22 KiB
构建数据库项目报告
实验一:在LevelDB的Value中实现字段功能
1. 字段存储
-
字段结构: 使用
std::pair<std::string, std::string>表示字段名和字段值的关系,构成一个字段数组FieldArray,即std::vector<std::pair<std::string, std::string>>。 -
序列化和反序列化
:
- 序列化: 实现
SerializeValue函数,将字段数组序列化为字符串,以便存储到 LevelDB 的 value 中。 - 反序列化: 实现
ParseValue函数,从存储的字符串中解析出字段数组。
- 序列化: 实现
2. 数据存储与解析
- 存储数据时,使用
db->Put()方法将序列化后的字符串作为 value 存储到 LevelDB 中。 - 在测试函数
TEST(TestSchema, Basic)中演示如何创建一个包含多个字段的 value,进行序列化和存储,并随后读取和反序列化。
3. 查询功能
- 字段查询: 实现函数
FindKeysByField,能够根据指定的字段名和字段值查找所有对应的 key。由于一个字段值可能对应多个 key,因此返回类型为std::vector<std::string>。
字段存储
思路:
字段数组 FieldArray 被定义为 std::vector<std::pair<std::string, std::string>> 类型,每个字段包含一个键值对。为了方便存储,需要将字段数组序列化为字符串格式 key:value,key:value,...。
在序列化过程中,字段 key 和 value 通过 ":" 拼接,字段之间用 "," 分隔,最后一个字段不加分隔符。
代码解释:
- 使用
resString存储最终的序列化结果。 - 遍历
FieldArray,将每对键值对拼接成key:value格式并追加到resString中。 - 为避免在最后一个字段后添加逗号,判断当前是否为最后一个字段。
这种序列化方式确保了数据的紧凑性,适合高效存储。
void MyLevelDB::SerializeValue(const FieldArray& fields,
std::string& resString) {
resString.clear();
for (int i = 0; i < fields.size(); i++) {
const std::string& key = fields[i].first;
const std::string& value = fields[i].second;
resString += key + ":" +value;
if (i != fields.size() - 1) {
resString += ",";
}
}
}
反序列化为字段数组
思路:
反序列化过程需要将序列化的字符串拆解为键值对,并存储到字段数组 FieldArray 中。具体操作包括:
- 按
","分割字符串,得到key:value格式的子字符串。 - 对每个子字符串,按
":"分割,提取key和value。 - 将解析出的
key和value存入字段数组。
代码解释:
- 使用
std::stringstream拆分字符串,第一层按","分割,第二层按":"分割。 - 如果分割成功且
key和value非空,将结果存入FieldArray。 - 对于解析失败的片段,输出错误信息,便于调试和排查异常数据。
该步骤将存储的数据还原为结构化的字段数组,便于后续的字段查找和处理。
void MyLevelDB::ParseValue(const std::string& value_str,
FieldArray& resFieldArray) {
std::stringstream ss(value_str);
std::string segment;
// 按逗号分割字符串
while (std::getline(ss, segment, ',')) {
std::string key;
std::string value;
std::stringstream kv(segment);
if (std::getline(kv, key, ':') && std::getline(kv, value, ':')) {
if (!key.empty() && !value.empty()) {
resFieldArray.push_back(std::make_pair(key, value));
// std::cout << ((resFieldArray.back()).first).data() << std::endl;
} else {
std::cerr << "Invalid key-value pair: " << segment << std::endl;
}
} else {
std::cerr << "Failed to parse segment: " << segment << std::endl;
}
}
}
字段查找
思路:
为了实现字段查找功能,需要遍历数据库中的所有数据,逐条反序列化后判断是否包含目标字段。如果匹配到查询的字段,则将对应的 key 存入结果集 keys 中。
代码解释:
- 调用
NewIterator遍历数据库的每条记录。 - 对每条记录,使用
ParseValue将字符串反序列化为字段数组。 - 遍历字段数组,判断是否存在与目标字段匹配的键值对。
- 如果匹配成功,将当前记录的
key提取并存入结果集中。
通过这种逐条解析和匹配的方式,可以实现对字段的灵活查询,支持模糊匹配和多条件过滤等扩展功能。
Status MyLevelDB::FindKeysByField(const ReadOptions& options, const Field field,
std::vector<std::string>* keys) {
auto it = _fields_db->NewIterator(options);
it->SeekToFirst();
keys->clear();
while (it->Valid()) {
auto val = it->value();
FieldArray arr;
auto str_val = std::string(val.data(), val.size());
ParseValue(str_val, arr);
for (auto pr : arr) {
if (pr.first == field.first && pr.second == field.second) {
Slice key = it->key();
keys->push_back(std::string(key.data(), key.size()));
break;
}
}
it->Next();
}
delete it;
return Status::OK();
}
字段插入并创建索引
思路: 为了支持快速查询,需要在插入数据时为部分字段创建索引。索引创建的核心步骤包括:
- 对字段数组进行序列化并使用WriteBatch进行原子存储。
- 遍历字段数组,检查是否需要为字段创建索引,使用互斥锁保护并发访问。
- 对需要创建索引的字段,将其值与主键
key组合存入批处理中,并跟踪所有变更以支持回滚。
代码解释:
- 调用
SerializeValue将字段数组序列化,通过WriteBatch原子写入_fields_db数据库。 - 使用互斥锁保护索引列表,遍历字段数组与
index_list_匹配需要创建索引的字段。 - 为匹配的字段构造索引键
field_value:key,加入批处理并记录变更,失败时可回滚所有操作。
Status MyLevelDB::PutWithFields(const WriteOptions& options,
const std::string& key,
const FieldArray& fields) {
std::string value;
SerializeValue(fields, value);
auto slice_key = Slice(key.c_str());
auto slice_value = Slice(value.c_str());
WriteBatch batch;
Status s = _fields_db->Put(options, slice_key, slice_value);
if (!s.ok()) {
return s;
}
std::vector<std::pair<std::string, std::string>> changes;
changes.push_back({key, value});
// 更新索引
std::unordered_map<int, int> match;
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> l(mutex_);
for (int i = 0; i < fields.size(); i++) {
for (size_t idx = 0; idx < index_list_.size(); idx++) {
const auto& i_name = index_list_[idx];
if (fields[i].first == i_name) {
match[i] = idx; // 找到匹配的字段
break;
}
}
}
for (auto item : match) {
std::string composed_key;
composed_key += fields[item.first].second + ":" + key;
batch.Put(Slice(composed_key.c_str()), Slice());
changes.push_back({composed_key, ""});
}
// 提交批处理
s = _fields_db->Write(options, &batch);
if (!s.ok()) {
// 如果批处理写入失败,回滚之前的操作
std::cerr << "Failed to commit batch, rolling back." << std::endl;
for (const auto& change : changes) {
_fields_db->Delete(WriteOptions(),
Slice(change.first));
}
return s;
}
return Status::OK();
}
实验二:二级索引
创建索引
思路:
CreateIndexOnField函数用于为指定字段field_name创建索引。索引的核心在于维护一个字段值到主键的映射关系,索引字段的存储格式为:value:key:null,其中value是字段值,key是主键。
在实现中,index_list_用于记录已创建索引的字段名,而index_db是索引数据库的集合,专门存储各字段的索引数据。
实现步骤:
- 检查索引是否已存在:
遍历
index_list_,判断指定字段是否已存在索引。如果存在,则返回错误状态,避免重复创建。 - 创建索引数据库:
- 将字段名加入
index_list_ - 使用批处理创建新的数据库实例
- 索引数据库以
_db_name + "_index_" + field_name命名
- 将字段名加入
- 提交与错误处理:
- 使用WriteBatch确保原子操作
- 记录所有变更用于可能的回滚
- 如果提交失败,执行完整的回滚操作
代码逻辑解释:
- 使用
index_list_和index_db实现索引的动态管理。 - 采用WriteBatch批处理确保索引创建的原子性。
- 通过变更跟踪(changes vector)支持失败时的回滚操作。
Status MyLevelDB::CreateIndexOnField(const std::string& field_name) {
// 检查索引是否已经存在
for (const auto& field : this->index_list_) {
if (field == field_name) {
return Status::InvalidArgument(field_name,
"Index already exists for this field");
}
}
// 将新的索引字段添加到索引列表
index_list_.push_back(field_name);
Options op = _op;
DB* field_db;
op.index_mode = true;
WriteBatch batch; // 创建批处理操作
Status status = DB::Open(op, _db_name + "_index_" + field_name, &field_db);
if (!status.ok()) {
std::cerr << "Failed to open index DB: " << status.ToString() << std::endl;
return status;
}
index_db.push_back(field_db); // 将新创建的索引数据库添加到列表
// 记录所有变更
std::vector<std::string> changes;
changes.push_back("index_" + field_name); // 记录索引字段的变更
// 在批处理中添加索引数据
batch.Put(Slice(("index_" + field_name).c_str()),
Slice()); // 添加索引记录到批处理中
// 提交批处理
status = _fields_db->Write(WriteOptions(), &batch);
if (!status.ok()) {
std::cerr << "Failed to commit index: " << status.ToString() << std::endl;
// 执行回滚
for (const auto& change : changes) {
