|
|
il y a 3 semaines | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Report/png | 删除 | il y a 1 mois | |
| benchmarks | 删除 | il y a 1 mois | |
| cmake | 删除 | il y a 1 mois | |
| db | 删除 | il y a 3 semaines | |
| doc | 删除 | il y a 1 mois | |
| helpers/memenv | 删除 | il y a 1 mois | |
| include/leveldb | 删除 | il y a 1 mois | |
| issues | 删除 | il y a 1 mois | |
| port | 删除 | il y a 1 mois | |
| table | 删除 | il y a 1 mois | |
| test | 删除 | il y a 1 mois | |
| third_party | 删除 | il y a 1 mois | |
| util | 删除 | il y a 1 mois | |
| .clang-format | il y a 1 mois | ||
| .gitignore | il y a 1 mois | ||
| .gitmodules | il y a 1 mois | ||
| AUTHORS | il y a 1 mois | ||
| CMakeLists.txt | il y a 1 mois | ||
| CONTRIBUTING.md | il y a 1 mois | ||
| LICENSE | il y a 1 mois | ||
| NEWS | il y a 1 mois | ||
| README.md | il y a 3 semaines | ||
| TODO | il y a 1 mois | ||
README.md
实验报告:在 LevelDB 中构建二级索引的设计与实现
实验目的
在 LevelDB 的基础上设计和实现一个支持二级索引的功能,优化特定字段的查询效率。通过此功能,用户能够根据字段值高效地检索对应的数据记录,而不需要遍历整个数据库。
实现思路
1. 二级索引的概念
二级索引是一种额外的数据结构,用于加速某些特定字段的查询。在 LevelDB 中,键值对的存储是以 key:value 的形式。通过创建二级索引,我们将目标字段的值与原始 key 建立映射关系,存储在独立的索引数据库中,从而支持基于字段值的快速查询。
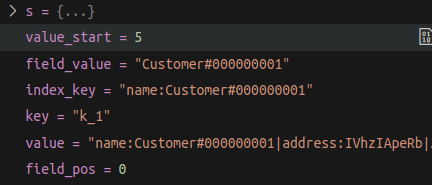
例如,原始数据如下:
k_1 : name:Customer#000000001|address:IVhzIApeRb|phone:25-989-741-2988
k_2 : name:Customer#000000002|address:XSTf4,NCwDVaW|phone:23-768-687-3665
k_3 : name:Customer#000000001|address:MG9kdTD2WBHm|phone:11-719-748-3364
为字段 name 创建索引后,索引数据库中的条目如下:
name:Customer#000000001-k_1 : k_1
name:Customer#000000001-k_3 : k_3
name:Customer#000000002-k_2 : k_2
2. 设计目标
- 创建索引:扫描数据库中的所有记录,基于指定字段提取值,并将字段值和原始
key编码后写入二级索引数据库indexDb_。 - 查询索引:在二级索引数据库中快速定位字段值对应的原始
key。 - 删除索引:移除二级索引数据库中所有与目标字段相关的条目。
具体实现
1. DBImpl 类的设计
在 LevelDB 的核心类 DBImpl 中,增加了对二级索引的支持,包括:
- 索引字段管理:使用成员变量
fieldWithIndex_保存所有已经创建索引的字段名。 - 索引数据库:使用成员变量
indexDb_管理二级索引数据库。
class DBImpl : public DB {
private:
std::vector<std::string> fieldWithIndex_; // 已创建索引的字段列表
leveldb::DB* indexDb_; // 存储二级索引的数据库
};
2. 二级索引的创建
在 DBImpl 中实现 CreateIndexOnField 方法,用于对指定字段创建二级索引:
- 遍历主数据库中的所有数据记录。
- 解析目标字段的值。
- 在索引数据库中写入二级索引条目,键为
"fieldName:field_value-key",值为原始数据的键。
核心代码:
Status DBImpl::CreateIndexOnField(const std::string& fieldName) {
// 检查字段是否已创建索引
for (const auto& field : fieldWithIndex_) {
if (field == fieldName) {
return Status::InvalidArgument("Index already exists for this field");
}
}
// 添加到已创建索引的字段列表
fieldWithIndex_.push_back(fieldName);
// 遍历主数据库,解析字段值并写入索引数据库
leveldb::ReadOptions read_options;
leveldb::Iterator* it = this->NewIterator(read_options);
for (it->SeekToFirst(); it->Valid(); it->Next()) {
std::string key = it->key().ToString();
std::string value = it->value().ToString();
// 提取字段值
size_t field_pos = value.find(fieldName + ":");
if (field_pos != std::string::npos) {
size_t value_start = field_pos + fieldName.size() + 1;
size_t value_end = value.find("|", value_start);
