$i]->{seq}\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| close OUTFILE; | |||
+ 57
- 0
traces/gen_realloc.pl
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,57 @@ | |||
| #!/usr/bin/perl | |||
| #!/usr/local/bin/perl | |||
| $out_filename = "realloc.rep"; | |||
| $realloc_size = 512; | |||
| $size_increment = 128; | |||
| $malloc_size = 128; | |||
| $num_iters = 4800; | |||
| # Open output file | |||
| open OUTFILE, ">$out_filename" or die "Cannot create $out_filename\n"; | |||
| # Calculate misc parameters | |||
| $suggested_heap_size = num_iters* ($realloc_size+$size_increment*2 )+100; | |||
| $num_blocks = $num_iters+1; | |||
| $num_ops = ($num_iters )*3 +1; | |||
| $blk = 1; | |||
| print OUTFILE "$suggested_heap_size\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "$num_blocks\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "$num_ops\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "1\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "a 0 $realloc_size\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "a $blk $malloc_size\n"; | |||
| for ($i = 1; $i < $num_iters; $i += 1) { | |||
| $blk += 1; | |||
| $realloc_size += $size_increment; | |||
| print OUTFILE "r 0 $realloc_size\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "a $blk $malloc_size\n"; | |||
| $prevblk = $blk-1; | |||
| print OUTFILE "f $prevblk\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| $finalblk = $blk; | |||
| print OUTFILE "f $finalblk\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "f 0"; | |||
| print OUTFILE | |||
| close OUTFILE; | |||
+ 46
- 0
traces/gen_realloc2.pl
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,46 @@ | |||
| #!/usr/bin/perl | |||
| #!/usr/local/bin/perl | |||
| $out_filename = "realloc2.rep"; | |||
| $realloc_size = 4092; | |||
| $size_increment = 5; | |||
| $malloc_size = 16; | |||
| $num_iters = 4800; | |||
| # Open output file | |||
