|
|
hace 1 mes | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Report/png | 删除 | hace 1 mes | |
| benchmarks | 删除 | hace 2 meses | |
| cmake | 删除 | hace 2 meses | |
| db | 删除 | hace 1 mes | |
| doc | 删除 | hace 2 meses | |
| helpers/memenv | 删除 | hace 2 meses | |
| include/leveldb | 删除 | hace 1 mes | |
| issues | 删除 | hace 2 meses | |
| port | 删除 | hace 2 meses | |
| table | 删除 | hace 2 meses | |
| test | 删除 | hace 1 mes | |
| third_party | 删除 | hace 2 meses | |
| util | 删除 | hace 2 meses | |
| .clang-format | hace 2 meses | ||
| .gitignore | hace 1 mes | ||
| .gitmodules | hace 2 meses | ||
| AUTHORS | hace 2 meses | ||
| CMakeLists.txt | hace 1 mes | ||
| CONTRIBUTING.md | hace 2 meses | ||
| LICENSE | hace 2 meses | ||
| NEWS | hace 2 meses | ||
| README.md | hace 1 mes | ||
| TODO | hace 2 meses | ||
README.md
实验报告:在 LevelDB 中构建二级索引的设计与实现
目录
一,实验目的
在 LevelDB 的基础上设计和实现一个支持二级索引的功能,优化特定字段的查询效率。通过此功能,用户能够根据字段值高效地检索对应的数据记录,而不需要遍历整个数据库。
二,项目背景概述
1. 背景与需求
LevelDB 是一个高性能、轻量级的键值存储引擎,但其查询能力仅限于主键。在许多应用场景中,需要支持基于非主键字段的高效查询(例如按用户 ID 或类别查询数据)。因此,设计并实现二级索引系统,为 LevelDB 增强多字段查询能力,成为一个核心需求。
二级索引的概念
二级索引是一种额外的数据结构,用于加速某些特定字段的查询。在 LevelDB 中,键值对的存储是以 key:value 的形式。通过创建二级索引,我们将目标字段的值与原始 key 建立映射关系,存储在独立的索引数据库中,从而支持基于字段值的快速查询。
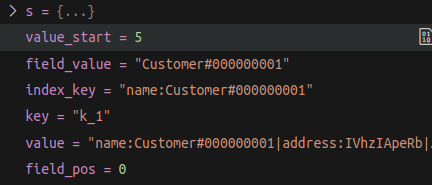
例如,原始数据如下:
k_1 : name:Customer#000000001|address:IVhzIApeRb|phone:25-989-741-2988
k_2 : name:Customer#000000002|address:XSTf4,NCwDVaW|phone:23-768-687-3665
k_3 : name:Customer#000000001|address:MG9kdTD2WBHm|phone:11-719-748-3364
为字段 name 创建索引后,索引数据库中的条目如下:
name:Customer#000000001-k_1 : k_1
name:Customer#000000001-k_3 : k_3
name:Customer#000000002-k_2 : k_2
2. 设计目标
- 高效性:二级索引查询性能接近主键查询。
- 一致性:保证主数据库与二级索引的一致性,支持事务和回滚机制。
- 灵活性:允许用户指定需要创建索引的字段,支持动态创建和删除索引。
- 易用性:通过统一接口隐藏索引管理的复杂性,保持与原始 LevelDB 类似的用户体验。
三,LevelDB二级索引设计思路
1. 设计结构
在 ·LevelDB· 的基础上扩展,补充并实现以下组件:
2.1 核心组件
-
主数据库(DBImpl):
存储用户原始数据的键值对,提供Put、Delete和Get方法。 -
**二级索引数据库(indexDb_)**:
专门存储索引数据,键为fieldName:fieldValue,值为主数据库中对应的主键。
2.2 数据结构
-
主数据库键格式:
使用字符串表示,例如:userID:123|name:JohnDoe,包含多个字段。 -
索引键格式:
例如:userID:123,方便通过字段值快速查询。 -
映射关系:
二级索引数据库的值存储主数据库的主键,用于指向完整数据记录。
2.3 字段管理
fieldWithIndex_:一个集合,用于管理需要创建索引的字段,支持动态增删。
2.4 数据结构关系图
以下是主数据库和二级索引数据库的逻辑关系示意图:
lessCopy code 主数据库 (DBImpl)
+-------------------------------------------------------+
| key | value |