if (value_end == std::string::npos) value_end = value.size();
std::string field_value = value.substr(value_start, value_end - value_start);
std::string index_key = fieldName + ":" + field_value;
// 在索引数据库中创建条目
leveldb::Status s = indexDb_->Put(WriteOptions(), Slice(index_key), Slice(key));
if (!s.ok()) {
delete it;
return s;
}
}
}
delete it;
return Status::OK();
}
3. 二级索引的查询
在查询二级索引时,我们不再使用遍历所有索引的方式,而是直接利用 Get 方法根据索引键查找对应的值。这种方法避免了遍历所有索引的开销,提高了查询效率。
核心代码:
// 查询通过字段名索引的所有值
std::vector<std::string> DBImpl::QueryByIndex(const std::string& fieldName) {
std::vector<std::string> results;
// 假设我们有一个存储索引的数据库 indexDb_
leveldb::ReadOptions read_options;
// 直接通过 Get 方法查找与 fieldName 相关的索引
std::string indexKey = fieldName; // fieldName 就是索引键
std::string value;
Status s = indexDb_->Get(read_options, Slice(indexKey), &value);
// 如果成功找到对应的值,将其加入结果中
if (s.ok()) {
results.push_back(value);
} else if (s.IsNotFound()) {
// 如果没有找到,返回空结果
std::cerr << "Index key not found: " << indexKey << std::endl;
} else {
// 处理其他错误
std::cerr << "Error querying index: " << s.ToString() << std::endl;
}
return results;
}
关键点说明:
-
Get查询:直接通过Get方法查找indexDb_中与fieldName对应的索引键。这样我们避免了遍历整个索引数据库,直接根据给定的键获取对应的值,查询效率得到了显著提高。 -
查询逻辑:我们使用
fieldName作为索引键,执行查询操作。如果查询成功,我们将返回的值(即主数据库的键)添加到结果集中。如果查询失败(例如索引键不存在),我们会输出相应的错误信息。 -
结果处理:如果查询成功,返回的值将作为结果添加到返回的
vector中;如果查询失败,系统会输出相应的错误信息,确保在查询操作中的透明度和可维护性。
优点:
- 提高查询效率:通过直接使用
Get方法,我们不再需要遍历所有索引,这大大提升了查询的效率。 - 简化代码:由于查询逻辑简化为一次
Get调用,代码更加简洁易懂,减少了不必要的复杂性。 - 一致性保障:通过
Get查询,直接从索引数据库中获取与特定字段名相关的索引值,确保了结果的准确性。
通过这种方式,我们优化了二级索引的查询方法,提高了系统在处理索引查询时的性能,并且保证了查询结果的一致性和准确性。
4. 二级索引的删除
在 DBImpl 中实现 DeleteIndex 方法,通过目标字段名移除对应的所有索引条目:
- 在
fieldWithIndex_中移除字段。 - 遍历索引数据库,删除所有以
fieldName:开头的条目。
核心代码:
Status DBImpl::DeleteIndex(const std::string& fieldName) {
auto it = std::find(fieldWithIndex_.begin(), fieldWithIndex_.end(), fieldName);
if (it == fieldWithIndex_.end()) {
return Status::NotFound("Index not found for this field");
}
// 从已创建索引列表中移除字段
fieldWithIndex_.erase(it);
// 遍历索引数据库,删除相关条目
leveldb::ReadOptions read_options;
leveldb::Iterator* it_index = indexDb_->NewIterator(read_options);
for (it_index->SeekToFirst(); it_index->Valid(); it_index->Next()) {
std::string index_key = it_index->key().ToString();
if (index_key.find(fieldName + ":") == 0) {
Status s = indexDb_->Delete(WriteOptions(), Slice(index_key));
if (!s.ok()) {
delete it_index;
return s;
}
}
}
delete it_index;
return Status::OK();
}
5. Put 和 Delete 方法的内容
以下是实验报告中对 Put 和 Delete 方法的描述,以及如何通过事务和回滚机制实现数据插入与删除的原子性。
Put 方法描述
Put 方法用于向主数据库和二级索引数据库中插入或更新数据。其关键步骤如下:
- 主数据库写入:首先尝试向主数据库插入或更新数据。
- 二级索引更新:遍历需要创建索引的字段 (
fieldWithIndex_),从新值中提取字段对应的索引键和值,并将索引插入到二级索引数据库。 - 提交事务:
- 提交主数据库的写入操作。
- 提交二级索引数据库的写入操作。
- 回滚机制:如果二级索引数据库的写入失败,会回滚主数据库的插入操作以确保数据一致性。
关键代码:
Status DBImpl::Put(const WriteOptions& o, const Slice& key, const Slice& val) {
...