| open OUTFILE, ">$out_filename" or die "Cannot create $out_filename\n"; | |||
| # Calculate misc parameters | |||
| $suggested_heap_size = $realloc_size+$size_increment*($num_iters-1)+$malloc_size*$num_iters+100; | |||
| $num_blocks = $num_iters + 1; | |||
| $num_ops = 3 * $num_iters + 1; | |||
| $blk = 1; | |||
| print OUTFILE "$suggested_heap_size\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "$num_blocks\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "$num_ops\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "1\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "a 0 $realloc_size\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "a $blk $malloc_size\n"; | |||
| for ($i = 1; $i < $num_iters; $i += 1) { | |||
| $blk += 1; | |||
| $realloc_size += $size_increment; | |||
| print OUTFILE "r 0 $realloc_size\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "a $blk $malloc_size\n"; | |||
| $prevblk = $blk-1; | |||
| print OUTFILE "f $prevblk\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| $finalblk = $blk; | |||
| print OUTFILE "f $finalblk\n"; | |||
| print OUTFILE "f 0"; | |||
| print OUTFILE | |||
| close OUTFILE; | |||
+ 4804
- 0
traces/random-bal.rep
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
+ 4804
- 0
traces/random.rep
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
+ 4804
- 0
traces/random2-bal.rep
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
+ 4804
- 0
traces/random2.rep
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
+ 14405
- 0
traces/realloc-bal.rep
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
+ 14405
- 0
traces/realloc.rep
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
+ 14405
- 0
traces/realloc2-bal.rep
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
+ 14405
- 0
traces/realloc2.rep
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
+ 16
- 0
traces/short1-bal.rep
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,16 @@ | |||
| 20000 | |||
| 6 | |||
| 12 | |||