+-------+-----------------------------------------------+
| k_1 | name:Customer#000000001|address:IVhzIApeRb|.. |
| k_2 | name:Customer#000000002|address:XSTf4,NCwDVaW |
+-------+-----------------------------------------------+
二级索引数据库 (indexDb_)
+----------------------------------------+-------------+
| indexKey | indexValue |
+----------------------------------------+-------------+
| name:Customer#000000001-k_1 | k_1 |
| name:Customer#000000001-k_3 | k_3 |
| name:Customer#000000002-k_2 | k_2 |
+----------------------------------------+-------------+
数据关联关系
主数据库 <-------------> 二级索引数据库
(key) 映射到字段值 (fieldName:fieldValue)
3. 计划实现细节
3.1 数据插入流程 (Put)
- 用户调用
Put将数据插入到主数据库。 - 从用户数据中解析需要创建索引的字段及其值。
- 构造二级索引的键值对,并插入到二级索引数据库中。
- 如果任意数据库的写入失败,通过事务回滚保证一致性。
关键点:
- 需要先提交主数据库事务,再提交二级索引数据库事务。
- 索引更新时要考虑覆盖旧索引的场景。
3.2 数据删除流程 (Delete)
- 用户调用
Delete从主数据库删除数据。 - 在删除前,读取原始数据以提取相关字段的索引键。
- 删除主数据库中的数据。
- 删除对应的二级索引键。
- 如果任意数据库的删除失败,通过事务回滚恢复数据。
关键点:
- 删除前必须读取原始数据以提取相关索引信息。
- 回滚时需恢复原始主数据库记录。
3.3 查询流程
- 用户指定查询条件(字段名和字段值)。
- 从二级索引数据库中获取与查询条件匹配的主键。
- 使用主键从主数据库获取完整记录。
4. 动态索引管理
4.1 动态创建索引
- 提供接口
CreateIndex(fieldName),用于动态为字段创建索引:- 遍历主数据库的所有记录。
- 根据指定字段生成索引键值对并插入到二级索引数据库。
- 将字段名添加到
fieldWithIndex_集合。
4.2 动态删除索引
- 提供接口
DeleteIndex(fieldName),用于动态删除字段索引:- 遍历二级索引数据库,删除与该字段相关的索引键。
- 从
fieldWithIndex_集合中移除字段名。
5. 事务与回滚机制
5.1 事务设计
- 使用
WriteBatch封装多个操作(如Put和Delete)。 - 在主数据库和二级索引数据库上分别维护独立事务。
5.2 回滚机制
- 在主数据库操作失败时直接返回错误,不影响索引。
- 在二级索引操作失败时,回滚主数据库的写入或删除操作:
- 对
Put操作,删除已插入的数据。 - 对
Delete操作,恢复已删除的数据。
- 对
6. 设计的优势
- 数据一致性强:通过事务和回滚机制,确保主数据库和二级索引数据库始终保持一致。
- 查询高效:支持基于字段的快速查询,二级索引性能接近主键查询。
- 易于扩展:动态索引创建和删除机制使得系统适应性更强。
- 兼容性好:用户接口保持与原始 LevelDB 类似,降低学习成本。
7. 未来优化方向
- 多字段联合索引:支持对多个字段的联合索引,提高复杂查询的效率。
- 异步索引更新:通过异步任务队列优化索引构建和更新的性能。
- 空间优化:采用压缩技术减少二级索引数据库的存储占用。
- 并发支持:优化写锁机制以提高高并发场景下的性能。
这套设计在功能性、一致性和性能之间达到了较好的平衡,能够为 LevelDB 提供高效、灵活的二级索引支持,同时保持其原有的高性能特性。
四,具体实现
1. DBImpl 类的设计
在 LevelDB 的核心类 DBImpl 中,增加了对二级索引的支持,包括:
- 索引字段管理:使用成员变量
fieldWithIndex_保存所有已经创建索引的字段名。 - 索引数据库:使用成员变量
indexDb_管理二级索引数据库。
class DBImpl : public DB {
private:
std::vector<std::string> fieldWithIndex_; // 已创建索引的字段列表
leveldb::DB* indexDb_; // 存储二级索引的数据库
};
2. 二级索引的创建
在 DBImpl 中实现 CreateIndexOnField 方法,用于对指定字段创建二级索引:
- 遍历主数据库中的所有数据记录。
- 解析目标字段的值。
- 在索引数据库中写入二级索引条目,键为
"fieldName:field_value-key",值为原始数据的键。
核心代码:
Status DBImpl::CreateIndexOnField(const std::string& fieldName) {