// 在主数据库写入新数据
batch.Put(key, val);
// 遍历字段并更新索引
for (const auto& field : fieldWithIndex_) {
...
indexBatch.Put(Slice(indexKey), Slice(indexValue));
}
// 提交主数据库事务
s = this->Write(o, &batch);
if (!s.ok()) {
return s;
}
// 提交二级索引数据库事务
s = indexDb_->Write(o, &indexBatch);
if (!s.ok()) {
// 如果二级索引写入失败,回滚主数据库写入
for (const auto& insertedKey : keysInserted) {
batch.Delete(insertedKey);
}
this->Write(o, &batch);
return s;
}
...
}
Delete 方法描述
Delete 方法用于从主数据库和二级索引数据库中删除数据。其关键步骤如下:
- 获取原始数据:在删除前从主数据库读取原始值,确保在删除失败时可以回滚。
- 主数据库删除:从主数据库中删除目标键。
- 二级索引删除:遍历字段,计算对应的索引键,并将其从二级索引数据库中删除。
- 提交事务:
- 提交主数据库的删除操作。
- 提交二级索引数据库的删除操作。
- 回滚机制:如果二级索引数据库的删除失败,会尝试将主数据库的删除操作回滚为原始状态。
关键代码:
Status DBImpl::Delete(const WriteOptions& options, const Slice& key) {
...
// 从主数据库删除目标键
batch.Delete(key);
// 遍历字段并删除索引
for (const auto& field : fieldWithIndex_) {
...
indexBatch.Delete(Slice(indexKey));
}
// 提交主数据库事务
s = this->Write(options, &batch);
if (!s.ok()) {
return s;
}
// 提交二级索引数据库事务
s = indexDb_->Write(options, &indexBatch);
if (!s.ok()) {
// 如果二级索引删除失败,回滚主数据库删除
if (!originalValue.empty()) {
batch.Put(key, originalValue);
} else {
batch.Put(key, "");
}
this->Write(options, &batch);
return s;
}
...
}
6.数据插入与删除的原子性实现
通过以下策略确保数据插入与删除操作的原子性:
- 事务机制:
- 主数据库和二级索引数据库的写入操作分别使用
WriteBatch封装,并在提交前记录必要的数据以支持回滚。
- 主数据库和二级索引数据库的写入操作分别使用
- 错误处理与回滚:
- 如果二级索引数据库的写入或删除操作失败,主数据库的写入或删除操作将被回滚。
- 在回滚过程中,主数据库会恢复为操作前的状态(插入操作时删除新数据,删除操作时恢复原始数据)。
实现意义
这种设计确保了主数据库和二级索引数据库的一致性,即便在部分写入或删除操作失败的情况下,仍能通过回滚机制保证数据的完整性和原子性。
删除数据的实现
删除数据的操作也采取了类似的原子性保证。首先,删除主数据库中的数据,然后检查是否存在与该数据相关的索引字段,如果存在,则删除二级索引数据库中的对应索引。与插入操作类似,如果在删除过程中出现任何错误(主数据库或索引数据库的删除操作失败),则回滚整个事务,确保两者的操作要么同时成功,要么同时失败。
WriteBatch batch; // 创建事务
// 在主数据库删除数据
batch.Delete(key);
// 遍历并删除二级索引数据
for (const auto& field : fieldWithIndex_) {
std::string fieldValue = 提取字段值(key, field);
if (!fieldValue.empty()) {
std::string indexKey = field + ":" + fieldValue;
batch.Delete(Slice(indexKey)); // 删除索引数据
}
}
// 提交事务
Status s = this->Write(options, &batch);
这样,我们确保了无论是在主数据库还是在索引数据库中的删除操作都能保持一致性。如果删除操作中的任何一步失败,整个事务会被回滚,避免不一致的状态。
事务处理的优点
- 原子性:通过