| 1 | |||
| a 0 2040 | |||
| a 1 2040 | |||
| f 1 | |||
| a 2 48 | |||
| a 3 4072 | |||
| f 3 | |||
| a 4 4072 | |||
| f 0 | |||
| f 2 | |||
| a 5 4072 | |||
| f 4 | |||
| f 5 | |||
+ 16
- 0
traces/short1.rep
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,16 @@ | |||
| 20000 | |||
| 6 | |||
| 12 | |||
| 1 | |||
| a 0 2040 | |||
| a 1 2040 | |||
| f 1 | |||
| a 2 48 | |||
| a 3 4072 | |||
| f 3 | |||
| a 4 4072 | |||
| f 0 | |||
| f 2 | |||
| a 5 4072 | |||
| f 4 | |||
| f 5 | |||
+ 16
- 0
traces/short2-bal.rep
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,16 @@ | |||
| 20000 | |||
| 6 | |||
| 12 | |||
| 1 | |||
| a 0 2040 | |||
| a 1 4010 | |||
| a 2 48 | |||
| a 3 4072 | |||
| a 4 4072 | |||
| a 5 4072 | |||
| f 0 | |||
| f 1 | |||
| f 2 | |||
| f 3 | |||
| f 4 | |||
| f 5 | |||
+ 16
- 0
traces/short2.rep
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,16 @@ | |||
| 20000 | |||
| 6 | |||
| 12 | |||
| 1 | |||
| a 0 2040 | |||
| a 1 4010 | |||
| a 2 48 | |||
| a 3 4072 | |||
| a 4 4072 | |||
| a 5 4072 | |||
| f 0 | |||
| f 1 | |||
| f 2 | |||
| f 3 | |||
| f 4 | |||
| f 5 | |||
+ 211
- 0
实验报告.md
View File
| @ -0,0 +1,211 @@ | |||
| # 总体设计 | |||
| 使用了 Segregated Fits 算法来管理内存。 | |||
| 将空闲块按照大小分成不同的类,并将每个类的空闲块用链表连接起来。 | |||
| 每个空闲块都有一个 header 和一个 footer,与 Implicit list 算法相同。 | |||
| 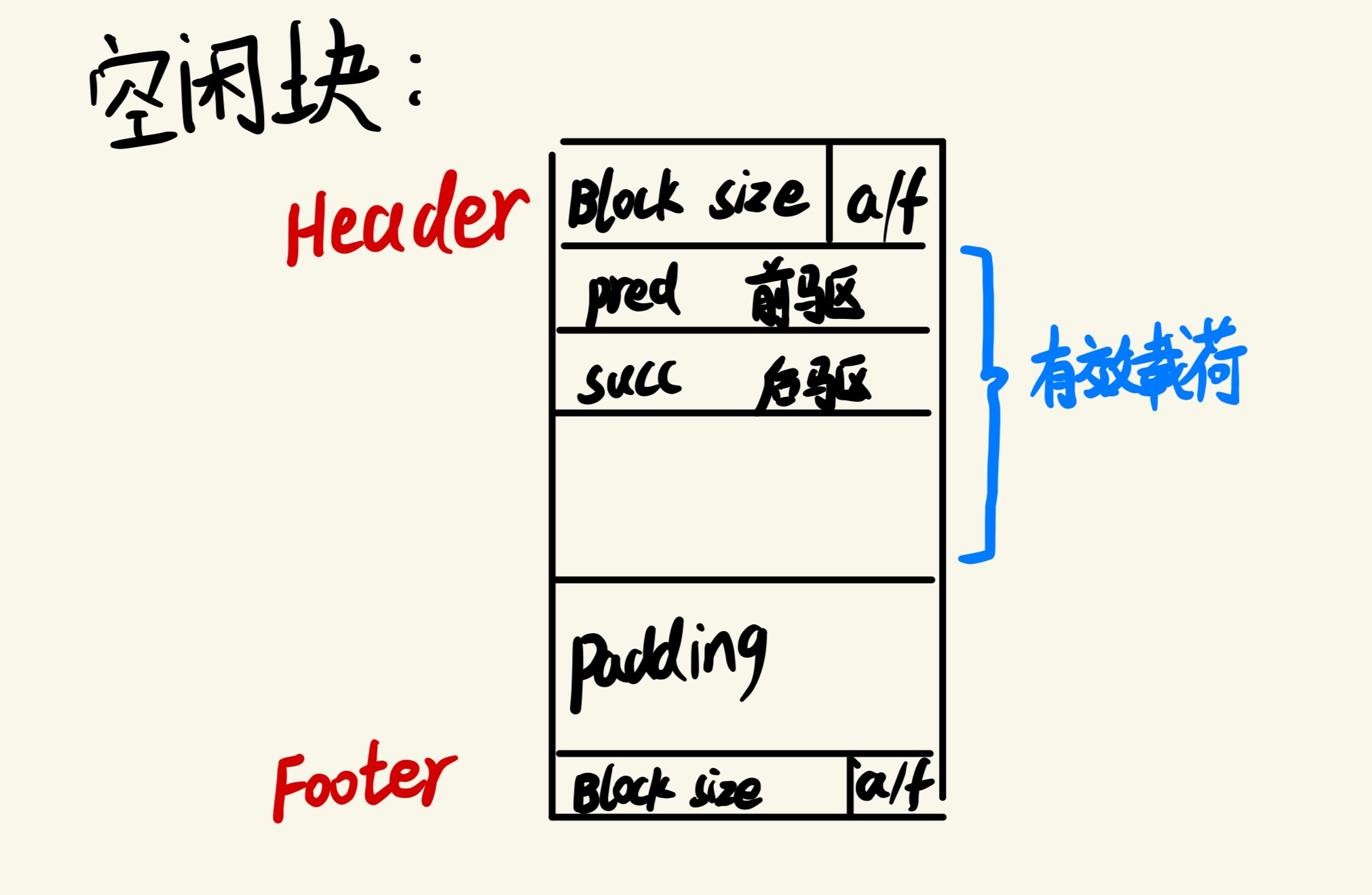 | |||
| 每个 free block 的第一个字保存指向 list 中下一个 free block 的指针,第二个字保存指向前一个 free block 的指针。 | |||
| 因此,每个 block 的最小值为 16 bytes,heap 地址的前 18 个字分别保存 18 个 list 的头指针,平衡了搜索时间和空间利用率. | |||
| 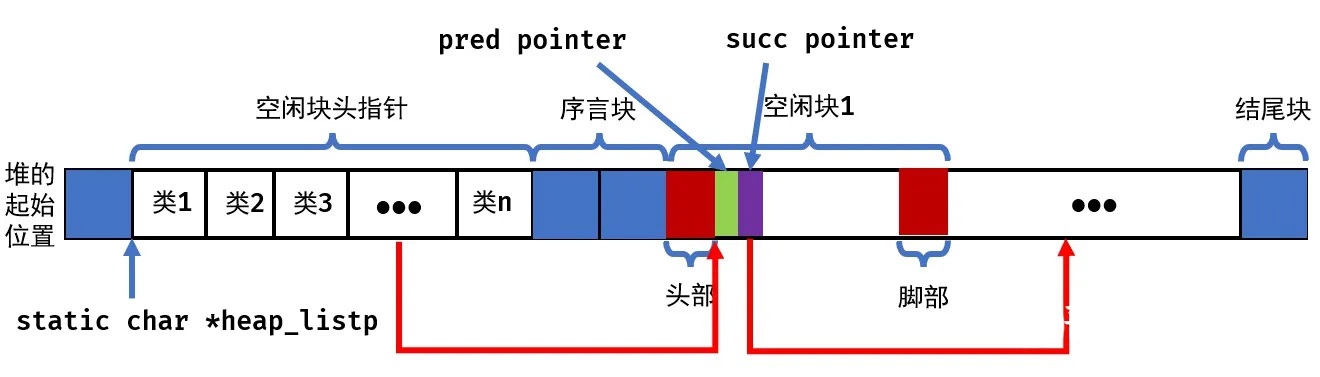 | |||
| ### 功能和算法 | |||
| - **空闲块链表**:将空闲块按照不同的大小类别分组管理,使用链表将相同大小的空闲块连接起来,方便查找合适大小的空闲块。 | |||
| - **合并相邻空闲块**:在释放内存块时,尝试合并相邻的空闲块,以便合理利用空间。 | |||
| - **扩展堆大小**:通过 `mem_sbrk` 来扩展堆的大小,以满足额外的内存需求。 | |||
| - **计算空闲块大小**:使用类似于分级的方式将不同大小的空闲块进行分组管理,便于快速查找合适大小的空闲块。 | |||
| ## 额外的函数设计 | |||
| ### extend_heap | |||
| 作用:扩展heap的大小 | |||
| 流程如下: | |||
| - 定义一个指针变量`bp`和一个大小变量`size`。 | |||