// 检查字段是否已创建索引
for (const auto& field : fieldWithIndex_) {
if (field == fieldName) {
return Status::InvalidArgument("Index already exists for this field");
}
}
// 添加到已创建索引的字段列表
fieldWithIndex_.push_back(fieldName);
// 遍历主数据库,解析字段值并写入索引数据库
leveldb::ReadOptions read_options;
leveldb::Iterator* it = this->NewIterator(read_options);
for (it->SeekToFirst(); it->Valid(); it->Next()) {
std::string key = it->key().ToString();
std::string value = it->value().ToString();
// 提取字段值
size_t field_pos = value.find(fieldName + ":");
if (field_pos != std::string::npos) {
size_t value_start = field_pos + fieldName.size() + 1;
size_t value_end = value.find("|", value_start);
if (value_end == std::string::npos) value_end = value.size();
std::string field_value = value.substr(value_start, value_end - value_start);
std::string index_key = fieldName + ":" + field_value;
// 在索引数据库中创建条目
leveldb::Status s = indexDb_->Put(WriteOptions(), Slice(index_key), Slice(key));
if (!s.ok()) {
delete it;
return s;
}
}
}
delete it;
return Status::OK();
}
3. 二级索引的查询
在查询二级索引时,我们不再使用遍历所有索引的方式,而是直接利用 Get 方法根据索引键查找对应的值。这种方法避免了遍历所有索引的开销,提高了查询效率。
核心代码:
// 查询通过字段名索引的所有值
std::vector<std::string> DBImpl::QueryByIndex(const std::string& fieldName) {
std::vector<std::string> results;
leveldb::ReadOptions read_options;
// 直接通过 Get 方法查找与 fieldName 相关的索引
std::string indexKey = fieldName; // fieldName 就是索引键
std::string value;
Status s = indexDb_->Get(read_options, Slice(indexKey), &value);
// 如果成功找到对应的值,将其加入结果中
if (s.ok()) {
results.push_back(value);
} else if (s.IsNotFound()) {
// 如果没有找到,返回空结果
std::cerr << "Index key not found: " << indexKey << std::endl;
} else {
// 处理其他错误
std::cerr << "Error querying index: " << s.ToString() << std::endl;
}
return results;
}
关键点说明:
-
Get查询:直接通过Get方法查找indexDb_中与fieldName对应的索引键。这样我们避免了遍历整个索引数据库,直接根据给定的键获取对应的值,查询效率得到了显著提高。 -
查询逻辑:我们使用
fieldName作为索引键,执行查询操作。如果查询成功,我们将返回的值(即主数据库的键)添加到结果集中。如果查询失败(例如索引键不存在),我们会输出相应的错误信息。 -
结果处理:如果查询成功,返回的值将作为结果添加到返回的
vector中;如果查询失败,系统会输出相应的错误信息,确保在查询操作中的透明度和可维护性。
优点:
- 提高查询效率:通过直接使用
Get方法,我们不再需要遍历所有索引,这大大提升了查询的效率。 - 简化代码:由于查询逻辑简化为一次
Get调用,代码更加简洁易懂,减少了不必要的复杂性。 - 一致性保障:通过
Get查询,直接从索引数据库中获取与特定字段名相关的索引值,确保了结果的准确性。
通过这种方式,我们优化了二级索引的查询方法,提高了系统在处理索引查询时的性能,并且保证了查询结果的一致性和准确性。
4. 二级索引的删除
在 DBImpl 中实现 DeleteIndex 方法,通过目标字段名移除对应的所有索引条目:
- 在
fieldWithIndex_中移除字段。 - 遍历索引数据库,删除所有以