_fields_db->Delete(WriteOptions(),
Slice(change.c_str()));
}
return status;
}
return Status::OK();
删除索引
思路:
DeleteIndex函数用于从系统中删除指定字段的索引。删除操作的核心是从index_list_和index_db中移除相关信息,同时通过批处理保证操作的原子性和可回滚性。
实现步骤:
- 检查索引是否存在:
使用
std::find在index_list_中查找指定字段。如果未找到,返回NotFound错误状态。 - 删除索引信息:
- 从
index_list_中移除字段名 - 使用WriteBatch创建原子删除操作
- 记录删除操作用于可能的回滚
- 从
- 提交与回滚处理:
- 提交批处理操作
- 如果提交失败,执行回滚操作恢复索引
- 确保操作的原子性和数据一致性
代码逻辑解释:
- 使用
std::find高效查找索引字段位置。 - 采用WriteBatch确保删除操作的原子性。
- 通过changes vector跟踪删除操作,支持失败时的完整回滚。
- 完整的错误处理确保即使在失败情况下也能维持系统一致性。
Status MyLevelDB::DeleteIndex(std::string& field_name) {
// 查找索引字段
auto it = std::find(index_list_.begin(), index_list_.end(), field_name);
if (it == index_list_.end()) {
return Status::NotFound("Index not found for this field");
}
WriteBatch batch;
// 删除索引字段
index_list_.erase(it);
batch.Delete(Slice(("index_" + field_name).c_str())); // 删除索引字段记录
// 记录已删除的索引
std::vector<std::string> changes;
changes.push_back("index_" + field_name);
// 提交批处理
Status s = _fields_db->Write(WriteOptions(), &batch);
if (!s.ok()) {
std::cerr << "Failed to delete index: " << s.ToString() << std::endl;
// 执行回滚
for (const auto& change : changes) {
batch.Put(Slice(change.c_str()), Slice()); // 恢复索引记录
}
_fields_db->Write(WriteOptions(), &batch); // 再次提交恢复的批处理
return s; // 返回失败,确保不会提交任何变化
}
return Status::OK();
}
基于二级索引的查找
思路:
QueryByIndex 函数利用二级索引实现高效的字段值查询。通过索引数据库,可以快速定位字段值对应的主键,避免全表扫描。
实现步骤:
- 定位索引数据库:
遍历
index_list_,查找指定字段名对应的索引数据库。如果未找到,触发异常。 - 遍历索引数据:
使用迭代器逐条读取索引数据库中的数据,按
value:key格式解析每条记录,提取字段值和主键。 - 匹配字段值: 如果当前字段值与查询条件匹配,则将对应的主键存入结果集中。
- 返回查询结果: 查询完成后,返回所有匹配的主键,用于后续操作。
代码逻辑解释:
- 索引数据库存储格式为
value:key:null,通过解析每条记录的键值对,实现字段值到主键的映射。 - 遍历过程中,使用条件判断过滤非目标记录,确保查询结果的准确性。
- 删除迭代器以释放资源,避免内存泄漏。
通过二级索引的设计,查询复杂度由全表扫描降低为按索引查找,显著提升了查询效率。
void MyLevelDB::QueryByIndex(const ReadOptions& options, Field& field,
std::vector<std::string>& keys) {
int i = 0;
for (; i < index_list_.size(); i++) {
if (index_list_[i] == field.first) {
break;
}
}
assert(i != index_list_.size());
auto it = index_db[i]->NewIterator(options);
it->SeekToFirst();
while (it->Valid()) {
auto val = it->key();
auto str_val = std::string(val.data(), val.size());
std::string key;
std::string value;
std::stringstream kv(str_val);
std::getline(kv, key, ':');
std::getline(kv, value, ':');
if (key == field.second) {
keys.push_back(value);
}
it->Next();
}
delete it;
}
实验三:实现Benchmark,测试性能
功能测试:
Options op;
op.create_if_missing = true;
MyLevelDB db(op, "testMyDB");
//序列化测试
std::string res1;
FieldArray fields1 = {
{"name", "Customer#000000001"}, {"address", "abc"}, {"phone", "def"}};
db.SerializeValue(fields1,res1);
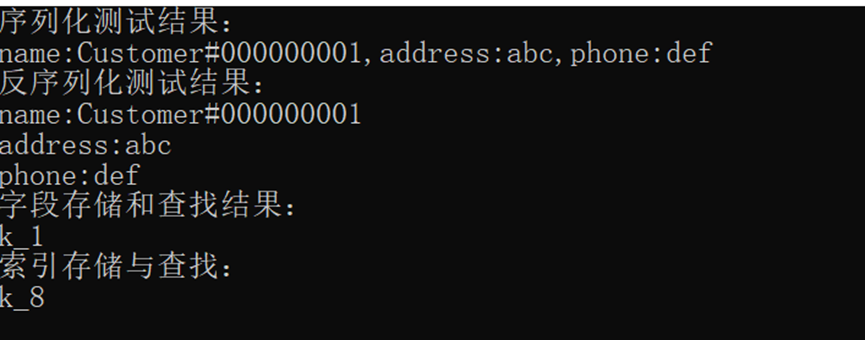
std::cout << "序列化测试结果:" << std::endl << res1 << std::endl;
//反序列化测试
FieldArray fields2;
db.ParseValue(res1,fields2);
std::cout << "反序列化测试结果:" << std::endl ;
for (int i = 0; i < fields2.size(); i++) {
std::cout << fields2[i].first << ":" << fields2[i].second << std::endl;
}
//字段存储
std::cout << "字段存储和查找结果:" << std::endl;
std::string key2 = "k_1";
std::string key3 = "k_2";
std::string key4 = "k_3";