| - 根据参数`words`来计算需要分配的字节大小`size`。并且保证了`size`是一个偶数,以维持对齐。 | |||
| - 调用了一个函数`mem_sbrk`用于增加堆的大小。返回一个指向新分配的内存块的指针`bp`,如果分配失败,就返回-1。 | |||
| - 检查`bp`是否为-1,如果是,就返回`NULL`,表示扩展堆失败。 | |||
| - 调用函数`coalesce`,用于合并相邻的空闲内存块的函数,以减少内存碎片。并且返回一个指向合并后的内存块的指针。 | |||
| ### coalesce | |||
| 作用:合并free block | |||
| 根据前后相邻的内存块的分配状态,进行不同的操作 | |||
| 流程如下: | |||
| - 如果前后都分配了,那么不需要合并,直接返回原来的指针。 | |||
| - 如果前分配,后未分配,那么把后面的空闲块从空闲链表中删除,然后把当前块和后面的块合并成一个更大的块,更新它的头部和尾部的大小和分配位,然后返回当前块的指针。 | |||
| - 如果前未分配,后分配,那么把前面的空闲块从空闲链表中删除,然后把前面的块和当前的块合并成一个更大的块,更新它的头部和尾部的大小和分配位,然后返回前面的块的指针。 | |||
| - 如果前后都未分配,那么把前后的空闲块都从空闲链表中删除,然后把前后的块和当前的块合并成一个更大的块,更新它的头部和尾部的大小和分配位,然后返回前面的块的指针。 | |||
| 最后,把合并后的空闲块插入到空闲链表中,然后返回合并后的块的指针。 | |||
| ### getListOffset | |||
| 作用:得到大小为size的块应该在哪个list中 | |||
| 根据`size`的值,返回一个对应的列表的偏移量。列表的偏移量是一个整数,表示这个数据应该存储在哪个列表中 | |||
| 流程如下: | |||
| * 使用一系列的`if-else`语句,来判断`size`的范围。 | |||
| * 每个`if-else`语句都有一个常量`SIZE1`到`SIZE17`,表示不同的大小的阈值。如果`size`小于等于某个阈值,就返回相应的偏移量。 | |||
| ### insert_list | |||
| 作用:将free block插入到相应大小的free list中, 插入位置为表头 | |||
| 流程如下: | |||
| * 调用`getListOffset`函数,根据内存块的大小`size`,得到一个列表的偏移量`index`。 | |||
| * 使用宏定义的函数,如`GET_PTR`,`PUT_PTR`,`HDRP`等,来操作内存块的头部和指针域。 | |||
| * 如果`heap_listp + WSIZE * index`处的指针为空,表示这个列表还没有任何内存块,那么就将`bp`作为第一个内存块插入到这个列表中,并将它的前驱和后继指针都设为`NULL`。 | |||
| * 如果`heap_listp + WSIZE * index`处的指针不为空,表示这个列表已经有一些内存块,那么就将`bp`作为第一个内存块插入到这个列表的头部,并将它的后继指针指向原来的第一个内存块,同时将原来的第一个内存块的前驱指针指向`bp`。 | |||
| * 最后,将`heap_listp + WSIZE * index`处的指针更新为`bp`。 | |||
| ### delete_list | |||
| 作用:删除链表结点 | |||
| 流程如下: | |||
| 首先,获取结点的大小和位置的偏移量。然后,根据结点在链表中的位置,分为四种情况来处理: | |||
| - 如果结点的前后指针都是NULL,说明这个结点是链表中唯一的结点,那么就把heap_listp数组中对应的头尾指针都设为NULL,表示链表为空。 | |||
| - 如果结点的前指针是NULL,后指针不是NULL,说明这个结点是链表中最后一个结点,但不是唯一一个,那么就把结点的后指针所指向的结点的前指针设为NULL,表示这个结点已经不在链表中了。 | |||
| - 如果结点的前指针不是NULL,后指针是NULL,说明这个结点是链表中第一个结点,但不是唯一一个,那么就把`heap_listp`数组中对应的头指针设为结点的前指针,表示链表的头部移动了,然后把结点的前指针所指向的结点的后指针设为NULL,表示这个结点已经不在链表中了。 | |||
| - 如果结点的前后指针都不是NULL,说明这个结点是链表中的中间结点,那么就把结点的后指针所指向的结点的前指针设为结点的前指针,表示跳过了这个结点,然后把结点的前指针所指向的结点的后指针设为结点的后指针,表示跳过了这个结点。 | |||