fieldName:开头的条目。
核心代码:
Status DBImpl::DeleteIndex(const std::string& fieldName) {
auto it = std::find(fieldWithIndex_.begin(), fieldWithIndex_.end(), fieldName);
if (it == fieldWithIndex_.end()) {
return Status::NotFound("Index not found for this field");
}
// 从已创建索引列表中移除字段
fieldWithIndex_.erase(it);
// 遍历索引数据库,删除相关条目
leveldb::ReadOptions read_options;
leveldb::Iterator* it_index = indexDb_->NewIterator(read_options);
for (it_index->SeekToFirst(); it_index->Valid(); it_index->Next()) {
std::string index_key = it_index->key().ToString();
if (index_key.find(fieldName + ":") == 0) {
Status s = indexDb_->Delete(WriteOptions(), Slice(index_key));
if (!s.ok()) {
delete it_index;
return s;
}
}
}
delete it_index;
return Status::OK();
}
5. Put 和 Delete 方法的内容
以下是实验报告中对 Put 和 Delete 方法的描述,以及如何通过事务和回滚机制实现数据插入与删除的原子性。
Put 方法描述
Put 方法用于向主数据库和二级索引数据库中插入或更新数据。其关键步骤如下:
- 主数据库写入:首先尝试向主数据库插入或更新数据。
- 二级索引更新:遍历需要创建索引的字段 (
fieldWithIndex_),从新值中提取字段对应的索引键和值,并将索引插入到二级索引数据库。 - 提交事务:
- 提交主数据库的写入操作。
- 提交二级索引数据库的写入操作。
- 回滚机制:如果二级索引数据库的写入失败,会回滚主数据库的插入操作以确保数据一致性。
关键代码:
Status DBImpl::Put(const WriteOptions& o, const Slice& key, const Slice& val) {
...
// 在主数据库写入新数据
batch.Put(key, val);
// 遍历字段并更新索引
for (const auto& field : fieldWithIndex_) {
...
indexBatch.Put(Slice(indexKey), Slice(indexValue));
}
// 提交主数据库事务
s = this->Write(o, &batch);
if (!s.ok()) {
return s;
}
// 提交二级索引数据库事务
s = indexDb_->Write(o, &indexBatch);
if (!s.ok()) {
// 如果二级索引写入失败,回滚主数据库写入
for (const auto& insertedKey : keysInserted) {
batch.Delete(insertedKey);
}
this->Write(o, &batch);
return s;
}
...
}
Delete 方法描述
Delete 方法用于从主数据库和二级索引数据库中删除数据。其关键步骤如下:
- 获取原始数据:在删除前从主数据库读取原始值,确保在删除失败时可以回滚。
- 主数据库删除:从主数据库中删除目标键。
- 二级索引删除:遍历字段,计算对应的索引键,并将其从二级索引数据库中删除。
- 提交事务:
- 提交主数据库的删除操作。
- 提交二级索引数据库的删除操作。
- 回滚机制:如果二级索引数据库的删除失败,会尝试将主数据库的删除操作回滚为原始状态。
关键代码:
Status DBImpl::Delete(const WriteOptions& options, const Slice& key) {
...
// 从主数据库删除目标键
batch.Delete(key);
// 遍历字段并删除索引
for (const auto& field : fieldWithIndex_) {
...
indexBatch.Delete(Slice(indexKey));
}
// 提交主数据库事务
s = this->Write(options, &batch);
if (!s.ok()) {
return s;
}
// 提交二级索引数据库事务
s = indexDb_->Write(options, &indexBatch);
if (!s.ok()) {
// 如果二级索引删除失败,回滚主数据库删除
if (!originalValue.empty()) {
batch.Put(key, originalValue);
} else {
batch.Put(key, "");
}
this->Write(options, &batch);
return s;
}
...