FieldArray field2 = {{"name", "Customer#000000001"},
{"address", "IVhzIApeRb"},
{"phone", "25-989-741-2988"}};
FieldArray field3 = {
{"name", "Customer#000000001"}, {"address", "abc"}, {"phone", "def"}};
FieldArray field4 = {
{"name", "Customer#000000001"}, {"address", "abc"}, {"phone", "def"}};
db.PutWithFields(WriteOptions(), key2, field2);
db.PutWithFields(WriteOptions(), key3, field3);
db.PutWithFields(WriteOptions(), key4, field4);
//字段查找
FieldArray value_ret;
std::vector<std::string> v;
db.FindKeysByField(ReadOptions(), field2[1], &v);
for (auto s : v) std::cout << s << "\n";
//创建索引
WriteOptions writeOptions;
ReadOptions readOptions;
Options options;
options.create_if_missing = true;
auto db1 = new MyLevelDB(options, "testdb2");
db1->CreateIndexOnField("address");
std::string key8 = "k_8";
std::string key9 = "k_9";
FieldArray fields8 = {
{"name", "Customer#000000001"}, {"address", "abc"}, {"phone", "def"}};
FieldArray fields9 = {{"name", "Customer#000000001"},
{"address", "IVhzIApeRb"},
{"phone", "25-989-741-2988"}};
FieldArray fields10 = {
{"name", "Customer#000000001"}, {"address", "abc"}, {"phone", "def"}};
FieldArray fields11 = {
{"name", "Customer#000000001"}, {"address", "abc"}, {"phone", "def"}};
FieldArray fields12 = {
{"name", "Customer#000000001"}, {"address", "abc"}, {"phone", "def"}};
Field query = {"address", "abc"};
db1->PutWithFields(WriteOptions(), key8, fields8);
db1->PutWithFields(WriteOptions(), key9, fields9);
std::cout << "索引存储与查找:" << std::endl;
std::vector<std::string> keys;
db1->QueryByIndex(readOptions, query,keys);
for (int i = 0; i < keys.size();i++) {
std::cout << keys[i] << std::endl;
}
测试结果
性能测试
这里主要进行了吞吐量测试和延迟测试
1. 吞吐量测试
- 写入操作:
- 初始化数据库并创建多个键(
k_0,k_1, ...)及其对应的字段。 - 记录开始时间,执行指定数量的写入操作,并计算所用时间,最后输出每秒的操作数(OPS)。
- 初始化数据库并创建多个键(
- 读取操作:
- 记录开始时间,进行大量的读取操作(每个键读取100次),计算所用时间并输出每秒的操作数。
- 字段查找:
- 记录开始时间,查找指定字段的键并计算所用时间,输出每秒的操作数。
2. 延迟测试
- 写入操作:
- 初始化数据库并执行大量的写入操作,同时记录每次写入的延迟,并计算总延迟,最后输出每个操作的平均延迟。
- 读取操作:
- 类似于写入,记录每次读取的延迟并输出每个操作的平均延迟。
- 字段查找:
- 进行字段查找操作,记录延迟并输出每个操作的平均延迟。
// 吞吐量
void TestThroughput(int num_operations) {
WriteOptions writeOptions;
ReadOptions readOptions;
Options options;
options.create_if_missing = true;
auto db1 = new MyLevelDB(options, "testThroughput");
std::string key = "k_";
FieldArray fields = {{"name", "Customer#000000001"},
{"address", "IVhzIApeRb"},
{"phone", "25-989-741-2988"}};
//写
auto start_time1 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
for (int i = 0; i < num_operations; ++i) {
db1->PutWithFields(WriteOptions(), key + to_string(i), fields);
}
auto end_time1 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto duration1 =
chrono::duration_cast<chrono::milliseconds>(end_time1 - start_time1)
.count();
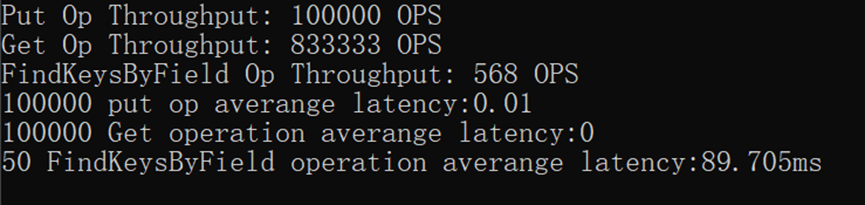
cout << "Put Op Throughput: " << num_operations * 1000 / duration1 << " OPS" << endl;
//读
string str;
auto start_time2 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
for (int i = 0; i < num_operations*100; ++i) {
db1->Get(ReadOptions(), key, &str);
}