| ### find_fit | |||
| 作用:寻找一个合适size的free list | |||
| 函数的具体逻辑如下: | |||
| - 调用一个函数`getListOffset`,根据`asize`的值来确定一个索引`index`,这个索引表示一个内存块的类别,也就是它的大小范围。 | |||
| - 进入一个循环,从`index`开始,一直到`17`为止 | |||
| - 在每次循环中,首先从一个全局变量`heap_listp`中获取一个指针`ptr`,这个指针指向当前类别的内存块链表的头部。 | |||
| - 进入另一个循环,沿着链表遍历所有的内存块,直到`ptr`为空为止。 | |||
| - 在每次遍历中,使用两个宏`HDRP`和`GET_SIZE`来获取当前内存块的头部和大小,然后判断是否满足`asize`的要求,如果是,就返回`ptr`作为结果。 | |||
| - 如果没有找到合适的内存块,就将`ptr`更新为下一个内存块的指针,这个指针是通过宏`GET_PTR`从当前内存块中获取的。 | |||
| - 如果遍历完当前类别的所有内存块,就将`index`加一,进入下一个类别的循环,直到找到合适的内存块或者遍历完所有的类别为止。 | |||
| - 如果最终没有找到合适的内存块,就返回`NULL`作为结果,表示失败。 | |||
| ### place | |||
| 作用:将一个空闲的内存块`bp`分割为两部分,一部分用于分配给用户,另一部分保持空闲 | |||
| 函数的具体逻辑如下: | |||
| - 调用函数`delete_list`,将`bp`从空闲链表中删除 | |||
| - 获取`bp`的当前大小`csize`,并判断是否可以将其分割为两个内存块,一个大小为`asize`,另一个大小为`csize - asize`。这里的条件是`csize - asize`必须大于等于`2 * DSIZE`,也就是最小的内存块大小。 | |||
| - 如果可以分割,就将`bp`的头部和尾部设置为`asize`和已分配的标志,然后将`bp`指向下一个内存块,将其头部和尾部设置为`csize - asize`和未分配的标志,最后将这个新的空闲内存块插入到空闲链表中,调用`insert_list`函数。 | |||
| - 如果不可以分割,就将`bp`的头部和尾部设置为`csize`和已分配的标志,不做其他操作。 | |||
| ## 四个主要函数实现过程 | |||
| ### mm_init | |||
| 1. **分配初始堆空间**: | |||
| - 调用 `mem_sbrk` 分配 `LISTS_NUM + 4` 个字(每个字是 4 字节),作为初始堆空间。 | |||
| - `LISTS_NUM` 是空闲块链表的数量。 | |||
| 2. **初始化空闲块链表**: | |||
| - 在初始化的堆空间中,初始化 `LISTS_NUM` 个空闲块链表头部,并将它们连接到堆的开头。 | |||
| - 每个链表头部是 4 字节的空间(因为用来存储指针),所以需要 `LISTS_NUM * WSIZE` 字节的空间。 | |||
| 3. **设置初始堆的结尾标志**: | |||
| - 设置堆的最后部分为结束标志,表示这是堆的结尾,没有更多可用空间。 | |||
| 4. **扩展堆空间**: | |||
| - 调用 `extend_heap` 函数,将堆的大小扩展为 `CHUNKSIZE` 字节。 | |||
| - `CHUNKSIZE` 是在没有足够空闲块的情况下,用来扩展堆空间的默认大小。 | |||
| ### mm_malloc | |||
| 1. **大小调整(Size Adjustment)**: | |||
| - 根据用户请求的大小,进行调整以满足内存对齐要求和额外的空间开销。在这个实现中,采用了最简单的方式:将请求的大小调整为双字大小的倍数,即 `asize = DSIZE * ((size + (DSIZE) + (DSIZE - 1)) / DSIZE)`。 | |||
| 2. **查找合适的空闲块(Find Fit)**: | |||
| - 在初始化的空闲块链表中查找一个大小合适的空闲块。 | |||
| - 调用 `find_fit` 函数,在空闲块链表中寻找第一个大小大于等于 `asize` 的空闲块。 | |||