}
6. 数据插入与删除的原子性实现
通过以下策略确保数据插入与删除操作的原子性:
- 事务机制:
- 主数据库和二级索引数据库的写入操作分别使用
WriteBatch封装,并在提交前记录必要的数据以支持回滚。
- 主数据库和二级索引数据库的写入操作分别使用
- 错误处理与回滚:
- 如果二级索引数据库的写入或删除操作失败,主数据库的写入或删除操作将被回滚。
- 在回滚过程中,主数据库会恢复为操作前的状态(插入操作时删除新数据,删除操作时恢复原始数据)。
实现意义
这种设计确保了主数据库和二级索引数据库的一致性,即便在部分写入或删除操作失败的情况下,仍能通过回滚机制保证数据的完整性和原子性。
五,性能测试
1.测试流程
单元测试:
- 插入原始数据:
k_1 : name:Customer#000000001|address:IVhzIApeRb|phone:25-989-741-2988 k_2 : name:Customer#000000002|address:XSTf4,NCwDVaW|phone:23-768-687-3665 - 创建索引:
- 调用
CreateIndexOnField("name"),索引数据库生成条目:name:Customer#000000001-k_1 : k_1 name:Customer#000000002-k_2 : k_2
- 调用
- 查询索引:
- 调用
QueryByIndex("name:Customer#000000001"),返回["k_1"]。
- 调用
- 删除索引:
- 调用
DeleteIndex("name"),移除所有name:开头的索引条目。
- 调用
测试结果:
性能测试:
2.结果分析
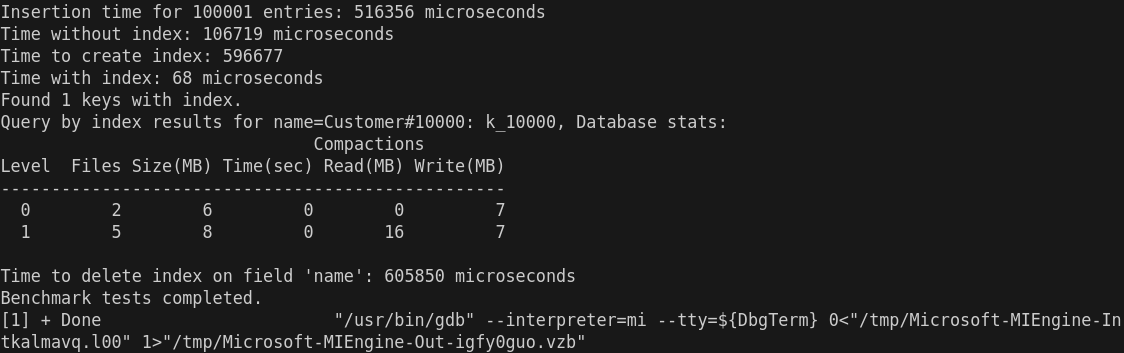
- 插入时间 (Insertion time for 100001 entries: 516356 microseconds)
这个时间(516356 微秒,约 516 毫秒)看起来是合理的,特别是对于 100001 条记录的插入操作。如果数据插入过程没有特别复杂的计算或操作,这个时间应该是正常的,除非硬件性能或其他因素导致延迟。
- 没有索引的查询时间 (Time without index: 106719 microseconds)
这个时间是查询在没有索引的情况下执行的时间。106719 微秒(大约 107 毫秒)对于没有索引的查询来说是可以接受的,尤其是在数据量较大时。如果数据库没有索引,查找所有相关条目会比较耗时。
- 创建索引的时间 (Time to create index: 596677 microseconds)
这个时间(596677 微秒,约 597 毫秒)对于创建索引来说是正常的,尤其是在插入了大量数据后。如果数据量非常大,索引创建时间可能会显得稍长。通常情况下,创建索引的时间会随着数据量的增加而增大。
- 有索引的查询时间 (Time with index: 68 microseconds)
这个时间(68 微秒)非常短,几乎可以认为是一个非常好的优化结果。通常,索引查询比没有索引时要快得多,因为它避免了全表扫描。因此,这个时间是非常正常且预期的,说明索引大大加速了查询。
- 查询结果 (Found 1 keys with index)
这里显示索引查询找到了 1 个键。是正常的, name=Customer#10000 应该返回 1 条记录。
- 数据库统计信息 (Database stats)
Compactions
Level Files Size(MB) Time(sec) Read(MB) Write(MB)
--------------------------------------------------