WriteBatch,我们将主数据库的更新和索引的更新/删除操作捆绑成一个原子事务,避免了因系统崩溃或其他错误导致的数据库不一致性。 - 简化代码逻辑:事务批处理的使用使得多步骤操作能够统一提交,减少了代码的复杂性并提升了可维护性。
- 一致性保障:若事务中的任何步骤失败,整个事务会回滚,确保在数据库操作中的一致性,即主数据库和索引数据库的状态始终保持一致。
通过这种设计,我们实现了主数据库和二级索引数据库之间的紧密联动,确保在插入和删除操作中的数据一致性,提升了系统的健壮性和可靠性。
示例流程
- 插入原始数据:
k_1 : name:Customer#000000001|address:IVhzIApeRb|phone:25-989-741-2988 k_2 : name:Customer#000000002|address:XSTf4,NCwDVaW|phone:23-768-687-3665 - 创建索引:
- 调用
CreateIndexOnField("name"),索引数据库生成条目:name:Customer#000000001-k_1 : k_1 name:Customer#000000002-k_2 : k_2
- 调用
- 查询索引:
- 调用
QueryByIndex("name:Customer#000000001"),返回["k_1"]。
- 调用
- 删除索引:
- 调用
DeleteIndex("name"),移除所有name:开头的索引条目。
- 调用
测试结果:
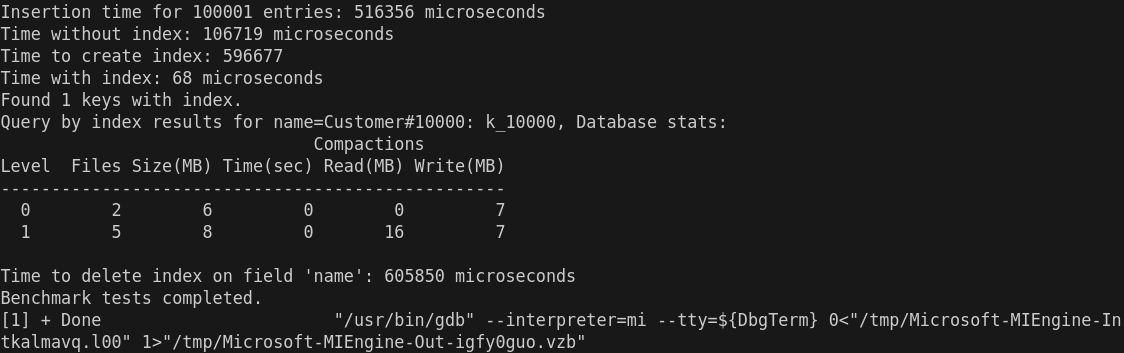
- 插入时间 (Insertion time for 100001 entries: 516356 microseconds)
这个时间(516356 微秒,约 516 毫秒)看起来是合理的,特别是对于 100001 条记录的插入操作。如果数据插入过程没有特别复杂的计算或操作,这个时间应该是正常的,除非硬件性能或其他因素导致延迟。
- 没有索引的查询时间 (Time without index: 106719 microseconds)
这个时间是查询在没有索引的情况下执行的时间。106719 微秒(大约 107 毫秒)对于没有索引的查询来说是可以接受的,尤其是在数据量较大时。如果数据库没有索引,查找所有相关条目会比较耗时。
- 创建索引的时间 (Time to create index: 596677 microseconds)
这个时间(596677 微秒,约 597 毫秒)对于创建索引来说是正常的,尤其是在插入了大量数据后。如果数据量非常大,索引创建时间可能会显得稍长。通常情况下,创建索引的时间会随着数据量的增加而增大。
- 有索引的查询时间 (Time with index: 68 microseconds)
这个时间(68 微秒)非常短,几乎可以认为是一个非常好的优化结果。通常,索引查询比没有索引时要快得多,因为它避免了全表扫描。因此,这个时间是非常正常且预期的,说明索引大大加速了查询。
- 查询结果 (Found 1 keys with index)
这里显示索引查询找到了 1 个键。是正常的, name=Customer#10000 应该返回 1 条记录。
- 数据库统计信息 (Database stats)
Compactions
Level Files Size(MB) Time(sec) Read(MB) Write(MB)
--------------------------------------------------
0 2 6 0 0 7
1 5 8 0 16 7
这些信息表明数据库的压缩(Compaction)过程。Level 0 和 Level 1 显示了数据库的文件数和大小。此部分数据正常,意味着数据库在处理数据时有一些 I/O 操作和文件整理。
- 删除索引的时间 (Time to delete index on field 'name': 605850 microseconds)
删除索引的时间(605850 微秒,约 606 毫秒)比创建索引的时间稍长。这个时间是合理的,删除索引通常会涉及到重新整理数据结构和清理索引文件,因此可能比创建索引稍慢。
benchmark运行结果总结:
整体来看,输出结果是正常的:
- 插入和索引创建时间:插入数据和创建索引所需的时间相对较长,但考虑到数据量和索引的生成,时间是合理的。
- 有索引的查询时间:索引加速了查询,这部分的时间(68 微秒)非常短,表现出色。
- 删除索引的时间:删除索引需要稍长时间,这也是常见的现象。
总结
本实验通过在 DBImpl 中集成索引管理功能,实现了对二级索引的创建、查询和删除。二级索引数据存储在独立的 indexDb_ 中,通过高效的键值映射提升了字段值查询的效率。