| 3. **分配空闲块(Allocate Block)**: | |||
| - 如果找到了合适大小的空闲块,调用 `place` 函数来将其分配出去。 | |||
| - 如果没有找到合适的空闲块,则调用 `extend_heap` 来扩展堆空间,并在新的空间上分配内存块。 | |||
| 4. **返回分配的块地址(Return Allocated Block Address)**: | |||
| - 返回指向已分配内存块的指针。 | |||
| ### mm_free | |||
| 1. **标记内存块为可用状态**: | |||
| - 根据传入的指针 `ptr`,标记对应内存块的头部和尾部为未分配状态。 | |||
| - 这里使用 `PUT` 函数将头部和尾部的标志位设置为未分配状态。 | |||
| 2. **尝试合并相邻的空闲块**: | |||
| - 调用 `coalesce` 函数来尝试合并释放的块与相邻的空闲块。 | |||
| - `coalesce` 函数会检查前后相邻的块是否也是未分配的,如果是,则会合并这些块,以释放更多连续的空间。 | |||
| ### mm_realloc | |||
| 1. **处理零大小的请求**: | |||
| - 如果传入的大小为零,则直接释放先前分配的内存块,并返回 `NULL`。 | |||
| 2. **调整新内存块大小**: | |||
| - 根据传入的大小,重新计算新内存块的大小 `asize`,这个过程与 `mm_malloc` 中的大小调整类似。 | |||
| 3. **比较新旧块大小**: | |||
| - 检查新的大小是否等于旧的块大小,如果相等,则不需要进行任何操作,直接返回旧的块地址。 | |||
| 4. **缩小内存块**: | |||
| - 如果新的大小小于旧的块大小,尝试使用 `mm_malloc` 分配一个新块,并将旧块的内容复制到新块中。 | |||
| - 接着释放旧的块,并返回新分配的块地址。 | |||
| 5. **扩大内存块**: | |||
| - 如果新的大小大于旧的块大小,则分配一个新块。 | |||
| - 将旧块的内容复制到新块中,接着释放旧的块。 | |||
| - 返回新分配的块地址。 | |||
| ## 策略 | |||
| ### 放置策略 | |||
| 首次适配:在 `mm_malloc` 中,采用 `find_fit` 函数来在空闲块链表中寻找第一个合适大小的空闲块。这个函数会顺序查找链表,返回第一个大小满足需求的空闲块。 | |||
| ### 分割策略 | |||
| 立即分割:当找到的空闲块大小大于请求大小时,在 `place` 函数中会立即将其分割成两部分,一部分满足用户请求,剩余部分作为新的空闲块。 | |||
| ### 合并策略 | |||
| 基本合并策略:在 `coalesce`函数中实现了合并相邻的空闲块的逻辑。 | |||
| - 当释放一个块时,会检查其前后相邻的块是否也是未分配状态,如果是,则尝试合并这些块。 | |||
| - 根据前后相邻块的状态,有四种情况: | |||
| 1. 前后均已分配:不做任何合并。 | |||
| 2. 前分配,后未分配:合并当前块与后面的块。 | |||
| 3. 前未分配,后分配:合并前面的块与当前块。 | |||
| 4. 前后均未分配:合并前后两块与当前块 | |||
| ## 时间复杂度 | |||
| ### mm_malloc | |||
| - **时间复杂度**:O(n) | |||
| - **描述**:`mm_malloc` 函数中使用了首次适配策略,需要在空闲块链表中顺序查找第一个满足大小的空闲块。当链表中的空闲块数量增多时,查找所需的时间可能会线性增长。 | |||
| ### mm_free | |||
| - **时间复杂度**:O(1) | |||
| - **描述**:`mm_free` 函数内部主要涉及标记内存块为未分配状态,并尝试进行合并操作。这些操作的时间复杂度主要取决于标记和合并的步骤,而不会随着空闲块链表的大小增加而增加。 | |||
| ### mm_realloc | |||
| - **时间复杂度**:最坏情况下为 O(n) | |||
| - **描述**:`mm_realloc` 函数会在重新分配内存块时,根据新旧大小的比较来决定是缩小、扩大还是重新分配内存块。如果需要重新分配内存块,可能需要调用 `mm_malloc` 和 `mm_free` 函数,其中 `mm_malloc` 的时间复杂度是 O(n)。 | |||