auto end_time2 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto duration2 =
chrono::duration_cast<chrono::milliseconds>(end_time2 - start_time2)
.count();
//cout << duration2 << endl;
cout << "Get Op Throughput: " << num_operations*100 * 1000 / duration2 << " OPS"
<< endl;
//字段查找
std::vector<std::string> keys;
auto start_time3 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
for (int i = 0; i < num_operations; ++i) {
db1->FindKeysByField(ReadOptions(), fields[0],&keys);
}
auto end_time3 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto duration3 =
chrono::duration_cast<chrono::milliseconds>(end_time3 - start_time3)
.count();
cout << "FindKeysByField Op Throughput: " << num_operations * 1000 / duration3 << " OPS"
<< endl;
}
// 延迟
void TestLatency(int num_operations) {
Options options;
options.create_if_missing = true;
auto db = new MyLevelDB(options, "testLatency");
std::string key = "k_";
FieldArray fields = {{"name", "Customer#000000001"},
{"address", "IVhzIApeRb"},
{"phone", "25-989-741-2988"}};
//Put
int64_t latency1 = 0;
int64_t tollatency = 0;
auto end_time1 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto last_time1 = end_time1;
for (int i = 0; i < num_operations*100; ++i) {
// Operations
db->PutWithFields(WriteOptions(), key + to_string(i), fields);
end_time1 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
latency1 = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end_time1 -
last_time1)
.count();
last_time1 = end_time1;
tollatency += latency1;
}
std::cout << num_operations*100<<" put op averange latency:" << (double)tollatency / num_operations<< std::endl;
//Get
int64_t latency2 = 0;
tollatency = 0;
auto end_time2 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto last_time2 = end_time2;
std::string str;
for (int i = 0; i < num_operations*100; ++i) {
// Operations
db->Get(ReadOptions(), key + to_string(i),&str );
end_time2 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
latency2 = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end_time2 -
last_time2)
.count();
last_time2 = end_time2;
tollatency += latency2;
}
std::cout << num_operations*100
<< " Get operation averange latency:" << (double)tollatency / num_operations
<< std::endl;
//FindKeysByField
int64_t latency3 = 0;
tollatency = 0;
auto end_time3 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto last_time3 = end_time3;
std::vector<std::string> keys;
for (int i = 0; i < 50; ++i) {
// Operations
db->FindKeysByField(ReadOptions(), fields[0], &keys);
end_time3 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
latency3 = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end_time3 -
last_time3)
.count();
last_time3 = end_time3;
tollatency += latency3;
}
std::cout << num_operations
<< " FindKeysByField operation averange latency:" << tollatency / num_operations
<< std::endl;
}
实验中遇到的问题
在反序列化为字符数组时,反序列化后的字符数组,除最后一个字段外全部乱码。经过调试排查,是因为将字符串反序列化后的字段转换成Slice类型时,每次访问的地址都是同一个地址,因此后边的数据会覆盖前边的数据,导致乱码。出函数后,该内存地址被释放,但是数组中存储的数据还是指向该内存地址,导致程序出现段错误。
解决方法:在序列化和反序列化时,不将字段从string类型转换成Slice类型,在putwhitefield进行字段存储时在进行转换。