0 2 6 0 0 7
1 5 8 0 16 7
这些信息表明数据库的压缩(Compaction)过程。Level 0 和 Level 1 显示了数据库的文件数和大小。此部分数据正常,意味着数据库在处理数据时有一些 I/O 操作和文件整理。
- 删除索引的时间 (Time to delete index on field 'name': 605850 microseconds)
删除索引的时间(605850 微秒,约 606 毫秒)比创建索引的时间稍长。这个时间是合理的,删除索引通常会涉及到重新整理数据结构和清理索引文件,因此可能比创建索引稍慢。
benchmark运行结果总结:
整体来看,输出结果是正常的:
- 插入和索引创建时间:插入数据和创建索引所需的时间相对较长,但考虑到数据量和索引的生成,时间是合理的。
- 有索引的查询时间:索引加速了查询,这部分的时间(68 微秒)非常短,表现出色。
- 删除索引的时间:删除索引需要稍长时间,这也是常见的现象。
六,问题与解决方案
1. 问题:如何避免 **indexDb_** 的递归调用?
在实现 Put 和 Delete 方法时,由于 indexDb_ 也调用了 DBImpl 的方法,可能导致递归调用的问题。具体表现为在 indexDb_ 内部操作时仍会试图更新索引。
解决方案:
在 Put 和 Delete 方法中,添加检查逻辑。如果当前对象是 indexDb_,则仅对主数据库进行操作,而不再更新索引。例如:
if (indexDb_ != nullptr) {
// 仅更新主数据库的事务
} else {
// 更新索引
}
2. 问题:二级索引的事务回滚机制如何设计?
在二级索引更新失败时,需要确保主数据库的修改也能回滚,以保持数据一致性。
解决方案:
使用 WriteBatch 记录每次操作。在二级索引更新失败后,通过读取原始值或删除新插入的键,恢复主数据库的状态。示例代码如下:
if (!s.ok()) {
for (const auto& insertedKey : keysInserted) {
if (!originalValue.empty()) {
batch.Put(insertedKey, Slice(originalValue));
} else {
batch.Delete(insertedKey);
}
}
this->Write(o, &batch); // 执行回滚
}
3. 问题:如何高效管理多字段的动态索引?
如果需要为多个字段动态创建和删除索引,可能导致额外的开销以及管理复杂性。
解决方案:
- 使用
fieldWithIndex_字段集中管理所有需要创建索引的字段。 - 在动态操作中,通过扫描主数据库快速生成或删除指定字段的索引条目。
- 提供统一的接口,用于添加和移除字段。
4. 问题:**Put** 和 **Delete** 方法如何确保原子性?
在更新主数据库和二级索引时,如果某一步骤失败,可能导致不一致。
解决方案:
通过事务 (WriteBatch) 确保多个操作要么全部成功,要么全部回滚。例如:
s = this->Write(o, &batch);
if (!s.ok()) {
return s; // 确保写入失败时停止后续操作
}
s = indexDb_->Write(o, &indexBatch);
if (!s.ok()) {
// 回滚主数据库操作
}
通过以上方案,有效解决了实验中遇到的问题,并提高了系统的稳定性和一致性。
总结
本实验通过在 DBImpl 中集成索引管理功能,实现了对二级索引的创建、查询和删除。二级索引数据存储在独立的 indexDb_ 中,通过高效的键值映射提升了字段值查询的效率。